Preparation method and application of pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane protein vaccine
A technology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and outer membrane protein, applied in chemical instruments and methods, medical preparations containing active ingredients, antibacterial drugs, etc., can solve the problems that there is no Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine on the market, and achieve Effects against infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] Expression, purification and coating of embodiment 1.His-OprH vaccine:
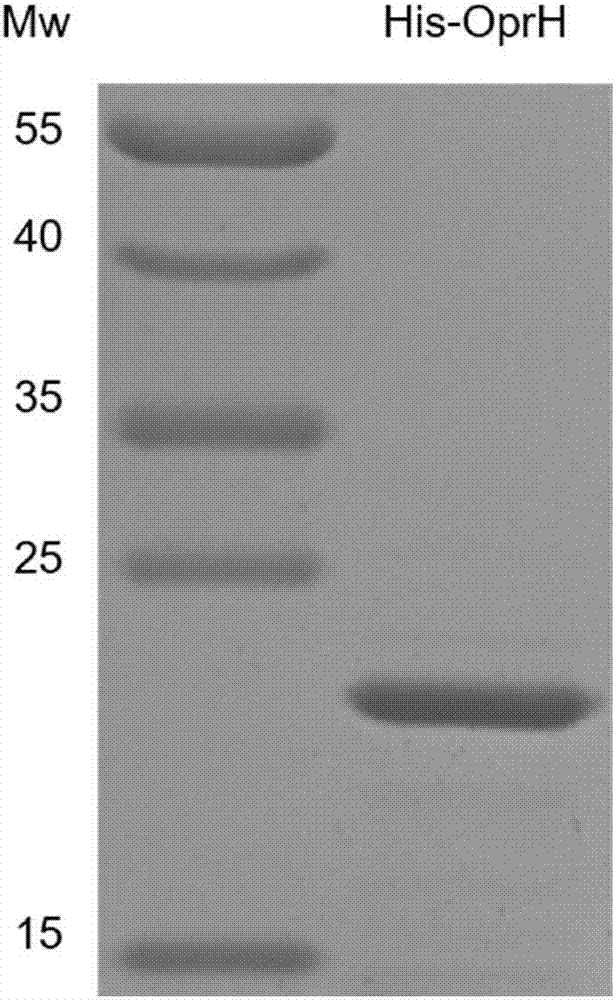
[0071] Using the genomic DNA of the PA14 strain as a template, the oprH gene fragment not containing the start codon was amplified by PCR. The above PCR product was digested and cloned into the plasmid pET28b to construct the protein expression plasmid pET28b-His-OprH. The protein expression plasmid stored in DH5α was extracted, and transformed into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) by electroporation. The expression of His-OprH fusion protein was induced by 1 mMIPTG, the bacteria expressing the protein were collected by centrifugation and sonicated, and the His-OprH fusion protein was purified by Ni-NTA, and the purified protein was further purified by molecular sieve ( figure 1 ). The finally obtained protein was concentrated by ultracentrifugation, diluted 10 times in a coating solution containing 3% DHPC, and placed at 37° C. for 72 hours. The coated fluid is dialyzed, and the protein is concentrat...
Embodiment 2
[0072] The immune effect measurement of embodiment 2.His-OprH vaccine:
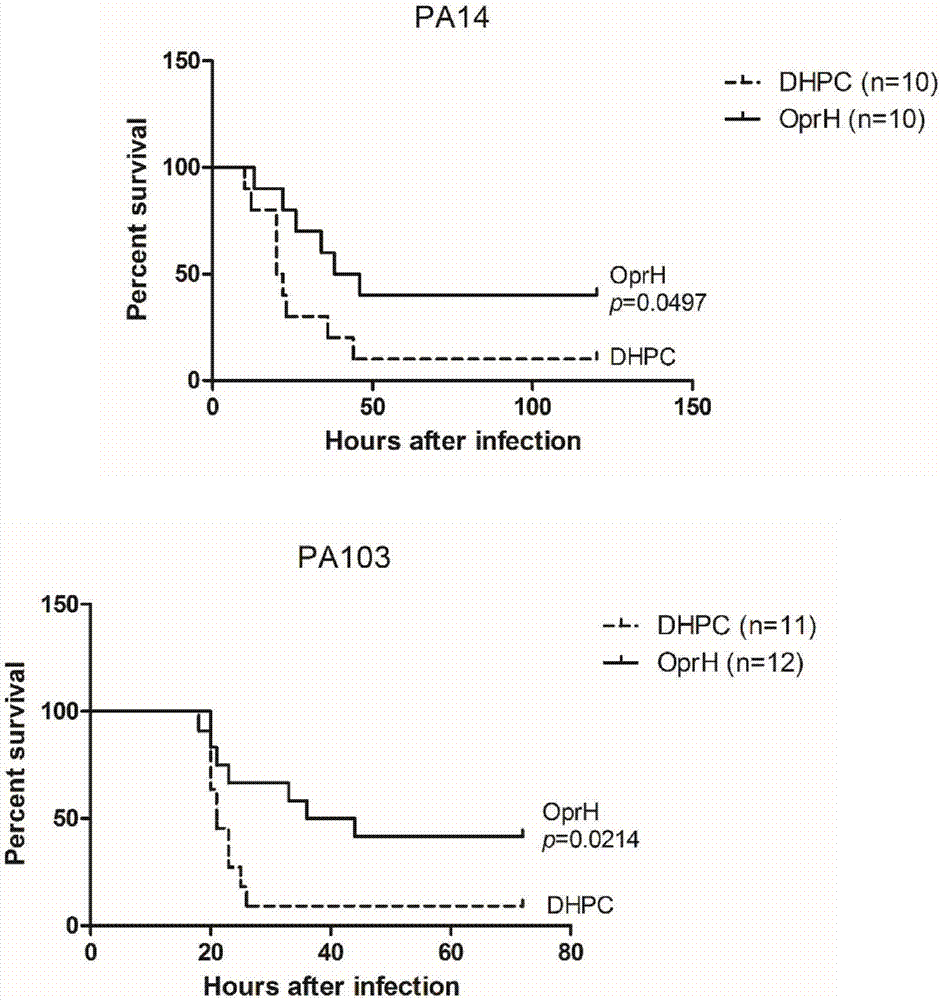
