Industrial saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolic engineering bacterium with low yield of citrulline
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and engineering bacteria, which is applied in the fields of fermentation and biology, can solve problems such as ununified conclusions, and achieve the effect of reducing EC content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Construction of Example 1ARG3 Gene Knockout Assembly
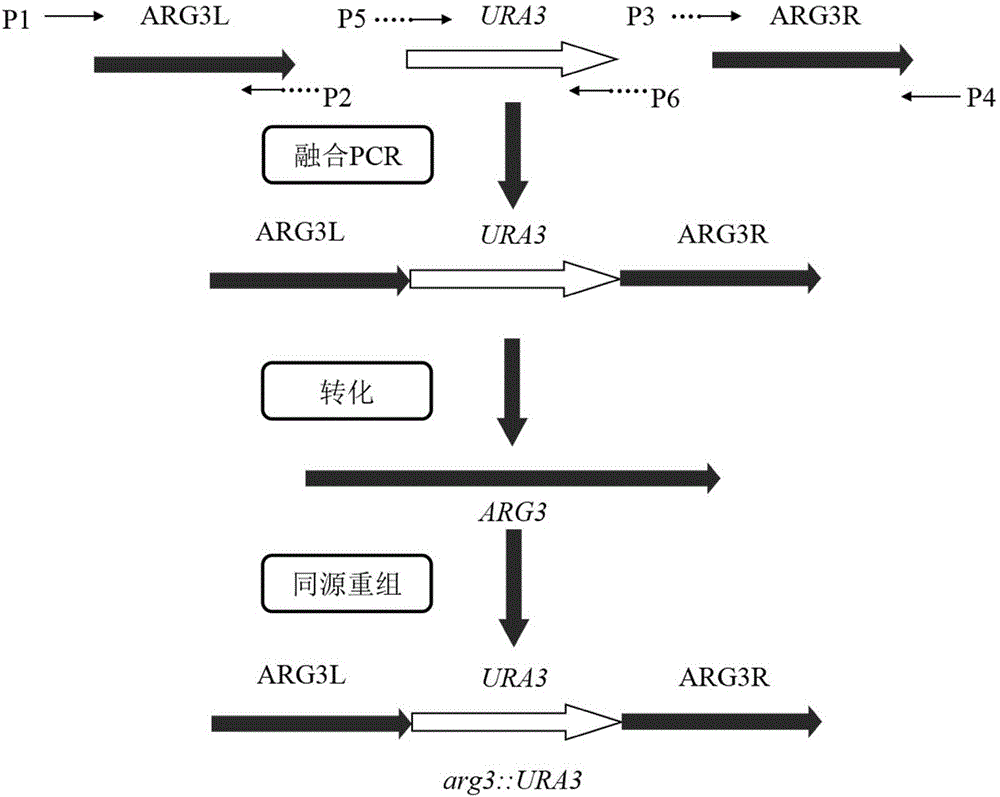
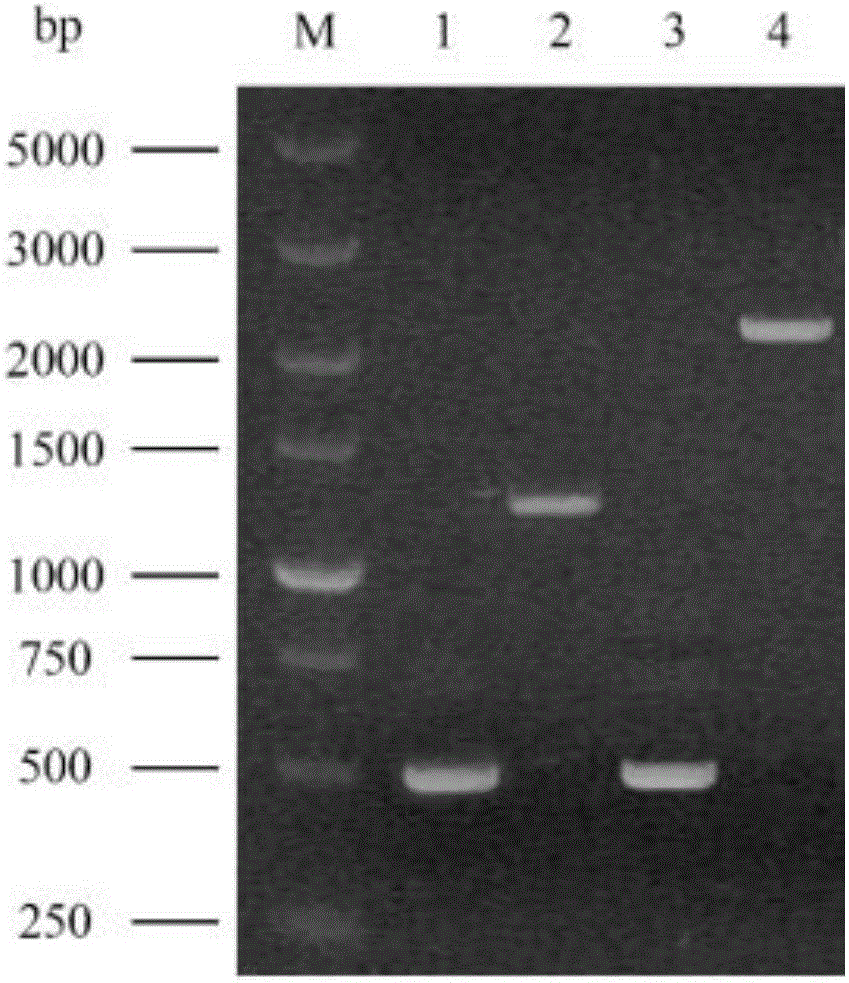
[0047] The construction of the ARG3 gene knockout module is as follows: figure 1 shown. First, extract the genomic DNA of industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae N85 (see the instruction manual of the MiniBEST Universal Genomic DNA Extraction Kit kit for the specific operation method), use the genomic DNA as a template, and use the Prime STAR DNA Polymerase with the numbers P1 / P2 and P3 / P4 respectively. The primer pair amplifies the upstream homology arm of the ARG3 gene (ARG3L, whose sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2) and the downstream homology arm (ARG3R, whose sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.4), using the primer pair P5 / P6 to amplify The complete URA3 gene (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.3), and then use primers P1 / P4 to fuse ARG3L, ARG3R and URA3 by fusion PCR to obtain the ARG3 gene knockout assembly (ARG3L-URA3-ARG3R) (PCR specific operation For the method and reaction system preparation, please refer to the instruc...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2 Knockout of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ARG3 gene
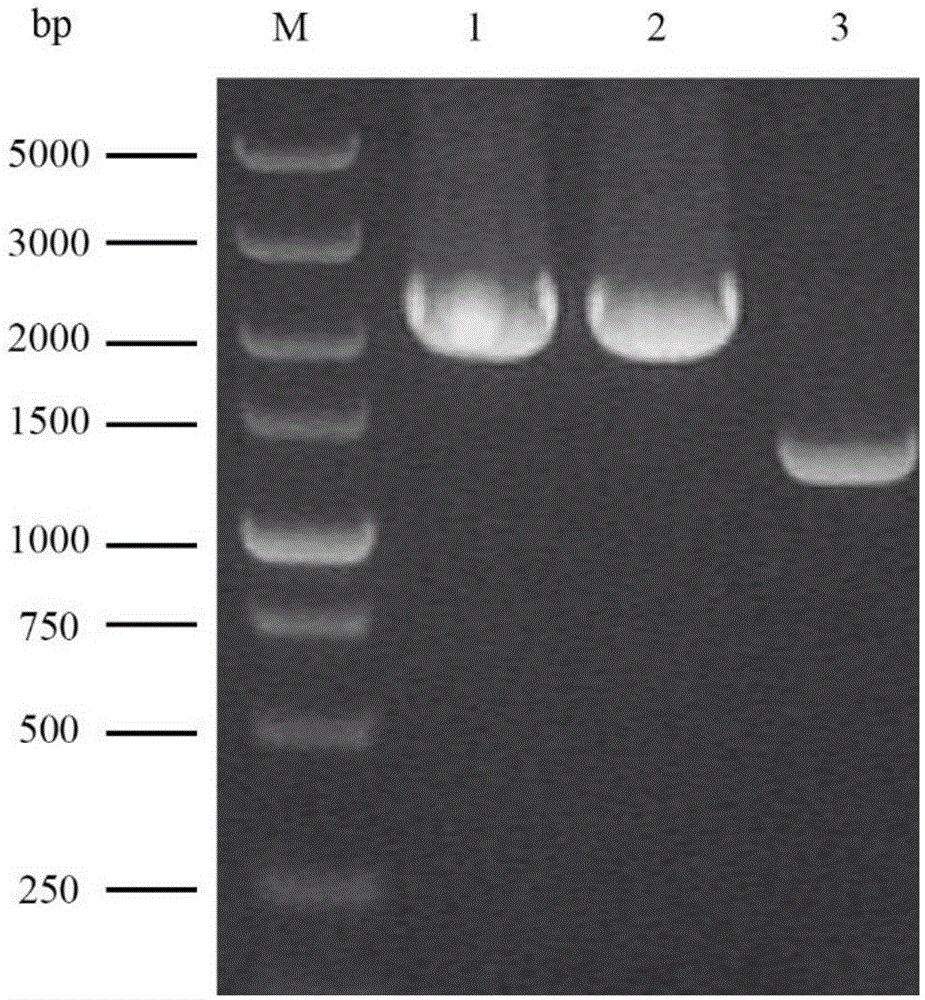
[0062] The gene knockout components ARG3L-URA3-ARG3R obtained above were transformed into a-type and a-type uracil-deficient haploids Na-u and Nα-u respectively by electroporation, and the specific steps were as follows:
