Preparation method of flame-retardant cellulose fiber
A technology of flame-retardant cellulose and cellulose, which is applied in the manufacture of artificial filaments in cellulose solution, fire-resistant and flame-retardant filaments, etc., and can solve the problem of long, usually 2 to 48 hours, or even up to 120 hours, limited functions The application and development of flame-retardant fibers, the impact of spinneret pressure resistance and drafting, etc., to achieve the effects of shortened dissolution time, easy industrial production, and no pollution to the environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
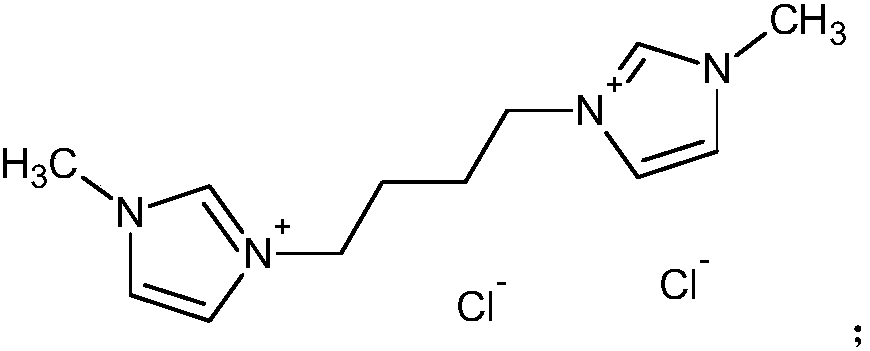
[0046] 1. Preparation of 1,4-bis[1-(3-methylimidazolium)]butyl dichloride:
[0047] Under nitrogen protection at 80°C, slowly drop 1.2mol N-methylimidazole into 1mol 1,4-dichlorobutane, after the dropwise addition, reflux for 72 hours to complete the reaction, and cool the reaction solution to room temperature to obtain The product was washed with ether to remove unreacted raw materials, and a white solid was obtained, which was bis-1,4-bis[1-(3-methylimidazole)]butyl dichloride (HPLC purity was 98.8%, yield 88 %).
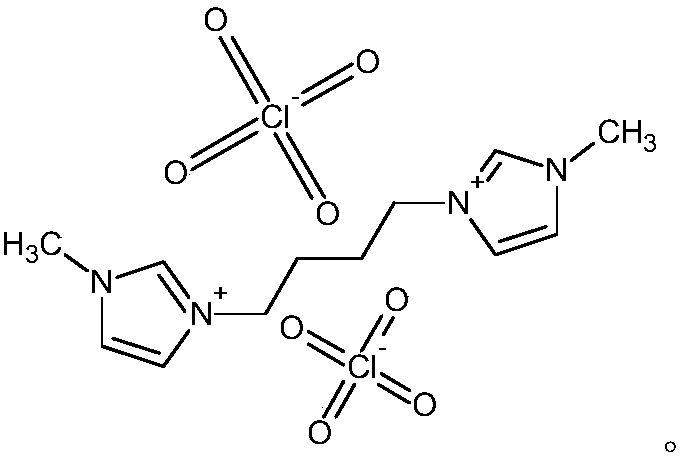
[0048] Two, the preparation of 1,4-bis[1-(3-methylimidazole)]butyl diperchlorate:
[0049] Dissolve 1 mol of 1,4-bis[1-(3-methylimidazolium)]butyl dichloride and 1.2 mol of lithium perchlorate in 1L of water, then stir and react at 80°C for 36 hours, then cool to room temperature, Stirring was continued at room temperature for 12 hours, the reaction solution was dispersed into an equal volume of chloroform, separated, the chloroform phase was washed with water u...
Embodiment 2
[0065] The only difference between this example and Example 1 is: 0.8 parts by mass of SFR-100 and 9.2 parts by mass of cotton pulp (the cellulose content is 99%, and the degree of polymerization is 600) are mixed uniformly, and then 100 parts by mass, 85wt % in the ionic liquid aqueous solution, all the other contents are the same as those described in Example 1.
[0066] After testing, the flame-retardant cellulose fiber prepared in this example has a breaking strength of about 3.2 cN / dtex when the monofilament fineness is 1.67 dtex; and the experiment shows that: under the same conditions, 85 wt% of 1- Butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride, 1,4-bis[1-(3-methylimidazolium)]butyl dichloride or 1,4-bis[1-(3-methylimidazolium)] When the single ionic liquid aqueous solution of butyl diperchlorate dissolves the flame retardant and cotton pulp, it needs to be stirred at 110-130°C for 3-5 hours to obtain a stable and uniform spinning solution, and the single fiber fineness is the same...
Embodiment 3
[0068] The only difference between this example and Example 1 is that 1.2 parts by mass of SFR-100 and 8.8 parts by mass of cotton pulp (the cellulose content is 99%, and the degree of polymerization is 600) are evenly mixed, and then 100 parts by mass, 85 wt. % in the ionic liquid aqueous solution, all the other contents are the same as those described in Example 1.
[0069]After testing, the flame-retardant cellulose fiber prepared in this example has a breaking strength of about 3.4 cN / dtex when the monofilament fineness is 1.67 dtex; and the experiment shows that: under the same conditions, using 85 wt% of 1- Butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride, 1,4-bis[1-(3-methylimidazolium)]butyl dichloride or 1,4-bis[1-(3-methylimidazolium)] When the single ionic liquid aqueous solution of butyl diperchlorate dissolves the flame retardant and cotton pulp, it needs to be stirred at 110-130°C for 3-5 hours to obtain a stable and uniform spinning solution, and the single fiber fineness is ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| limiting oxygen index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| limiting oxygen index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| limiting oxygen index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com