Thermal decay resistant composite fiber reinforced type brake pad
A composite fiber and heat-resistance technology, applied in the field of brake pads, can solve the problems of reducing braking performance and wear resistance, and achieve the effects of reducing brake noise, small temperature changes, and high wear resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
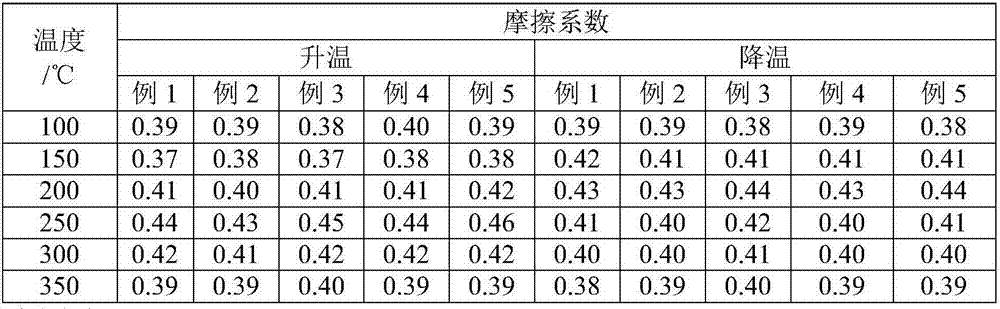
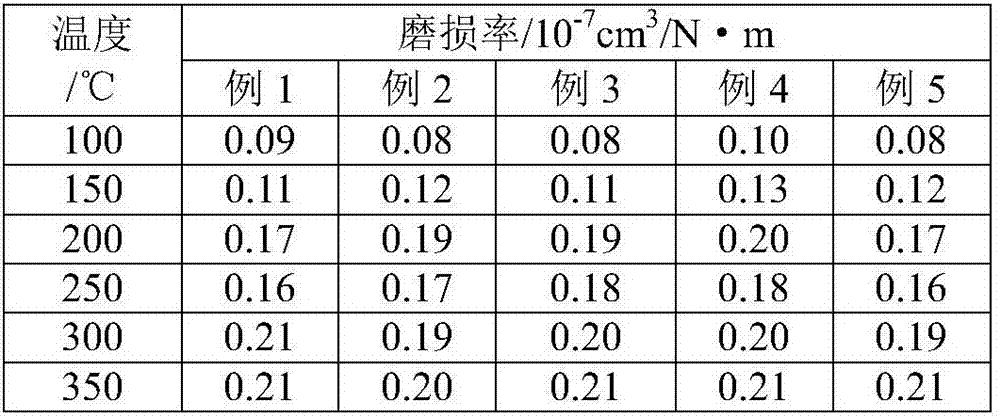
[0025]A composite fiber-reinforced brake pad resistant to heat decay, made of the following components: phenolic resin 7g, reinforced composite fiber 5g, mineral fiber 3g, glass fiber 2g, barium sulfate 5g, nitrile powder 3g, coke powder 4~11g, montmorillonite nano powder 3g, 2,4,6-tris(dimethylaminomethyl)phenol 0.3g, friction powder 5g, graphite 5g, tire powder 5g, carbon black 3g, nano fluorite powder 4g, nano Sepiolite powder 2g, nano silica airgel powder 3g, heavy calcium carbonate 2g, silane coupling agent 5g. The montmorillonite nano powder is preferably used after being modified by the following process: add 0.1 times the weight of epoxy resin liquid dropwise to the montmorillonite nano powder and stir in a water bath at 75°C for 90min at a stirring rate of 25r / min, then 120°C Keep it for 10 hours, and keep it at 160°C for 2 hours to obtain a soaking powder, and then grind and disperse to make the particle size of the soaking powder reach 100-300nm.
[0026] Preferred...
Embodiment 2
[0035] A composite fiber-reinforced brake pad resistant to heat decay, made of the following components: phenolic resin 12g, reinforced composite fiber 7g, mineral fiber 7g, glass fiber 4g, barium sulfate 8g, nitrile powder 5g, coke powder 6g, montmorillonite nano powder 4g, 2,4,6-tris(dimethylaminomethyl)phenol 0.5g, friction powder 7g, graphite 7g, tire powder 7g, carbon black 4g, nano fluorite powder 5g, nano sea foam Stone powder 3g, nano silica airgel powder 5g, heavy calcium carbonate 3g, silane coupling agent 8g. The montmorillonite nano powder is preferably used after being modified by the following process: drop 0.21 times the weight of epoxy resin liquid into the montmorillonite nano powder and stir in a water bath at 80°C for 120min at a stirring rate of 30r / min, then 130°C Keep it for 11 hours, and keep it at 170°C for 3.5 hours to obtain a soaking powder, and then grind and disperse to make the particle size of the soaking powder reach 100-300nm.
[0036] Preferr...
Embodiment 3
[0045] A composite fiber-reinforced brake pad resistant to heat decay, made of the following components: 15g of phenolic resin, 10g of reinforced composite fiber, 10g of mineral fiber, 5g of glass fiber, 10g of barium sulfate, 7.5g of nitrile powder, coke Powder 7.5g, montmorillonite nano powder 5.5g, 2,4,6-tris(dimethylaminomethyl)phenol 0.6g, friction powder 10g, graphite 10g, tire powder 10g, carbon black 5g, nano fluorite powder 7g, Nano sepiolite powder 4.5g, nano silica airgel powder 6g, heavy calcium carbonate 4g, silane coupling agent 10g. The montmorillonite nano powder is preferably used after being modified by the following process: drop 0.21 times the weight of epoxy resin liquid into the montmorillonite nano powder and stir in a water bath at 80°C for 120min at a stirring rate of 30r / min, then 130°C Keep it for 11 hours, and keep it at 170°C for 3.5 hours to obtain a soaking powder, and then grind and disperse to make the particle size of the soaking powder reach ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mohs hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com