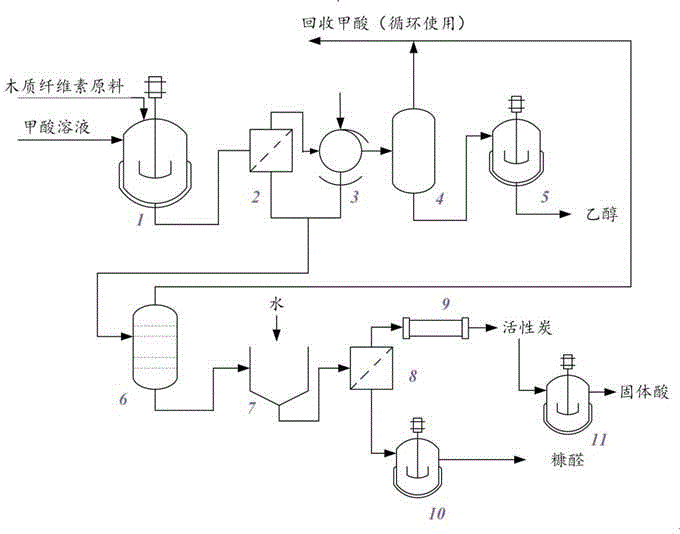
Bio-refinery method for co-producing multiple products by using lignocellulose as raw material
A lignocellulose and biorefinery technology, applied in the separation/purification of biofuels, carboxylic acid compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as efficient separation of components, achieve high profit margins, easy recovery, and increase added value Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Formic acid pretreatment of wheat straw
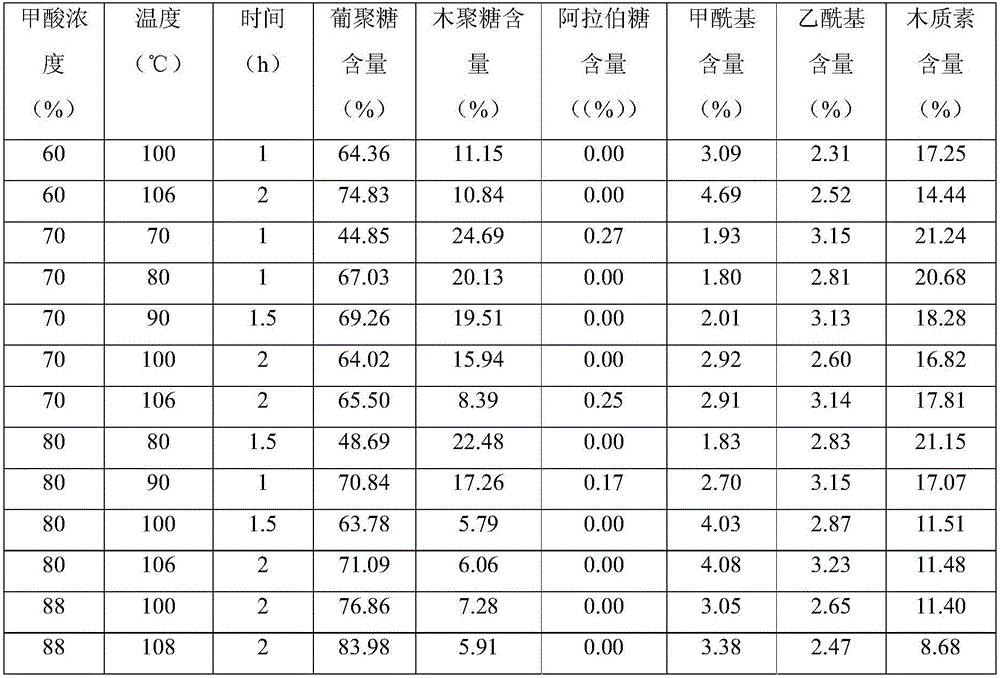
[0028] The lignocellulosic raw material used is wheat straw, and the place of origin is Shandong Province. Straws are cut into 1-2cm lengths for later use. According to the lignocellulose component determination method of the US Renewable Energy Laboratory, the main components of the used wheat straw were analyzed, and the results were: moisture 5.1%, dextran 33.40%, xylan 22.26%, arabinan 3.10% , lignin 20.08%, acetyl 2.01%, ash 6.48%, other soluble solids 7.57%.
[0029] Using different concentrations of formic acid solutions at a liquid-solid ratio (L / kg) of 10:1 to pretreat for different times at different temperatures, the mixture after pretreatment is vacuum filtered, and the solid matter is treated with the same concentration of formic acid as in the pretreatment process based on the initial The dry weight of the solid was washed once at a liquid-solid ratio of 5:1, and then vacuum filtered. The solid was evaporated und...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Enzymolysis performance of cellulose solids after pretreatment
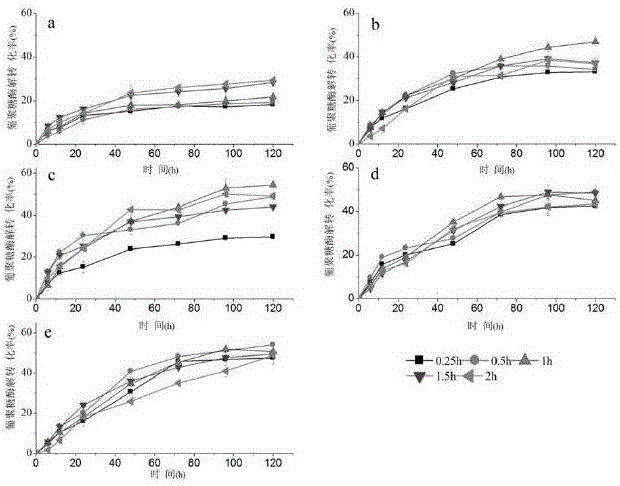
[0033] The raw materials used and the pretreatment process are the same as in Example 1. Wheat straw was pretreated with 88% formic acid at different temperatures. After pretreatment, the cellulose solid was hydrolyzed under the conditions of 2.5% initial solid content, 20 FPU / g solid cellulase dosage, 50° C., pH 4.8, and 150 rpm. The enzymatic hydrolysis time curve is attached figure 2 Show.
[0034] Result analysis: within a certain period of time, increasing the temperature and pretreatment time can increase the enzymatic conversion rate of dextran, and the enzymatic conversion rate began to decrease after the pretreatment time exceeded a certain period of time. The main reason is that with the increase of pretreatment time, the degree of formylation of cellulose increases, which is not conducive to the recognition of cellulose by cellulase. Therefore, the pretreatment process needs to c...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3: Conversion of cellulosic solids to ethanol after pretreatment
[0036] The raw materials used and the pretreatment process are the same as in Example 1. After pretreatment with 80% formic acid at 100°C for 1.5h, use 15% of the initial solid content, 25FPU / g solid cellulase dosage, 50°C, pH 5.0, 150rpm after prehydrolysis for 24h, adjust the pH to 5.5, the temperature dropped to 38°C, and synchronous saccharification and fermentation were carried out after inoculation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. After 48 hours, the ethanol concentration in the fermentation broth was 35.2g / L, and the ethanol yield was 72.3%.
[0037] Result analysis: The pretreated cellulose solid can be effectively converted into ethanol.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com