A method of removing sulfates and Cu (II) in waste water through combining sponge iron and microbes
A technology of sponge iron and sulfate, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biological water/sewage treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of low microbial content per unit, poor sedimentation performance, loose structure, etc., and achieve simple equipment and easy operation Convenience, high specific surface energy effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
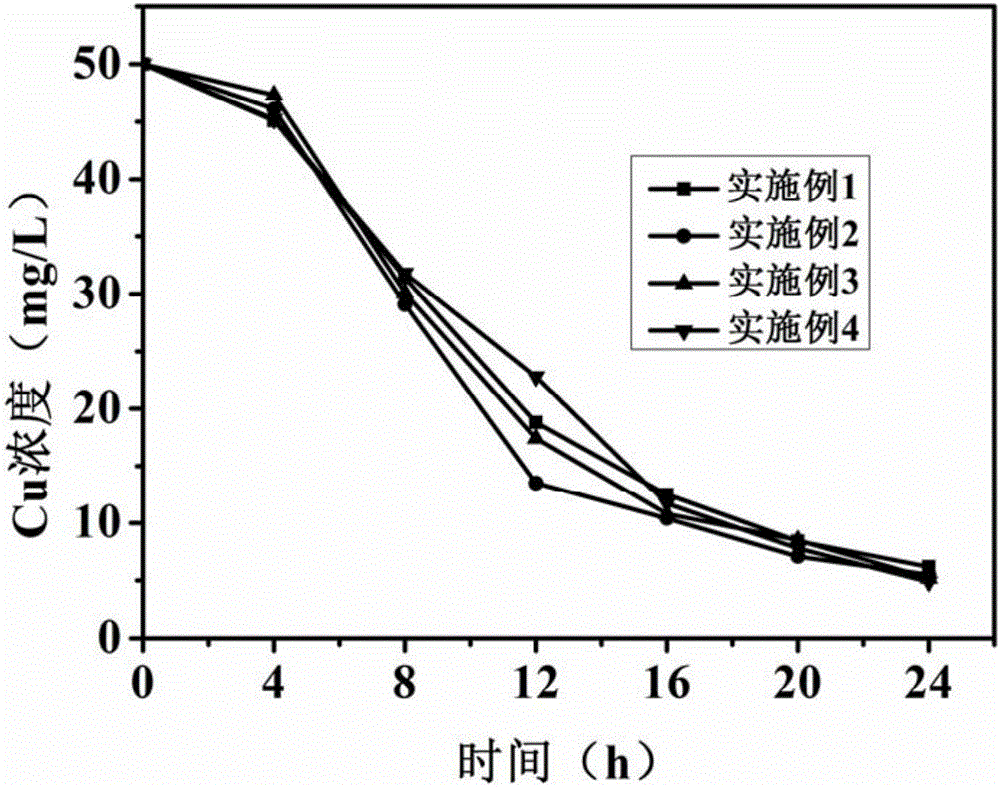
Embodiment 1
[0039] A kind of method that sponge iron and microorganism synergistically remove sulfate and Cu (II) waste water comprises the following steps:
[0040] (1) Preparation of sponge iron
[0041] Under the conditions of carbon content (mass ratio of simple carbon powder to iron slime) 1:3, reaction temperature 1100°C, and reaction time 20 minutes, iron slime was used as raw material to calcinate to prepare conventional sponge iron solid. Activate with dilute hydrochloric acid to prepare a sponge iron solution with a concentration of 0.4 g / L, which is designated as reaction solution A.
[0042] (2) Extraction of sulfate-reducing bacteria SRB
[0043] Select 2 rings from a sulfate-reducing bacterium—Desulfovibrio (Desulfovibrio; Desulfovibrio subsp. Transfer to 30ml Desulfovibrio nutrient medium and culture in the dark at 35°C for 3 days, use Desulfovibrio proliferation medium with 5wt% inoculum to expand culture for 2 days, and centrifuge at 3000r / min for 10min to obtain the lo...
Embodiment 2
[0055] A kind of method that sponge iron and microorganism synergistically remove sulfate and Cu (II) waste water comprises the following steps:
[0056] (1) Preparation of sponge iron
[0057] Under the conditions of carbon content (mass ratio of simple carbon powder to iron slime) 1:3, reaction temperature 1100°C, and reaction time 20 minutes, iron slime was used as raw material to calcinate to prepare conventional sponge iron solid. Activate with dilute hydrochloric acid to prepare a sponge iron solution with a concentration of 0.8 g / L, which is designated as reaction solution A.
[0058] (2) Preparation of sulfate reducing bacteria SRB
[0059] Select 2 rings from a kind of sulfate-reducing bacterium—Desulfovibrio (same as Example 1) purchased by China Common Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center, transfer it to 40ml of nutrient solution, and cultivate it in the dark at 35°C for 3d, with 5% of the inoculum was expanded with proliferation medium for 3 day...
Embodiment 3
[0071] A kind of method that sponge iron and microorganism synergistically remove sulfate and Cu (II) waste water comprises the following steps:
[0072] (1) Preparation of sponge iron
[0073] Under the conditions of carbon content (mass ratio of simple carbon powder to iron slime) 1:3, reaction temperature 1100°C, and reaction time 20 minutes, iron slime was used as raw material to calcinate to prepare conventional sponge iron solid. Activate with dilute hydrochloric acid to prepare a sponge iron solution with a concentration of 0.2 g / L, which is designated as reaction solution A.
[0074] (2) Preparation of sulfate reducing bacteria SRB
[0075] Select 2 rings from a kind of sulfate-reducing bacterium—Desulfovibrio (same as Example 1) purchased by China Common Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center, transfer it to 40ml of nutrient solution, and cultivate it in the dark at 35°C for 3d, with 5% of the inoculum was expanded with proliferation medium for 3 day...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com