Application of transcription factor VP1 in regulating crop plant height and grain starch content
A technology of transcription factor and starch content, applied in the field of genetic engineering breeding of crops, can solve the problem of not being able to significantly increase starch content, and achieve the effects of improving plant type, improving grain quality, and increasing starch content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] The preparation of embodiment 1 transcription factor VP1 gene
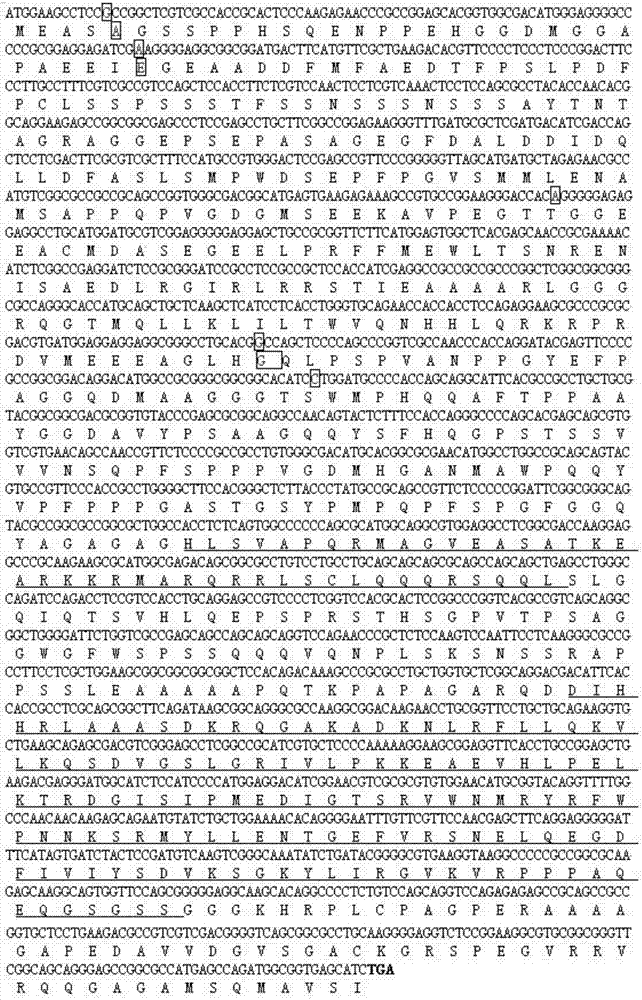
[0045] The invention uses the mRNA of immature corn seeds as a template to synthesize a corn grain cDNA library and clones the corn transcription factor VP1 gene by using a PCR method. Using grain cDNA as a template, the maize VP1 gene was amplified with KOD enzyme, and a specific target product band was amplified with a molecular weight of about 2.1 kb, which was consistent with the expected value. The PCR product of the VP1 gene was directly connected to the pMD19-T vector after purification, and the plasmid DNA was extracted from the positive clone and analyzed by restriction endonuclease. It was confirmed that the size of VP1 cloned by PCR method was correct, and the DNA sequence sequence confirmed it. The cloned gene is VP1. The primer sequence used to amplify the full-length sequence of the VP1 coding region is: 5' end primer 5'- GGATCC ATGGAAGCCTCCTCCGGCTC-3' (SEQ ID NO.3), 3' end primer 5'- GAG...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Transformation of corn backbone inbred lines with plant expression vectors containing the VP1 gene
