A genetically engineered bacterium producing phospholipase d and its construction method and application
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and phospholipase, applied in genetic engineering, microorganism-based methods, applications, etc., can solve the problems of no PLD product, immature PLD, etc., and achieve low cost, convenient enzyme source and high yield. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
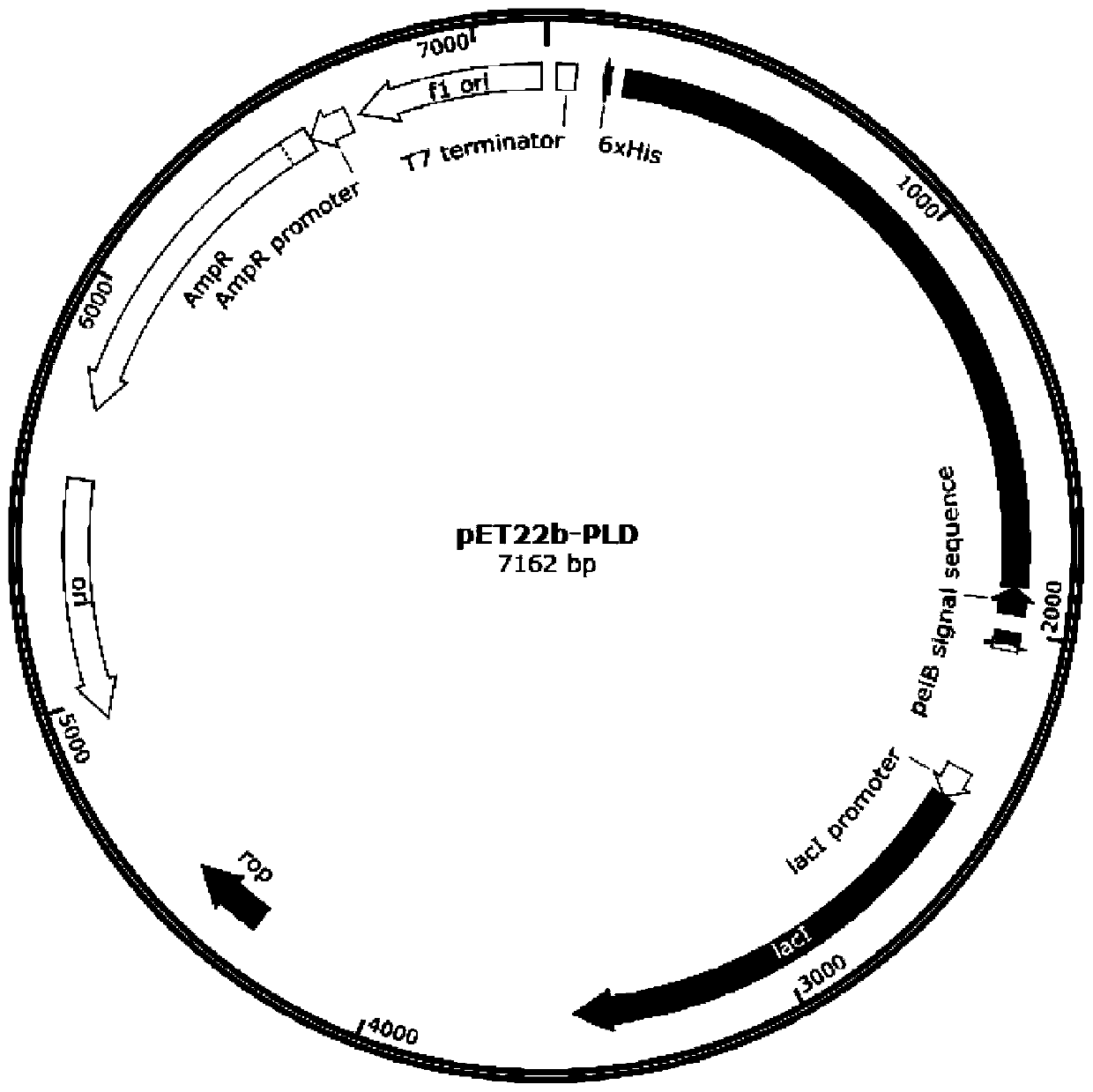
[0035] Example 1: Construction of recombinant Escherichia coli BL21(DE3)-pET22b-PLD.
