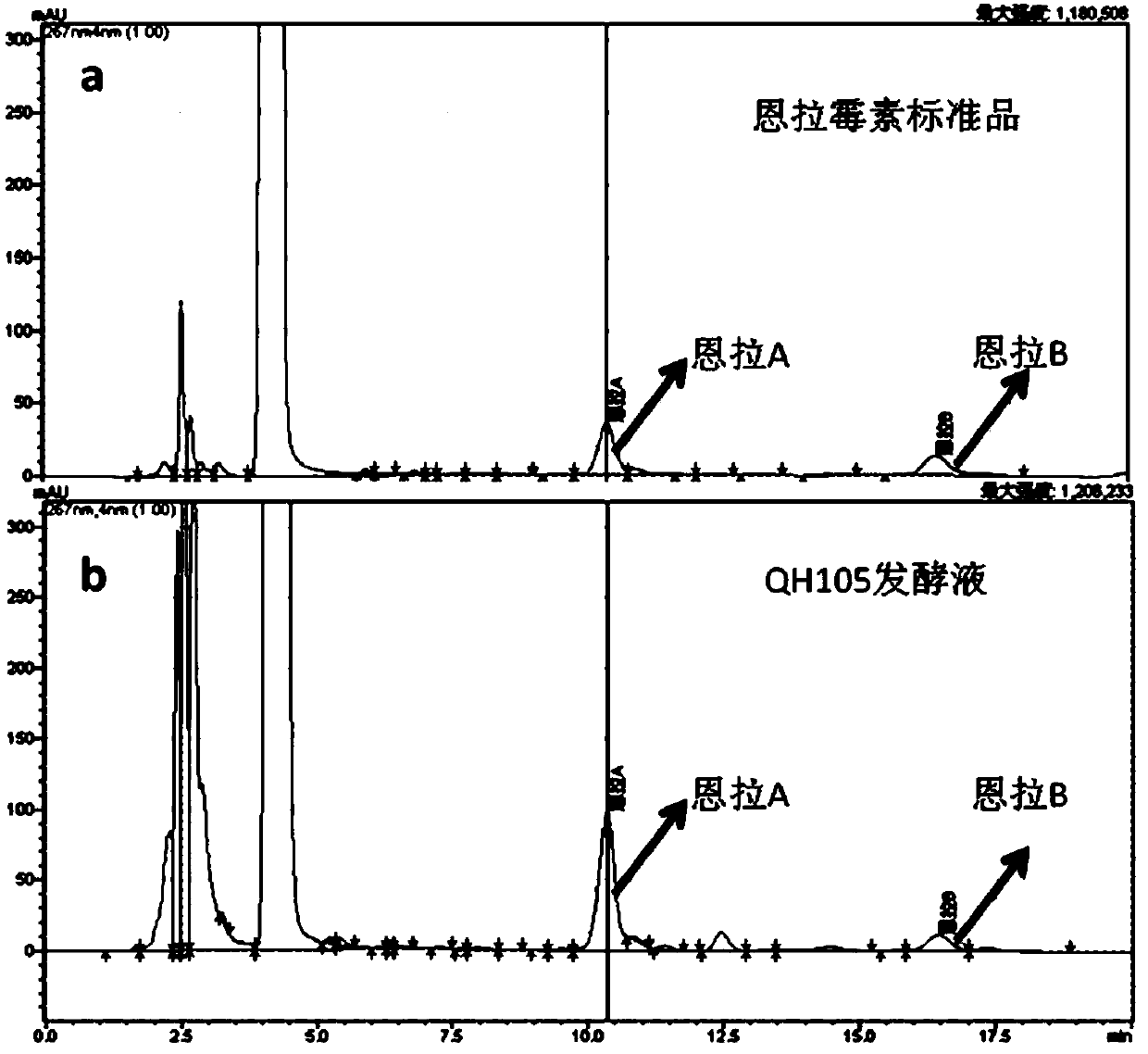
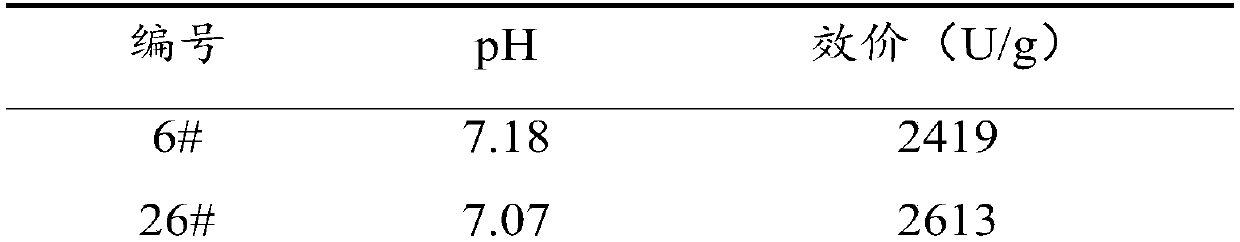Enramycin high-yield bacterial strain and screening method thereof
A technology of enramycin and high-yielding strains, applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems of long fermentation period, unfavorable large-scale production and promotion of enramycin, low yield and the like, To achieve the effect of simple method, reduced breeding cost and good reproducibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0041] The preparation method of the spore suspension includes but is not limited to: In the ultra-clean bench, the antifungal Streptomyces slant that has been cultivated for 8 days is washed with 10ml of 5% sterile glycerin water and placed in a triangular flask with glass beads, and shaken at 200rpm for 20min to make the spores Fully disperse and filter with cotton to obtain spore suspension. The spore suspension is used for mutagenesis. After the spores are prepared into single cells, they not only fully contact with the nutrient solution, but also make each single cell exposed to the mutagenic conditions, and also make the cells unaffected, which is convenient for the experiment. .
