Preparation method of nano zero-valent iron loaded hydrophilic porous biochar composite material
A technology of nano-zero-valent iron and composite materials, which is applied in the direction of water pollutants, chemical instruments and methods, and alkali metal compounds, etc., can solve the problems of low performance of adsorption and removal of heavy metals, instability of nano-zero-valent iron, and high cost of substrates. Achieve the effect of increasing utilization value, reducing synthesis cost and improving utilization efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
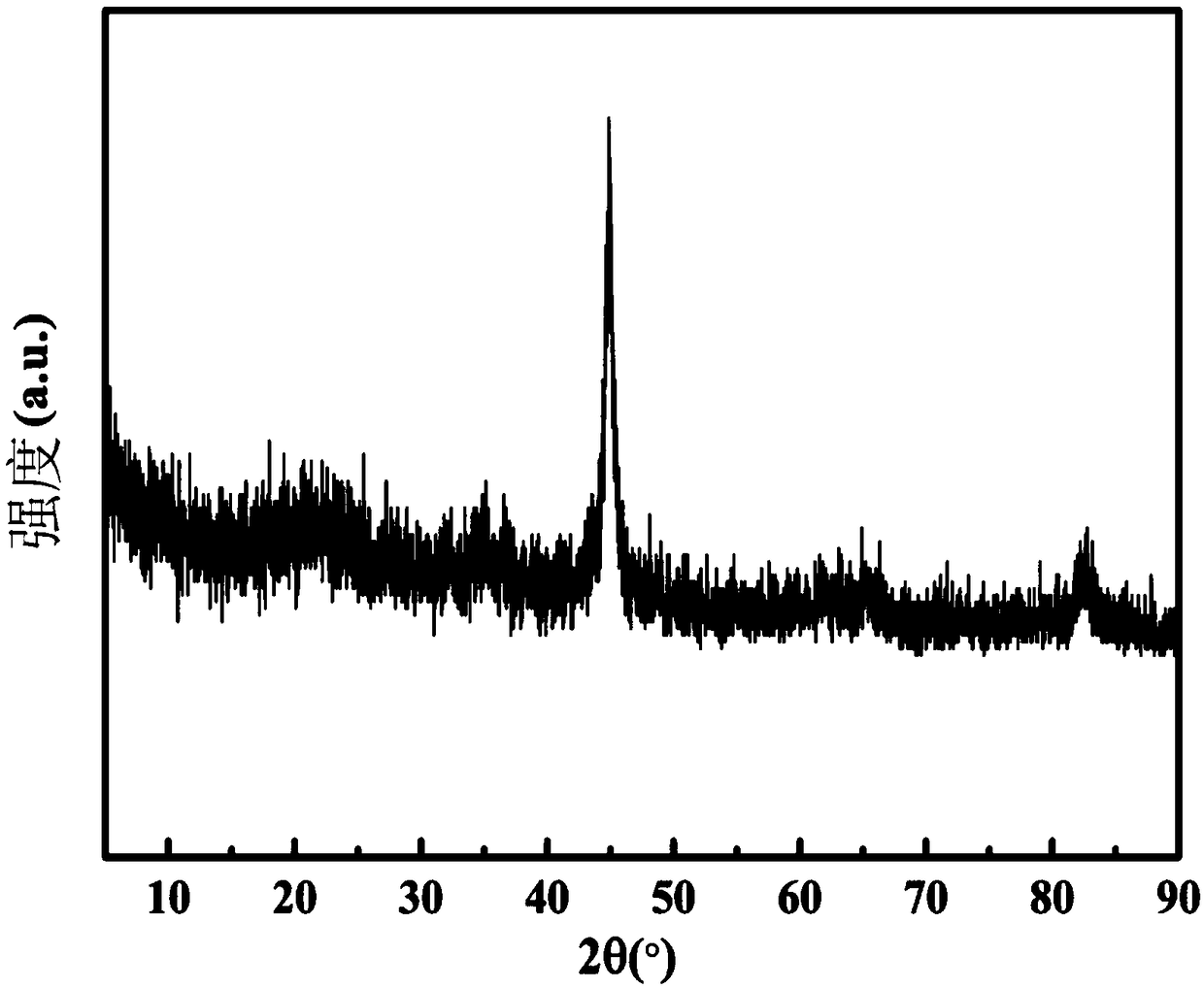
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0028] Specific embodiment 1: This embodiment is a preparation method of nano zero valent iron supported hydrophilic porous biochar composite material, which is specifically completed according to the following steps:
[0029] 1. Biomass pyrolysis molten salt activation:
[0030] ① Cut and crush the raw material of biochar, wash it 5-10 times with distilled water, and then dry it at a temperature of 70℃~90℃, and then pass the dried biochar raw material through a 100-200 mesh sieve to obtain a biological Fine powder of carbon raw materials;
[0031] ②. Grind and mix the fine powder of biochar raw material and metal salt to obtain reactants; place the reactants in a tube furnace, pass inert gas into the tube furnace, and heat the tube furnace to 700 under the protection of inert gas ℃~900℃, and then pyrolyze 1h~3h under the protection of inert gas atmosphere at 700℃~900℃ to obtain porous biochar material after pyrolysis and carbonization;
[0032] The inert gas mentioned in step 1 ② is...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0048] Specific embodiment two: this embodiment is different from specific embodiment one in that: the biochar raw material mentioned in step one ① is one or several of corn stalk, wheat stalk, soybean stalk, rice stalk and rice husk mixture. Others are the same as the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0049] Specific embodiment three: this embodiment is different from specific embodiment one or two in that the metal salt described in step one (2) is KHCO 3 Or NaHCO 3 . Others are the same as the first or second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com