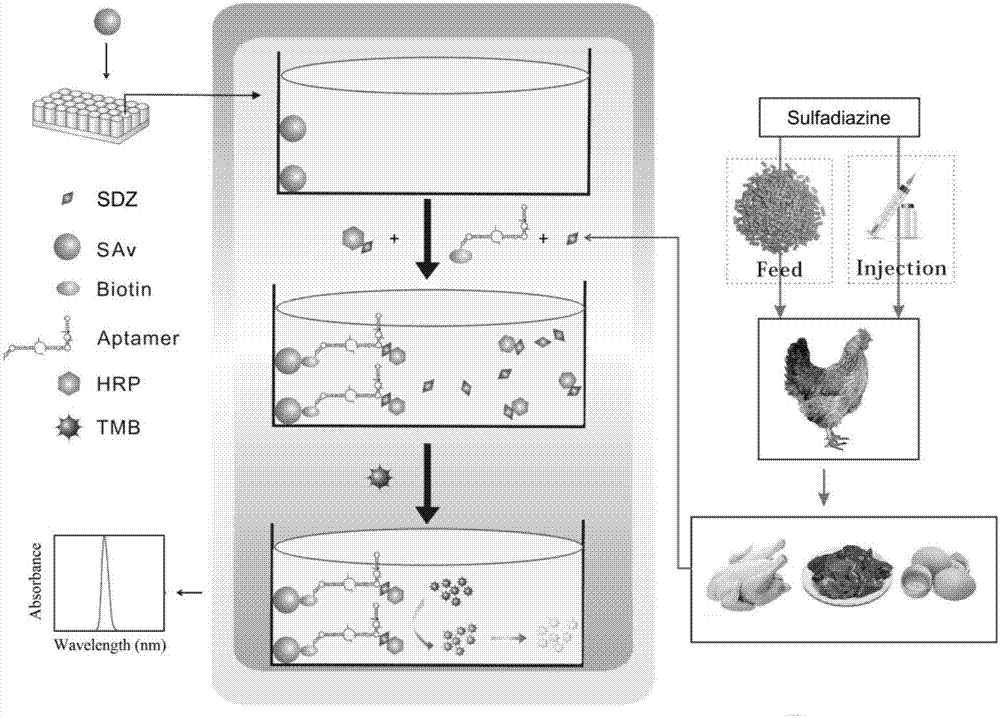
Biosensing probe kit for detecting sulfadiazine on basis of nucleotide aptamer specificity, and application thereof
A technology of nucleic acid aptamer and sulfadiazine, which is applied in the field of biology and food safety analysis, can solve the problems of high specificity of aptamers, failure of detection methods, change of ion concentration in reaction system, etc., and achieve broad application prospects and rapid detection , the effect of high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Embodiment 1 prepares the nucleic acid aptamer of SDZ
[0058] (1) SDZ and sulfamethoxine coupled with agarose magnetic beads
[0059] Take 10mg of SDZ, first dissolve in 2mL of DMF, and then add 2mL of coupling buffer after it is completely dissolved, then add 30mg of NHS (N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide) and 26mg of EDC to the solution in sequence [1-Ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide, then completely dissolve NHS and EDC; place the solution in a shaker, react at 4°C for 15 minutes, and activate the amino group in SDZ; 2mL Amino Sepharose magnetic beads were washed 3 times with coupling buffer, mixed with the above-mentioned activated SDZ solution, and placed in a shaker at room temperature to react for 2 hours; after the reaction was completed, the reactant was washed 5 times with an acid-base alternating buffer solution, Wash with PBS for 5 times, and finally store in PBS at 4°C; the same method is used for the coupling reaction of sulfamethoxine and amino-seph...