[0073] The coated His-OprH vaccine was mixed with 20mg / ml immune adjuvant Curdlan suspension 1:1, and the control sample was mixed with Curdlan by exchange buffer 1:1. After the mice were anesthetized with 7.5% anhydrous chloral, the mice were immunized through the nasal cavity, and 10 μl of the vaccine or control sample was dripped into each nostril, and each mouse was immunized with a total of 20 μl. A total of three immunizations were performed at intervals of one week, and follow-up experiments could be carried out three weeks after the last immunization was completed.
[0074] The strains required for infection were cultured to the logarithmic phase, the bacteria were washed twice with PBS, and then resuspended to the desired concentration. After the mice were anesthetized with 7.5% anhydrous chloral, the mice were infected through the nasal cavity, 10 μl was instilled into each nostril, and each mo...
Embodiment 3
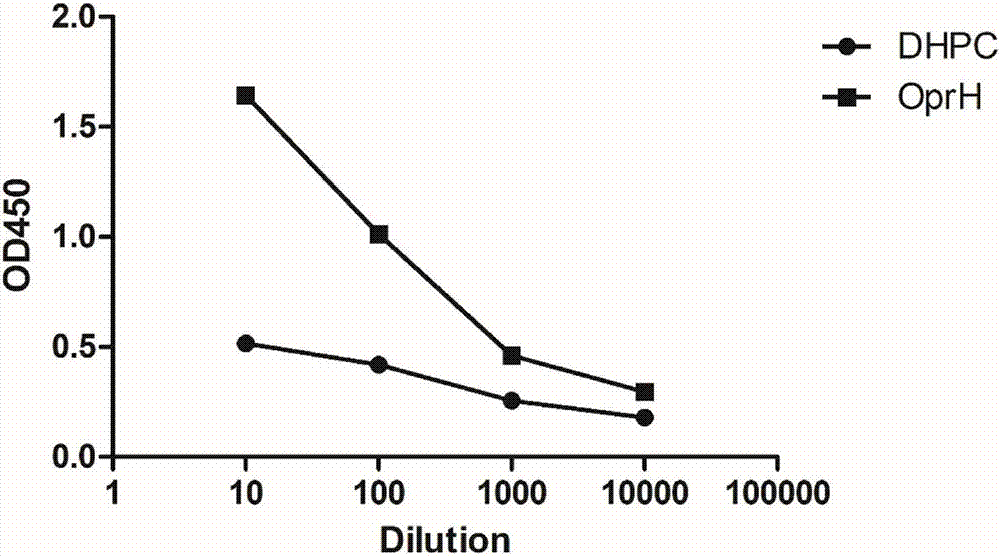
[0075] Example 3. Detection of antibody levels against OprH in mouse serum after immunization:
[0076] Three weeks after the last immunization, the sera of the mice in the OprH immunized group and the control group were taken out for the experiment. The OprH protein dissolved in PBS at a concentration of 1 mg / ml was used to coat the microtiter plate at 4°C overnight, and the protein solution in each well was 100 μl. After the coating was completed, the coating solution was removed, and 200 μl of PBST solution containing 1% BSA was added for blocking, and incubated at 37° C. for 2 h. After blocking, add 100 μl of mouse serum after doubling dilution to each well, and incubate at 37°C for 1 hour. Each well was washed 3 times with PBST, then 100 μl of diluted HRP-crosslinked anti-mouse IgG antibody was added, and incubated at 37°C for 1 h. Wash again with PBST for 3 times, add 200 μl TMB horseradish peroxidase color development solution, and carry out color reaction in the dark...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com