[0049] Contain the plant expression vector construction of VP1 gene: the plant overexpression vector that the present invention selects is pCAMBIA3301, at first design contains HindIII and BamHI specific primer (5 ' end primer: AAGCTT ATCAGTGGCCAGCTTTTGTTCTA (SEQ ID NO.5) and 3' end primer: GGATCC AAGTAACACCAAACAACAGGGT (SEQ ID NO.6)), the promoter sequence of Ubiquitin gene (GenBank accession number: U29159.1) is amplified with maize genomic DNA as a template, and then the VP1 specific primer containing BamHI and SacI described in Example 1 is used (5'- GGATCC ATGGAAGCCTCCTCCGGCTC-3' (SEQ ID NO.3), 5'- GAGCTC AGATGCTCACCGCCATCTGG-3'(SEQ ID NO.4)), using the corn cDNA library as a template to amplify the full-length sequence of the VP1 gene, and then connecting the two fragments into the intermediate vector pBI221 containing the Nos terminator, and finall...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3 Detection and Utilization of Transgenic Corn Plants
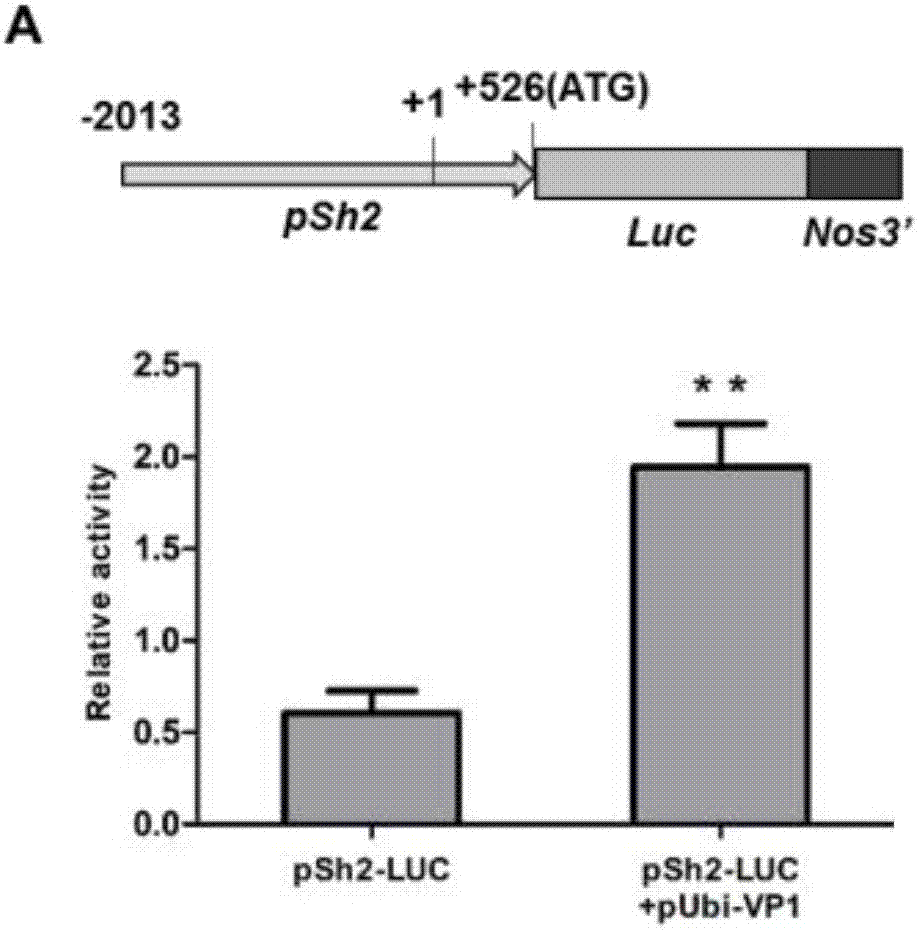
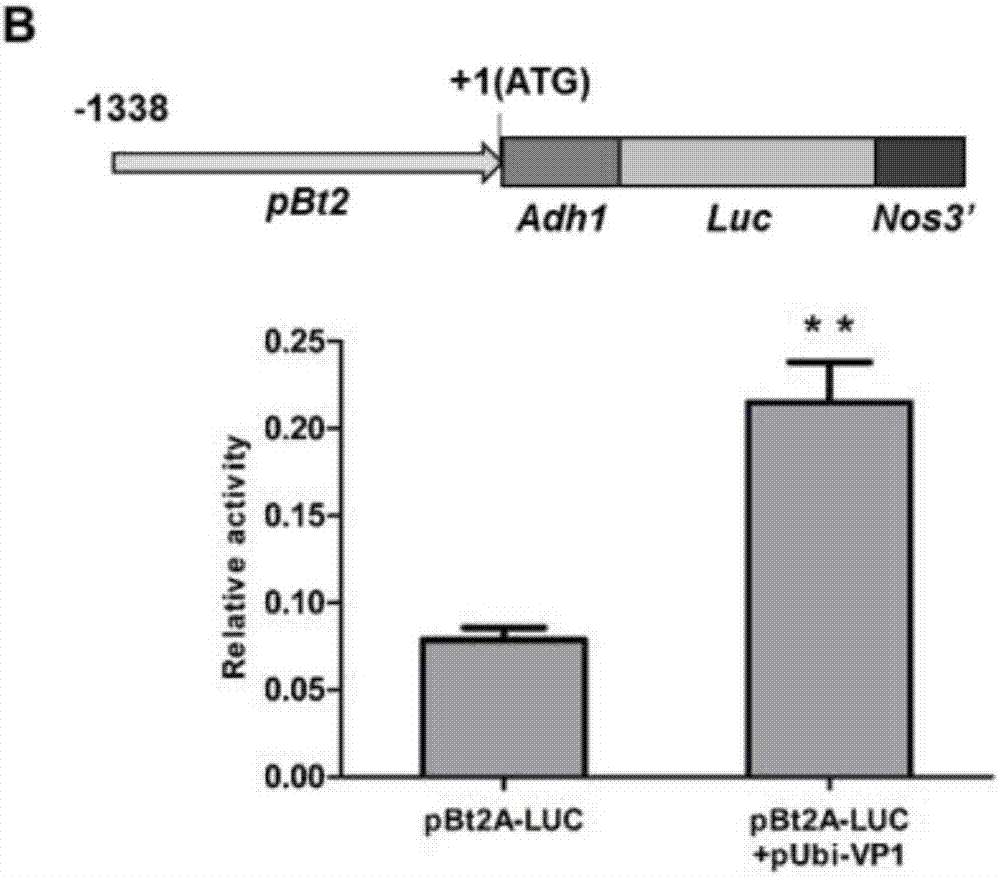
[0053] After the transgenic T0 generation seedlings were transplanted into the field, the leaves of the seedlings were taken for GUS staining, and leaf DNA was extracted, and the gene transformation was detected by PCR method, and the seedling plants with GUS staining blue and PCR target bands were regarded as transgenic positive plants ( Figure 10 ), extract RNA from leaves of positive plants, carry out RT-PCR analysis after reverse transcribing cDNA, and detect the expression of VP1 gene in transgenic plants ( Figure 11 ), to screen the transgenic plants with significant overexpression of VP1 gene, bagged self-cross or sister cross to set fruit.
[0054] The seeds produced by the positive T0 generation plants were planted in addition (in order to prevent the problem of different stages of male and female development, they were planted in two batches with an interval of 10 days), and the T1 generation p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com