Embodiment 2
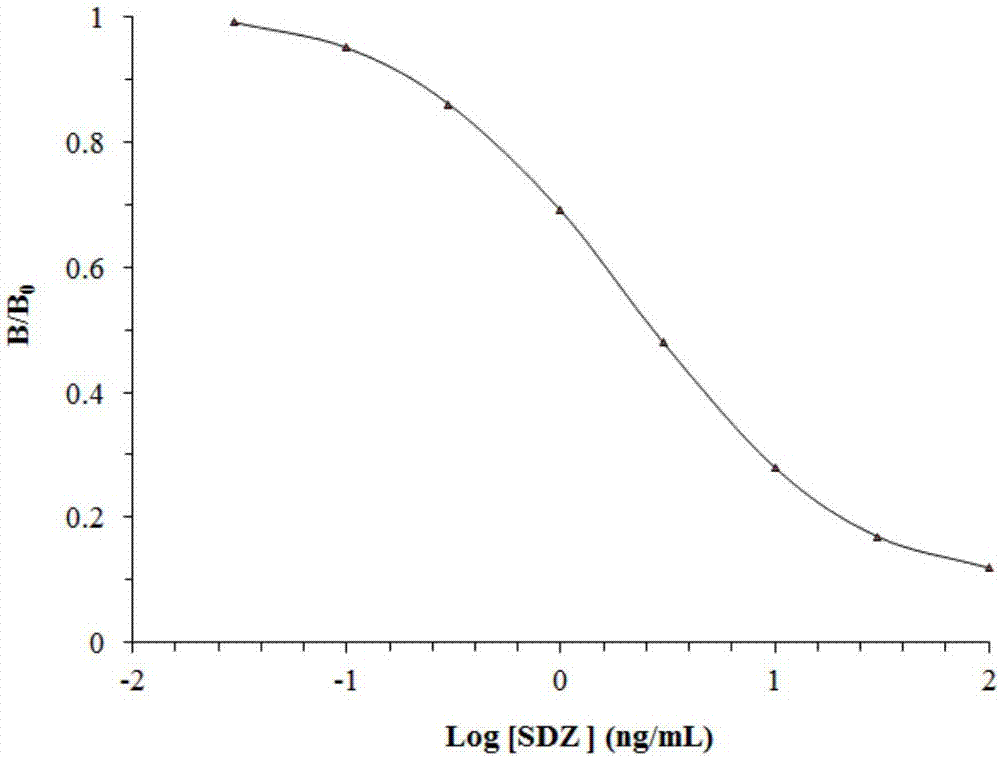
[0076] The determination test of embodiment 2 equilibrium dissociation constant
[0077] The nucleic acid aptamers obtained by synthesis and sequencing were measured by fluorescence method for their equilibrium dissociation constant Kd. The synthesized 5'-FAM-labeled aptamer was configured into different concentration gradient solutions (0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 0.16, 0.32 and 0.64 μmol / L) with binding buffer, and 10 μL of SDZ-modified agarose beads were taken, Mix 200 μL of 5'-FAM-labeled aptamers with different concentration gradients and 10 μL of SDZ-modified agarose beads, incubate at room temperature for 30 minutes, centrifuge to discard unbound DNA; then wash the agarose magnetic beads 3 times with binding buffer , use 200 μL of binding buffer each time; then elute the DNA bound to SDZ with 100 μL of 2mol / L NaOH solution at 95°C, and elute twice to obtain a total of 200 μL of eluent; dilute the same eluate with different eluents multiple, then placed in a 96-well black...
Embodiment 3
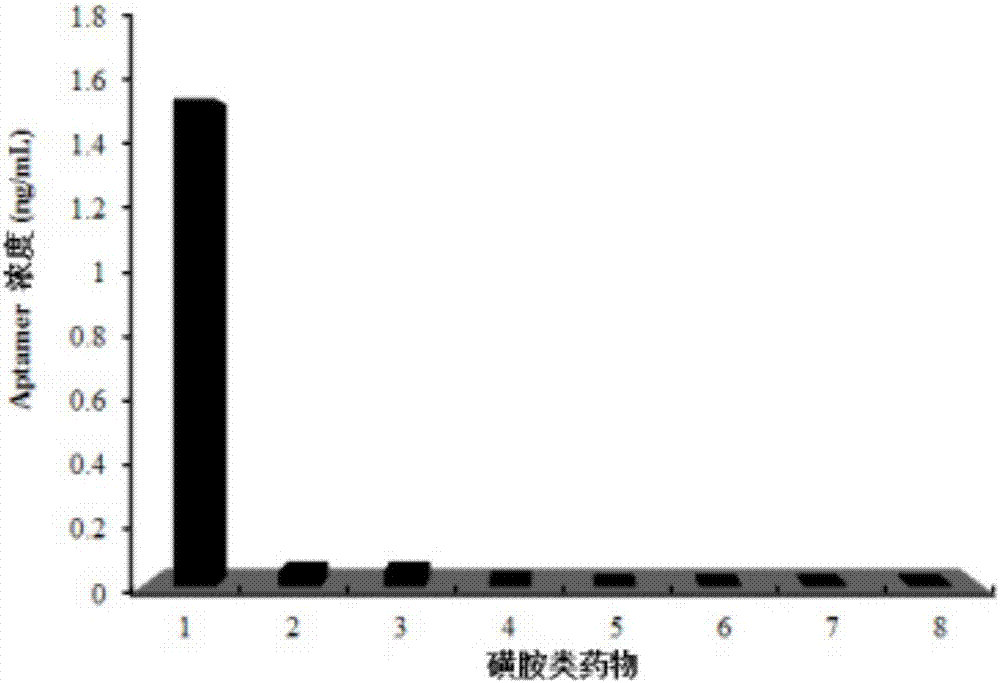
[0078] Example 3 Aptamer specificity test
[0079] Take standard stock solutions of SDZ, sulfamethoxine, sulfamethoxine, sulfadimethoxine, sulfamethoxine, sulfaquinoxaline, sulfamethoxazine and sulfamethoxazole, and dilute to The final concentration is 5 μmol / L. Dissolve 5 μg of nucleic acid aptamer in 100 μL of binding buffer, denature at 95°C, place it on ice for 10 minutes, and then place it at room temperature for 5 minutes. Take 100 μL of the prepared SDZ and other standard solutions into the pretreated aptamer solution, and incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes. Then add the above mixed solution to the SDZ-agarose magnetic bead conjugate, and incubate at 37°C for 30min. The supernatant after incubation was taken out, and the concentration of ssDNA in the supernatant was measured by NanoDrop. For the reference group, a drug-free binding buffer was used to incubate with the pretreated nucleic acid aptamer (the operation was the same as above), and then the incubation solution...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com