Purification method of crude glycerine obtained from kitchen waste and application thereof
A purification method, a technology for kitchen waste, applied in chemical instruments and methods, separation/purification of hydroxyl compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as limiting the speed at which the film can be processed, sticking to the roller, and the film cannot be collected. , to maximize resource utilization and prevent waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] In this example, the pretreatment of purified crude glycerol for PHA fermentation is demonstrated. Methanol was first removed from crude glycerol by evaporation under vacuum at 50-90°C over 2 hours. The crude glycerol is then acidified to the desired pH level (pH 5-6) with an acid (such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid and / or phosphoric acid at a mass concentration of 5-6%) and held for a time long enough to allow the formation of three separate The layers: the upper layer is the fatty acid phase, the middle layer is the glycerol-rich phase, and the bottom layer is the inorganic salt phase and other aqueous residues. The bottom phase was separated by simple decantation. The fatty acid-rich upper phase was separated from the glycerol-rich phase by using a separating funnel. The extracted glycerol was neutralized with 12M KOH solution, and then evaporated to remove water at 110° C. for 2 hours, and then filtered with activated carbon to remove the solid residue, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0021] In this example, the fermentation and extraction of PHA using the purified glycerol in Example 1 is demonstrated.
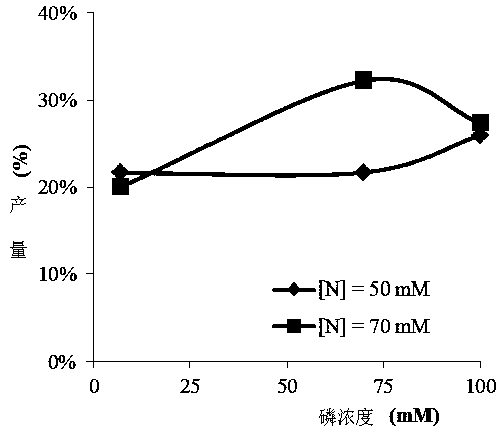
[0022] The yield of PHA production varied with different nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations. Therefore, nitrogen concentrations (50 mM and 70 mM NH 4+ ) and phosphorus concentration (7 mM, 70 mM and 100 mM PO 4 3- ) on the production of PHA. Different concentrations of NH 4+ and PO 4 3- Add glycerol (32 g / L) to the Erlenmeyer flask, and then incubate aerobically at 100 rpm at 35°C in a shaking incubator.
[0023] After 28 h and 96 h of fermentation, the bacterial cells were collected by centrifugation and then freeze-dried for the subsequent PHA extraction process. The hypochlorite method has been found to be a simple and quick method of extracting PHA. The hypochlorite dissolves the non-PHA cellular material while precipitating insoluble polymers in solution. PHA was extracted with hypochlorite in 2% (w / v) active chlorine, and the remaining l...
Embodiment 3
[0025] In this example, PHA formulations for film production by cast film extrusion and / or blown film extrusion are shown. The key to film formation is to increase the crystallization rate of PHA. The solution in this example is to add a nucleating agent to the formula to accelerate crystallization.
[0026] Conventional nucleating agents include, for example, talc, micronized mica, calcium carbonate, boron nitride, ammonium chloride, and the like. In addition to those, carboxylates of metals of Groups I and II of the periodic table can also be used as nucleating agents. Examples of carboxylic acids are acetic, propionic, caproic, palmitic, stearic, oleic, behenic, montanic, etc.; while group I and II metals include sodium, potassium, lithium, magnesium, calcium, barium, and zinc. The addition amount may be in the range of 0.5 wt% to 5 wt%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com