Application of tannic acid in antithrombotic drugs
An antithrombotic drug, tannic acid technology, applied in the field of prevention and treatment of thrombosis, tannic acid, to achieve broad application prospects, stable physical and chemical properties, and mature production technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
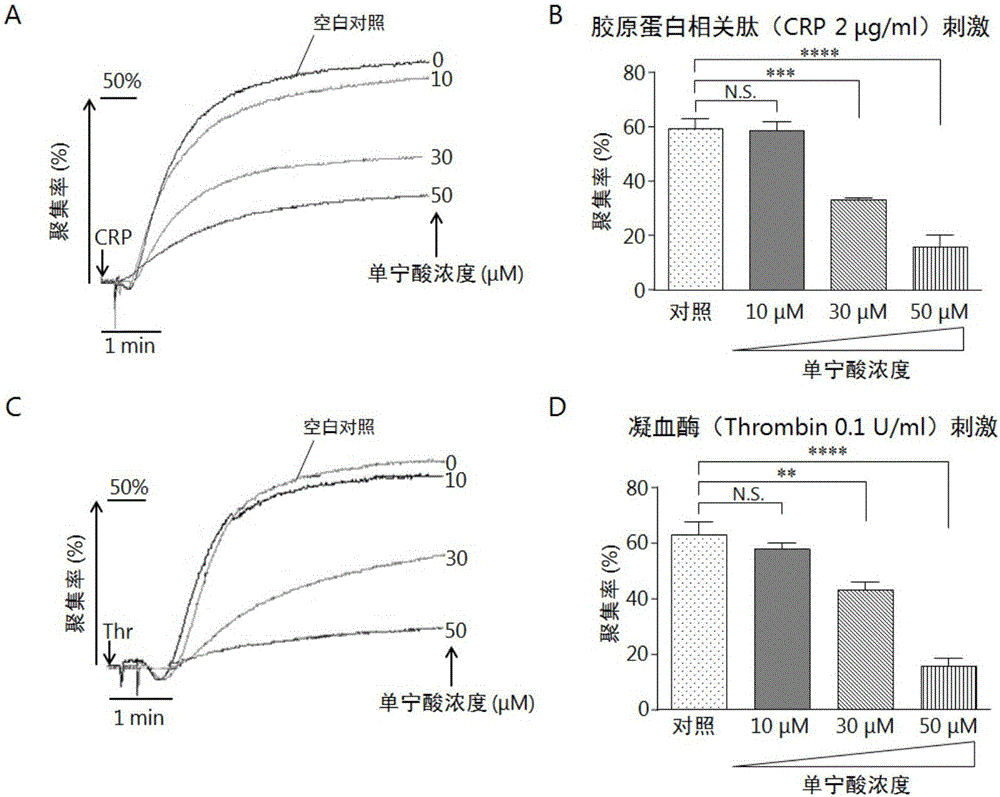
[0026] The inhibitory effect of tannic acid on isolated platelet aggregation is as follows:
[0027] (1) Preparation of washed platelets
[0028]20% citric acid-glucose solution (ACD, pH4.4) (recipe: trisodium citrate 65mM, citric acid 70mM, glucose 100mM) anticoagulant venous blood from healthy volunteers, centrifuged at 900r / min for 20min to prepare platelet-rich Plasma (PRP), PRP passed through the agarose gel sepharose2BTM column that had been washed and equilibrated with Tyrode's buffer, and the washed platelets for experiments were collected from the lower end of the column. Platelets were counted, and the platelet concentration was adjusted to 250×10 with Tyrode's buffer 6 ml -1 .
[0029] (2) Determination of platelet aggregation stimulated by CRP
[0030] The platelet aggregation instrument (CHRONO-LOG) was turned on and warmed up 30 minutes before the experiment. Take 4 cuvettes (CHRONO-LOG, model P / N312) specially used for platelet aggregation analyzer (CHRONO-...