[0063] (1) Pick a single colony of yeast and inoculate it in 1mL of LYPD liquid medium, and culture it overnight at 30°C and 200r / min to obtain an activated seed solution;
[0064] (2) According to the inoculation ratio of 10% by volume, transfer the seed solution to 50mL fresh YPD liquid medium, and continue to cultivate at 200r / min at 30°C until the OD of the bacterial solution 600 between 1.2 and 1.5;
[0065] (3) Collect the thalline by centrifugation at 5000r / min for 5min, and wash the thalline twice with 25mL sterile water;
[0066] (4) Resuspend the bacteria in 8 mL of 10 mM dithiothreitol solution, shake in a water bath at 30°C for 30 minutes, and centrifuge at 5000 r / min for 5 minut...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Embodiment 3 Industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae Engineering Bacteria Fermentation
[0074] Inoculate the two types of engineering bacteria (type a and type α) obtained above to knock out ARG3 into YPD medium respectively, carry out activation culture at 30°C, and then transfer the two bacterial solutions to fresh YPD culture medium at the same time. culture medium, and obtain diploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered bacteria (equivalent to Saccharomyces cerevisiae N85 knocked out of ARG3 gene) after fusion, specific operation method reference document 1 (Wu DH, et al.International Journal of Food Microbiology.2014,180: 19-23). The starting strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae N85 without genetic engineering transformation was used as a control, and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria constructed in the present invention were fermented under the same conditions to investigate the ability of the engineering bacteria to reduce the content of citrulline. The sp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com