Preparing and decomposing technology for Lewis acid and base adduct saturated solution and application of preparing and decomposing technology
A preparation process and technology for adducts, applied in the engineering field of energy storage and conversion, can solve problems such as increasing decomposition temperature, and achieve the effect of good reversibility and high energy storage density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1: with reference to technique described in the present invention, adopt following technical scheme:
[0035] Ammonia is a Lewis base, and HCl contains a Lewis acid, the proton H + , they can react in the gas phase and solution phase at room temperature to form ammonium chloride, while the solid ammonium chloride decomposes significantly above 300°C:
[0036]
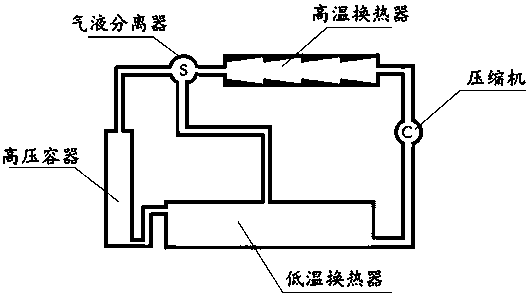
[0037] Therefore, NH 4 Cl can be used as a heat storage material above 300°C, and the heat storage energy density is about 3.23kJ / g, which is much higher than that of calcium carbonate. But NH 4 Cl has several fatal disadvantages, that is, the decomposition product NH 3Both HCl and HCl are gases, and phase separation cannot occur automatically. HCl has strong acidity and is severely corrosive to metal equipment, and they are recombined to form NH 4 Cl is a solid, not favorable for NH 4 Cl is returned to the pyrolysis endotherm. For this, we also need to use a solvent like water to help it flow...
Embodiment 2
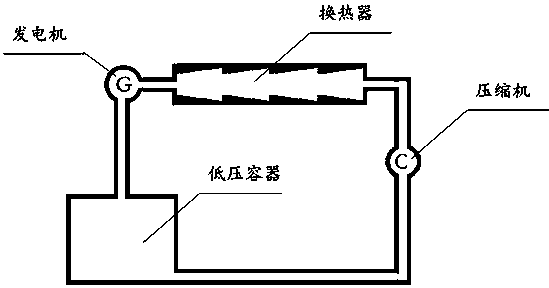
[0039] Embodiment 2: according to the deficiencies in embodiment 1, by using weak acids, such as carbonic acid, organic carboxylic acids, etc. to reduce acid corrosion, thermal decomposition temperature, etc., also make the energy of the low-temperature heat source be used for heat storage or power generation.
[0040] Using a weak acid—such as carbonic acid and amines to react, the thermal decomposition temperature of the resulting ammonium carbonate or ammonium bicarbonate in aqueous solution is below 100°C, and the heat of reaction is between 60 and 120kJ / mol (calculated according to thermochemical data .For example, NH 4 HCO 3 It is 65kJ / mol or 0.82kJ / g; (NH 4 ) 2 CO 3 is 102kJ / mol or 1.06kJ / g):
[0041]
[0042]
[0043] In the formula, R=H or an organic group. It should be noted that when organic amine carbonate or acid carbonate is thermally decomposed, CO 2 Gases, even organic amine vapors, will promote the flow of the medium, thereby increasing the heat ex...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: the preparation method of the carbonate or acid carbonate of organic amine:
[0045] 1) Mix the amine with a certain amount of water, and pass CO under stirring 2 gas;
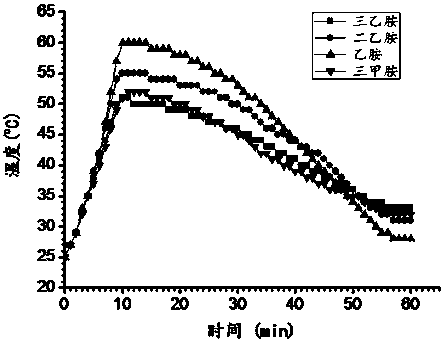
[0046] 2) Detect the pH value of the solution, it can be found that with the CO 2 There are two platforms: the first platform is about pH=10, and the second is about pH=7; when the first platform ends and the pH drops further, that is, all the amines are converted into (organic) ammonium carbonate The moment; when the second plateau ends, it is the sign that amine is all converted into bicarbonate (organic) ammonium.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com