[0036] (1) Using the genomic DNA of Streptomyces sp. (strain PMF) as a template to clone the phospholipase gene, the base sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO.2;
[0037] (2) Cloning the phospholipase D gene obtained in (1) into the pET-22b(+) expression vector to construct a recombinant expression plasmid;
[0038] (3) The recombinant plasmid obtained in (2) was transformed into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) competent cells to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli BL21(DE3)-pET22b-PLD1.
Embodiment 2
[0040] The composition of the seed medium is: NaCl 5g / L, peptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, pH 7.4, sterilized at 121°C for 20min.
[0041] The components of the fermentation medium are: peptone 10g / L, yeast extract 5g / L, NaCl 5g / L, sterilized at 121°C for 20min.
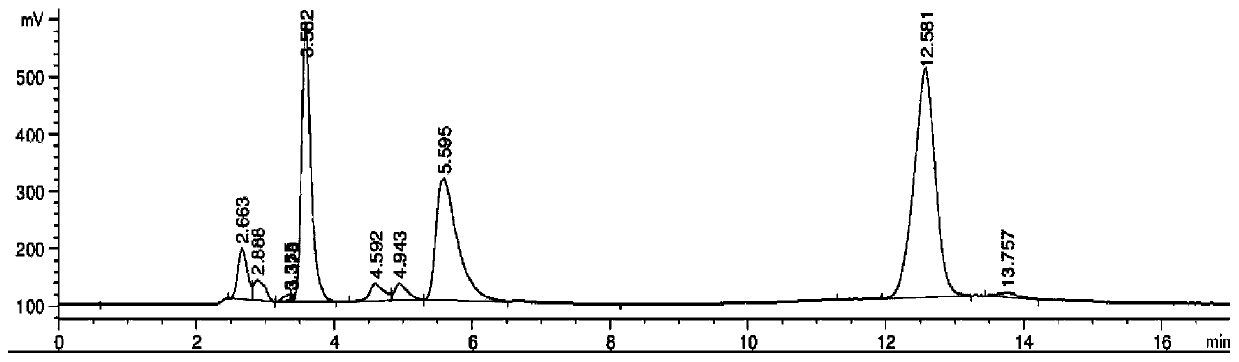
[0042] Inoculate the recombinant Escherichia coli BL21(DE3)-pET22b-PLD1 in the seed medium containing 50mg / mL ampicillin, and culture it in the shake flask at 37°C and 200r / min until the logarithmic growth phase, as the seed liquid; then the seed liquid Inoculate into 100mL fermentation medium containing ampicillin 50mg / mL according to 5% inoculum amount, and culture in shake flask at 37°C and 200r / min until OD 600 =0.6, then add IPTG to a final concentration of 0.05mM, induce culture at 30°C, 200r / min for 12h; centrifuge the fermentation broth at 4°C, 8000r / min for 10min, and take the supernatant to obtain a crude phospholipase D enzyme solution.
[0043]Dissolve lecithin in dichloromethane at a concentration of 10...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Embodiment 3: Phospholipase D gene codon optimization
[0047] (1) Escherichia coli codon optimization was performed on the phospholipase D gene derived from Streptomyces sp. (strain PMF) to obtain the optimized phospholipase D gene, whose sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1:
[0048] (2) Cloning the phospholipase D gene obtained in (1) into the pET-22b(+) expression vector to construct a recombinant expression plasmid;
[0049] (3) The recombinant plasmid obtained in (2) was transformed into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) competent cells to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli BL21(DE3)-pET22b-PLD2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com