Method for identifying homokaryotic strains in T. trogii S0301
A technology of trachemetes and homokaryon, which is applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of heavy workload, difficult strains, and time-consuming, and achieve reliable results, simple methods, and obvious advanced effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1: the preparation of protoplast and regenerated bacterial strain of heat-resistant trachemetrichum S0301
[0037] Bacterial blocks (0.5 cm in diameter) were inoculated from the edge of the colony on the MA medium plate and inoculated into the GYP liquid medium, cultured at a low speed for 4-6 days, and continued to culture for 3-4 days after the mycelium was broken; Collect the mycelium, wash the bacteria three times with isotonic buffer (0.6 M mannitol, 100 mM citric acid-phosphate buffer, pH 5.4), centrifuge at 8000 g for 10 min, and then use the push-filtered enzymatic hydrolyzate (containing 1% lysozyme (isotonic buffer solution) was fully suspended, enzymatically hydrolyzed at 28°C and 80 rpm for 1.5 h; the enzymolyzed solution was filtered through three layers of mirror paper, the filtrate was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 15 min, and the protoplasts were precipitated in isotonic buffer The solution was washed several times and centrifuged to obtain 1-2 ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: Cloning and Gene Analysis of the Mating Type Gene b1 and b2 Sites of Thermostable Trametes Trichomyosus S0301
[0039] Pick the fresh hyphae of Trametes tracheiformis S0301 cultured at 28 °C for 6 days on the MA medium plate, grind it to powder under liquid nitrogen freezing conditions, take 0.1 g of the powder to extract genomic DNA, and the extraction method refers to the fungal genome extraction kit ( Biomega).
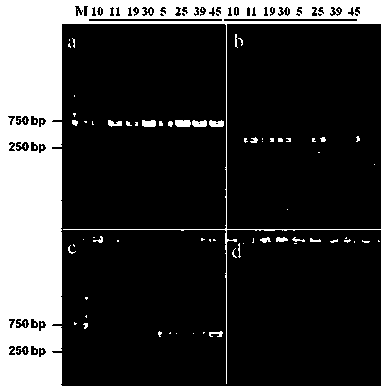
[0040] Based on the genetic sequence of the mating type b locus in the laboratory data of the second-generation genome data of the thermostable Trametes trichomes S0301, 4 pairs of primers were designed in the border regions corresponding to the b1 and b2 genes. The design results are shown in Table 1. Synthesize relevant primer pairs according to the sequence, wherein primers M1-1F / R and M1-2F / R correspond to the two genes b1-1 and b1-2 genes near the b1 site, respectively; primers M2-1F / R and M2-2F / R corresponds to the two genes b2-1 and b2-2 ...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3: Mycelia culture of Thermostable Trachemetes S0301 and combined observation of lock-shaped regenerated single bacterial strains
[0049] A total of 45 regenerated strains were obtained through the protoplast regeneration of Trametes trachees S0301; the regenerated single bacteria block was picked to the GYP solid plate, and three sterile loading plates were inserted near, middle and far away from the block by the inserting method. Slide, when the hyphae spread to the edge of the glass slide, observe the microscopic characteristics of the hyphae and the presence or absence of lock joints under a 100× oil lens and a 10× eyepiece.
[0050] According to the diameter of colonies on the regeneration plate, 45 regenerated strains were randomly selected for microscopic observation. Trametes T. trogii The S0301 mycelia are fine and thin, and the characteristic structures such as cell separation and lock joints need to be observed with an oil microscope. figure 1 ; ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com