Embodiment 2
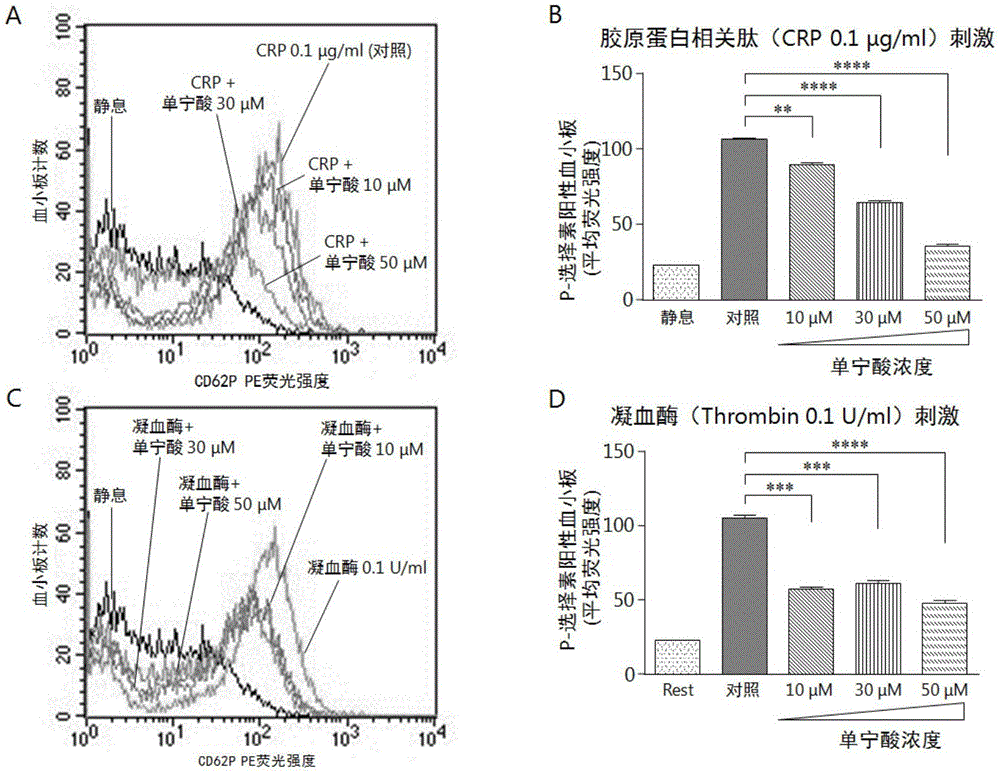
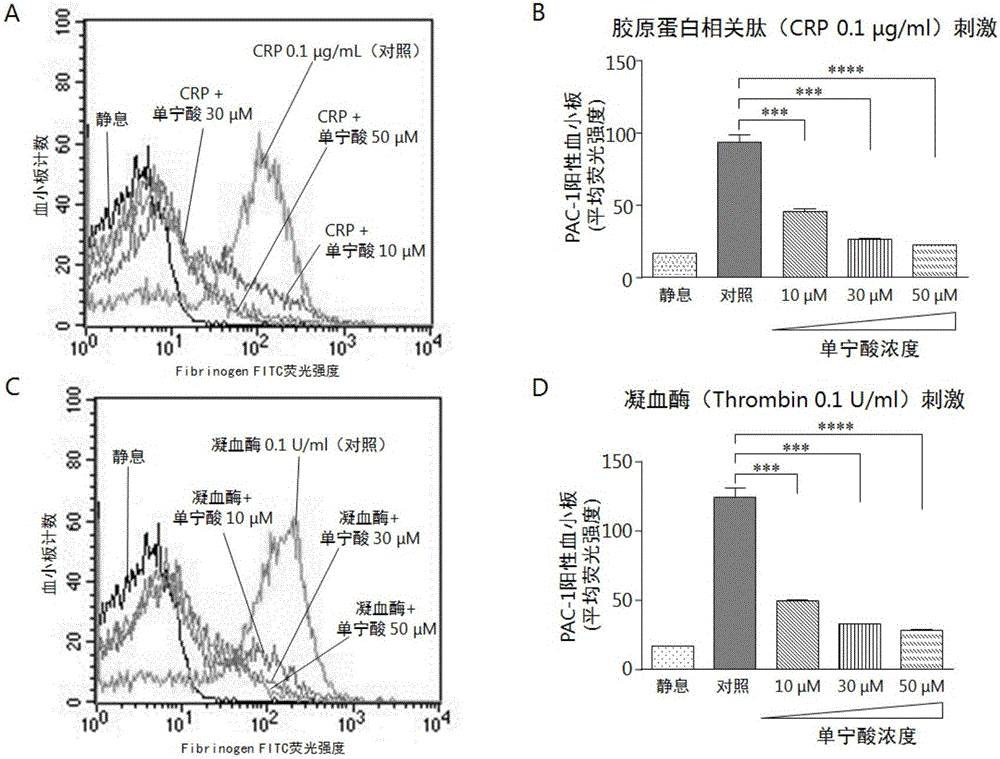
[0035] Inhibitory effect of tannic acid on activation of isolated platelets, as follows:
[0036] (1) Preparation of washed platelets
[0037] 20% ACD (pH4.4) (recipe: trisodium citrate 65mM, citric acid 70mM, glucose 100mM) anticoagulant venous blood from healthy volunteers, centrifuged at 900r / min for 20min to prepare platelet-rich plasma (PRP), PRP Wash and equilibrate the sepharose2BTM gel column with Tyrode's buffer, pick up the platelets used for the experiment from the lower end of the column, count the platelets, adjust the platelet concentration to 250×10 with Tyrode's buffer 6 ml -1 .
[0038] (2) P-selectin expression test
[0039] 100 μL of the washed platelets prepared above were added to the 4 sample loading tubes respectively, and 1 μL of tannic acid solutions with concentrations of 10, 30 and 50 μM (normal saline as solvent) and 1 μL of normal saline (blank control group) were added to the washed platelets. Under the condition of adding fluorescent PE-P-sel...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Effects of tannic acid on laser-induced arterial thrombus in the cremaster muscle of mice, as follows:
[0046] Inject tannic acid (7.5 mg / kg) and an equal volume of normal saline (blank control group) into the wild-type mice intraperitoneally, anesthetize half an hour later, inject DIOC6 dye intravenously, and damage the free cremaster muscle artery with laser pulses. Thrombosis was observed and recorded under a microscope. see results Figure 4 , A shows the curve of thrombus size changing with time, D is the microscopic magnified view of the largest thrombus formed, the results all show that compared with the blank control group, tannic acid has the effect on the laser when the dose is 7.5mg / kg (intraperitoneal injection). Induced arterial thrombus of cremaster muscle in mice has obvious inhibitory effect. Figure 4 In B and C, the total volume and peak volume of the thrombus in the tannic acid administration group were smaller than those in the blank control group...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com