[0042] In a preferred embodiment, the screening is followed by microbial identification followed by high performance liquid chromatography.
[0043] Using the microbial identification method to screen the mutagenic strains first, and high-performance liquid chromatography to screen again, you...
Embodiment 1
[0058] The preparation of embodiment 1 spore suspension
[0059] The slant medium includes: tryptone 1g / L, skipjack extract 0.8g / L, yeast extract 0.8g / L, maltose 8g / L, agar 30g / L, pH 7.0±0.3. Cultured at 28°C for 8 days.
[0060] In an ultra-clean bench, wash the QH105 slant cultivated for 8 days with 10ml of 5% sterile glycerin water, transfer it to a conical flask with glass beads, vibrate at 200rpm for 20min to fully disperse the spores, filter with cotton to obtain a spore suspension, and set aside.
Embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2 Atmospheric room temperature plasma mutagenesis
[0062] The plane medium includes: tryptone 1g / L, skipjack extract 0.8g / L, yeast extract 0.8g / L, maltose 8g / L, agar 30g / L, pH 7.0±0.3.
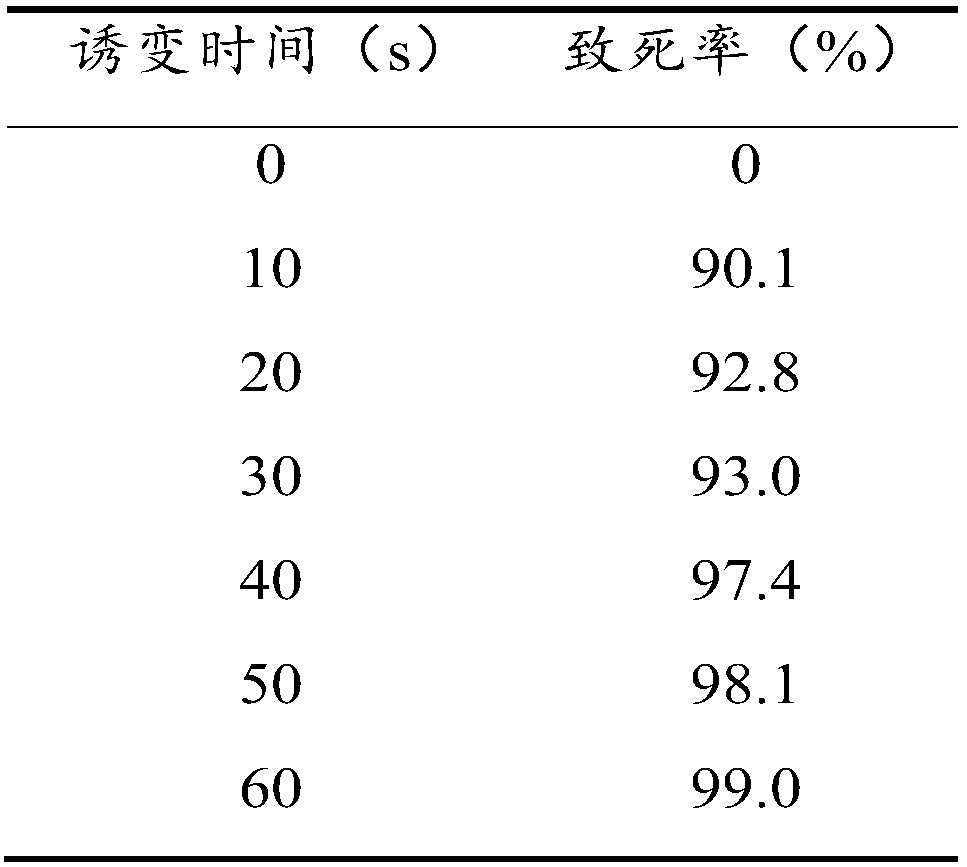
[0063] In the ultra-clean bench, take 10 μl of the QH105 spore suspension in Example 1 on the surface of the slide, and use sterile tweezers to move the slide coated with the bacterial solution to the ARTP instrument for mutagenesis treatment, with a power of 100W and a gas flow rate of 10L / min Irradiate for 0s, 10s, 20s, 30s, 40s, 50s, 60s respectively under the conditions, dilute the bacterial solution on the slide, take 100μl and spread it on the plate. Incubate at 28°C for 8 days and calculate the lethal rate. The results are shown in Table 1:
[0064] The lethality of table 1QH105 different processing time
[0065]
[0066] It can be seen from the table that atmospheric room temperature plasma mutagenesis has a strong lethality to bacterial strain QH105. When the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com