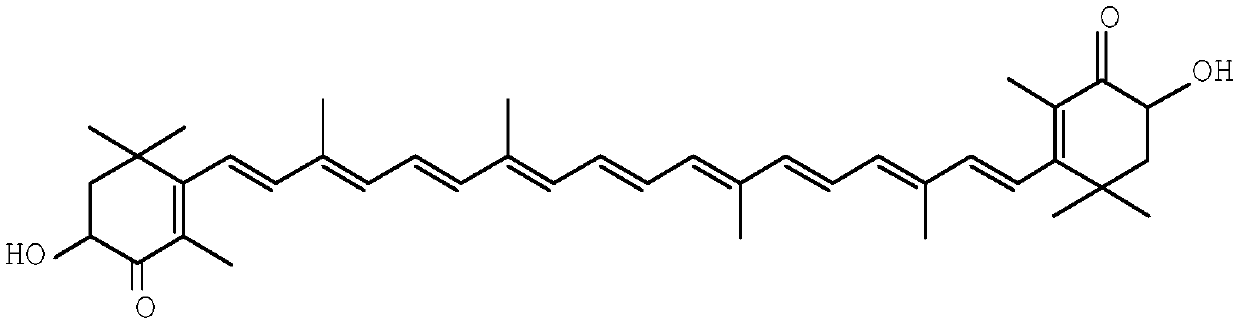
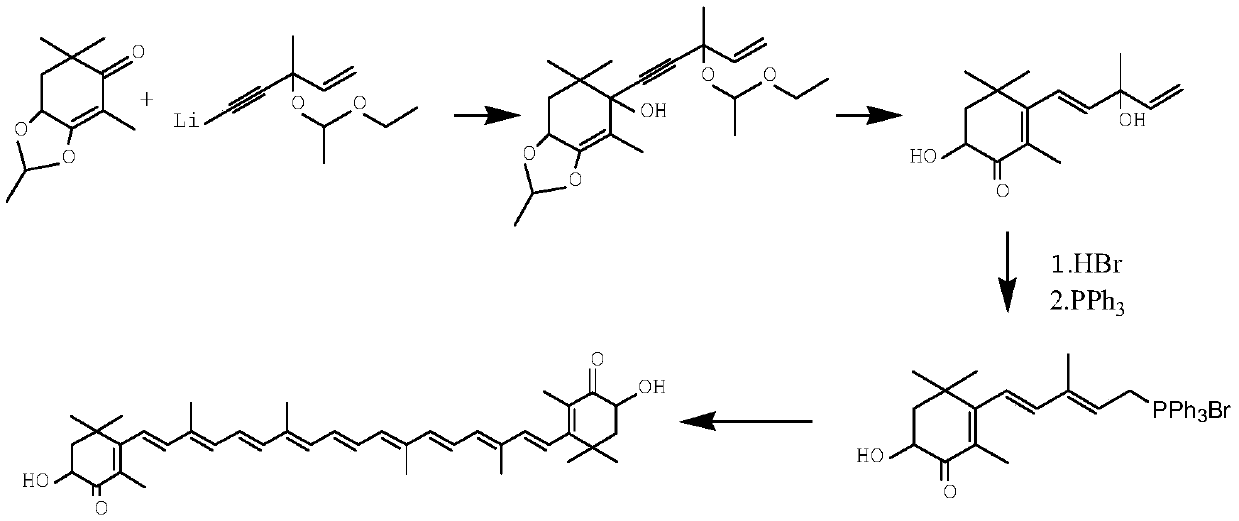
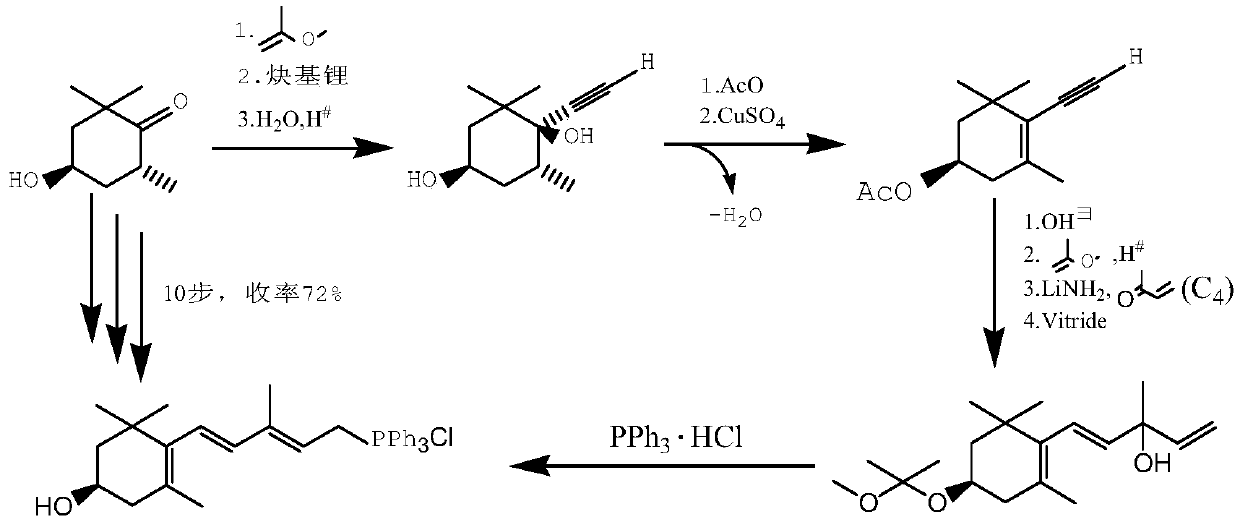
A kind of synthetic method of astaxanthin intermediate
A synthesis method and intermediate technology, applied in the field of astaxanthin preparation, can solve the problems of increasing reaction route steps and costs, complex reaction route, cumbersome operation, etc., avoiding multiple introductions and repeated hydrolysis, simplifying the process, and ensuring Yield effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] (1) Synthesis of 3-methyl-1-pentene-4-yn-3-alcohol lithium
[0052] Take 800ml of liquid ammonia, and cool it to -45°C with dry ice alcohol, take 10.5g of lithium particles, put it into the liquid ammonia, and put it in for 20 minutes. The system temperature is -40°C, the temperature difference is within 2°C, and keep warm for 40 minutes;
[0053] Pass acetylene for 1 hour, the flow rate is 0.6L / min, the temperature is controlled at -35°C, and then the alcohol bath is raised to 0°C to volatilize the liquid ammonia. As the liquid ammonia decreases to the remaining 500-600ml, start to drop 450g of toluene, raise the temperature to 10°C, continue to volatilize the liquid ammonia, and cool to -10°C after the addition of toluene is complete.
[0054] Dissolve 90g of 1-buten-3-one in 50g of toluene and add it dropwise to the above reaction system. Control the temperature to -5°C ~ -10°C, keep the temperature for 30 minutes after dropping, and generate lithium 3-methyl-1-pent...
Embodiment 2
[0067] The reaction condition of embodiment 2 is identical with embodiment 1, but the heterodiketone added in step (3) is 3,5,5,7-tetramethyl-1,2-dioxocyclopentabicyclo[ 4,1,0]-3-conen-4-one, the added mass is 240g.
[0068] Step (3) After the condensation reaction, the sample was measured, and the total yield of the first three steps was calculated to be 87%. The final product purity of embodiment 2 is 96%, and the total yield is 76%.
Embodiment 3
[0070] The reaction condition of embodiment 3 is identical with embodiment 1, but adopts sherwood oil to replace toluene to carry out liquid ammonia replacement in step (1).
[0071] After the condensation reaction in step (3) was completed, the sample was measured, and the total yield of the first three steps was calculated to be 85%. The final product purity of embodiment 2 is 94%, and the total yield is 74%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com