Construction method and application of high-yield engineering strain for optically pure meso-2,3-butanediol
A meso-2 and engineering strain technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low optical purity, low yield and high raw material cost, and achieve the effects of convenient and simple operation, high strain yield and high production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
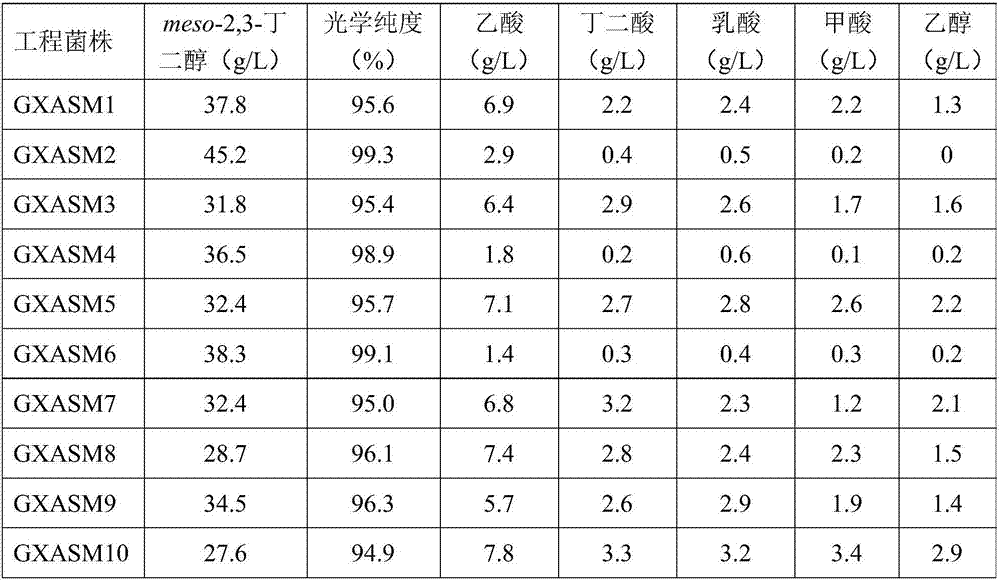
[0030] Construction of the genetic engineering strain GXASM1 producing meso-2,3-butanediol:
[0031] The nucleosides of α-acetolactate synthase gene KpbudB, α-acetolactate decarboxylase gene KpbudA derived from K.pneumoniae strain and meso-2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase gene EcbudC derived from E.cloacae strain The codon-optimized acid sequence was added in front of each gene with the nucleotide sequence TAAGGAGGATATACA containing the ribosome binding site; the codon-optimized α-acetolactate synthase gene, α-acetolactate decarboxylase gene and meso- The 2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase gene was spliced by artificial synthesis, and a gene cluster KpbudB-KpbudA-EcbudC comprising three genes was obtained. The nucleotide sequence length was 3292 bases, and the nucleotide sequence was as follows: As described in SEQ ID NO.1; the KpbudB-KpbudA-EcbudC gene cluster is inserted into the expression vector pTrc99A by double enzyme digestion and ligation method to obtain the pTrc99A-KpbudB-Kp...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Construction of the genetically engineered strain GXASM2 producing meso-2,3-butanediol:
[0034] The main by-products of the fermentation of the engineering strain GXASM1 were (2R,3R)-2,3-butanediol, (2S,3S)-2,3-butanediol, succinic acid, lactic acid, acetic acid, ethanol and formic acid , the key genes of its synthetic pathway are gldA, dar, frdABCD, ldhA, pta, adhE and pflB. Using the principle that the Red recombination system derived from Escherichia coli phage can efficiently mediate homologous recombination in bacteria, first replace the above target gene with the resistance gene with FRT sites on both sides, and then induce the expression of exogenous temperature-sensitive plasmid FLP recombinase deletes the resistance gene to achieve the purpose of knocking out the target gene. The specific steps are as follows:
[0035] Transform the pKD46 plasmid into host cells to prepare electroporation-competent cells; use primers to carry out PCR to construct the targetin...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Construction of the genetically engineered strain GXASM3 producing meso-2,3-butanediol:
[0053] The difference between this example and Example 1 is: the source strain of α-acetolactate synthase gene and α-acetolactate decarboxylase gene is Enterobacter cloacae, the source of meso-2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase gene The strain is Klebsiella oxytoca.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com