Method for selectively recovering lithium in waste lithium iron phosphate anode material by high temperature solid phase method
A technology of lithium iron phosphate and cathode material is applied in the field of selective recovery of lithium in waste lithium iron phosphate cathode material by high-temperature solid-phase method, which can solve the problems of waste of phosphorus resources, complicated process and high processing cost, and achieves clean and simple process. , the effect of high leaching rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
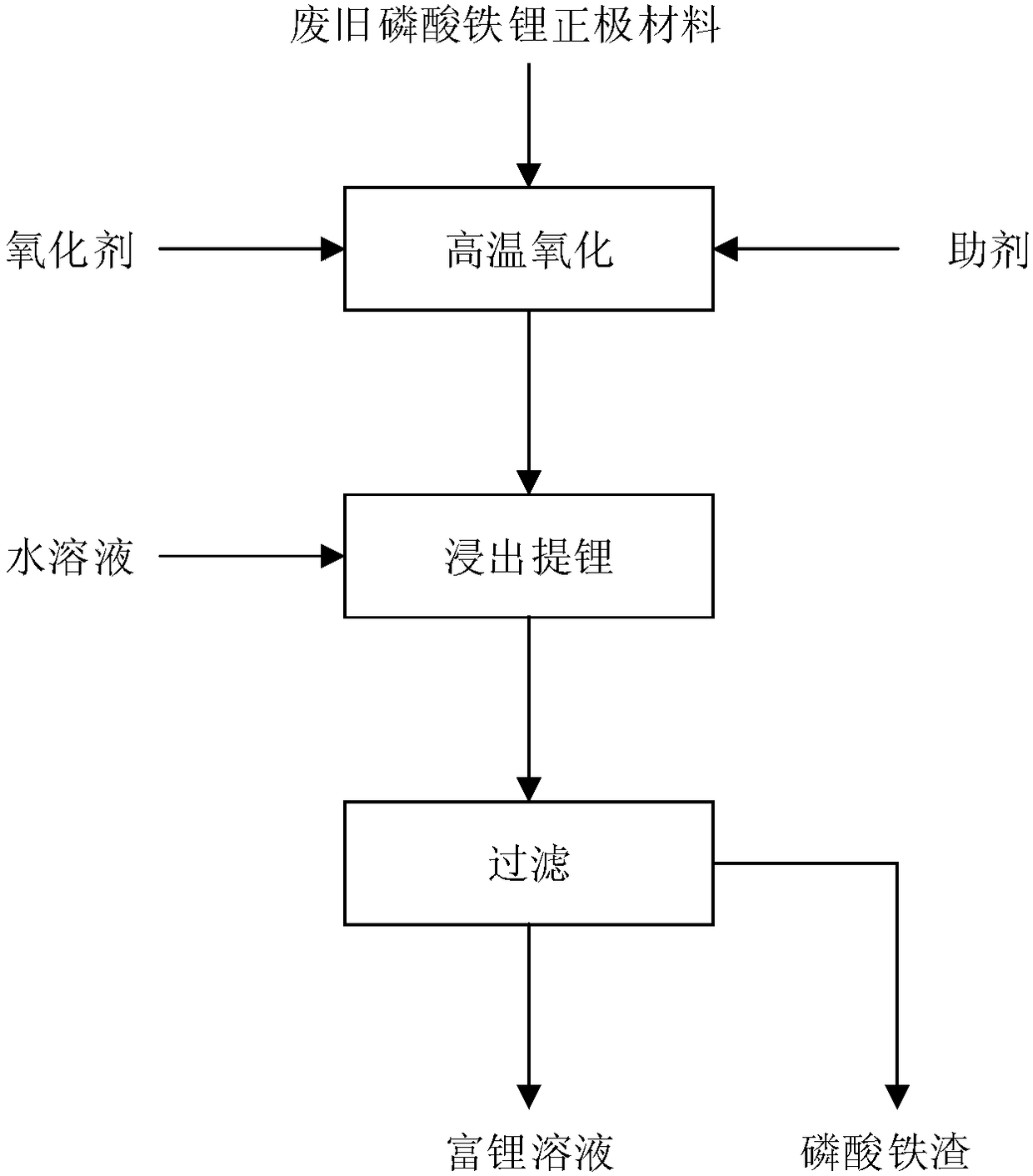
[0042] This embodiment provides a method for recovering lithium in waste lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material by solid phase method, the specific method is:
[0043] (1) After mixing the waste lithium iron phosphate cathode material with sodium sulfate (auxiliary agent), oxidize and calcinate it at 600°C under the condition of introducing a large amount of ozone (oxidant), so that the binder in the waste lithium iron phosphate cathode material Decomposition and volatilization, the added mass of sodium sulfate is 1.5 times the theoretical mass required to form lithium sulfate, and the calcination time is 360min to obtain clinker. The ferrous ion in lithium iron phosphate is oxidized to trivalent at high temperature, and the sulfuric acid in lithium and additive The water-soluble lithium salt formed by the combination of roots;
[0044] (2) After the calcined clinker is cooled, it is leached in water at 25°C for 240 minutes, and the lithium salt is leached into the...
Embodiment 2
[0049] This embodiment provides a method for recovering lithium in waste lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material by solid phase method, the specific method is:
[0050] (1) After mixing the waste lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material with potassium hydrogen sulfate, oxidize and calcinate it at 800°C under the condition of feeding a large amount of oxygen, so that the binder in the waste lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material is decomposed and volatilized, and potassium hydrogen sulfate The added mass is 1.5 times of the theoretical mass required to form lithium sulfate, and the calcination time is 240min to obtain clinker, a water-soluble lithium salt formed by the combination of lithium and hydrogen sulfate in the auxiliary agent;
[0051] (2) After the calcined clinker is cooled, it is leached in water at 60°C for 120 minutes, and the lithium salt is leached into the liquid phase, while iron and phosphorus exist in the solid phase in the fo...
Embodiment 3
[0055] This embodiment provides a method for recovering lithium in waste lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material by solid phase method, the specific method is:
[0056] (1) After mixing the waste lithium iron phosphate cathode material with ammonium sulfate, oxidize and calcinate it at 1200°C under the condition of introducing a large amount of air to decompose and volatilize the binder in the waste lithium iron phosphate cathode material, and add a mass of ammonium sulfate To form 1.5 times the theoretical mass required for lithium sulfate, the calcination time is 120min to obtain clinker, a water-soluble lithium salt formed by the combination of lithium and sulfate in the auxiliary agent;
[0057] (2) After the calcined clinker is cooled, it is leached in water at 110° C. for 30 minutes, and the lithium salt is leached into the liquid phase, while iron and phosphorus exist in the solid phase in the form of ferric phosphate precipitation to obtain a slurry;
[0058...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com