Method for removing salt by virtue of sphagnum-derived biomass carbon electrode
A biomass carbon and peat moss technology, applied in separation methods, dispersed particle separation, seawater treatment, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the wide application of CDI, secondary pollution of the environment, and high cost, improving the transmission and diffusion capacity, and improving environmental protection. the effect of increasing the contact area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
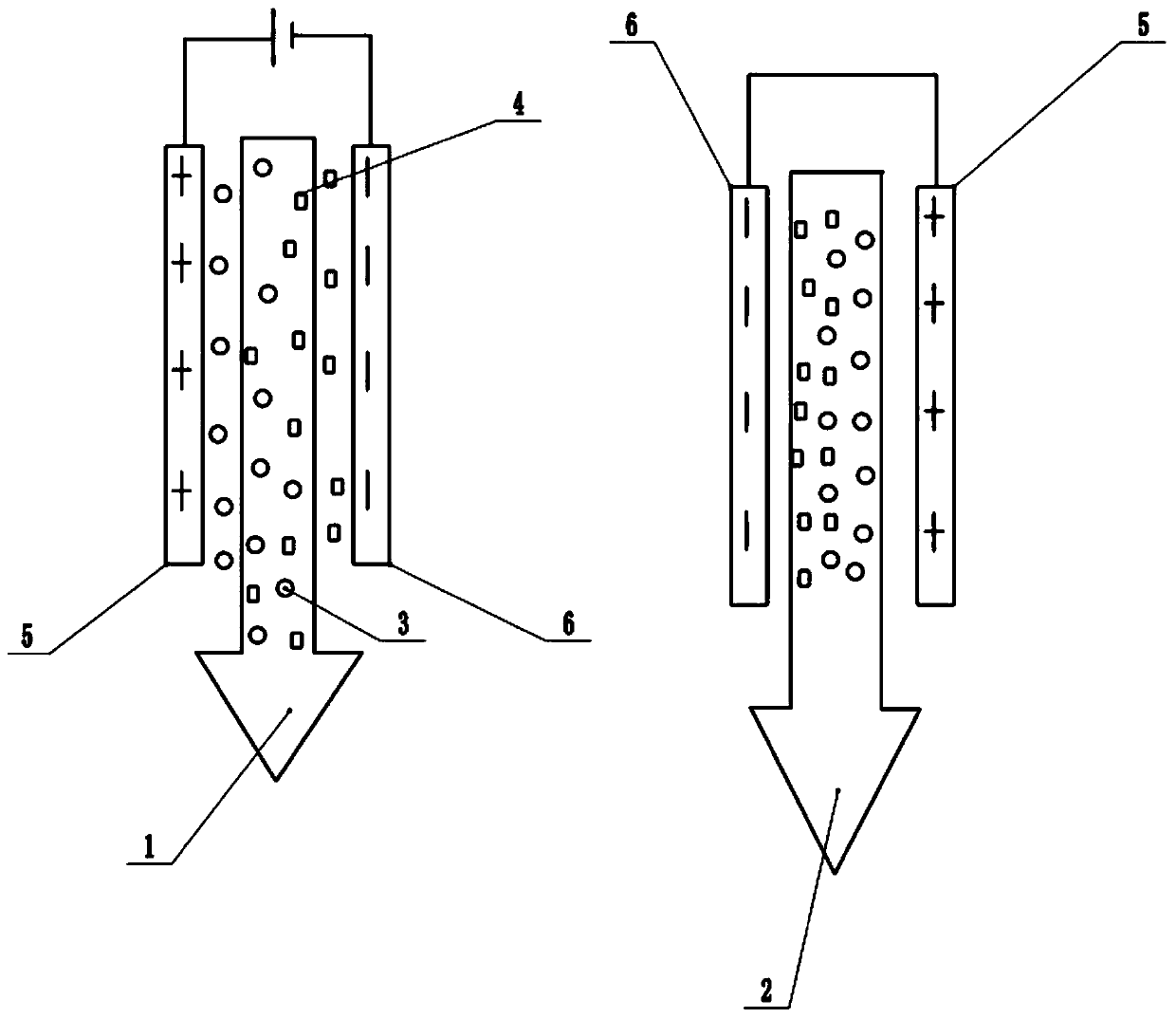
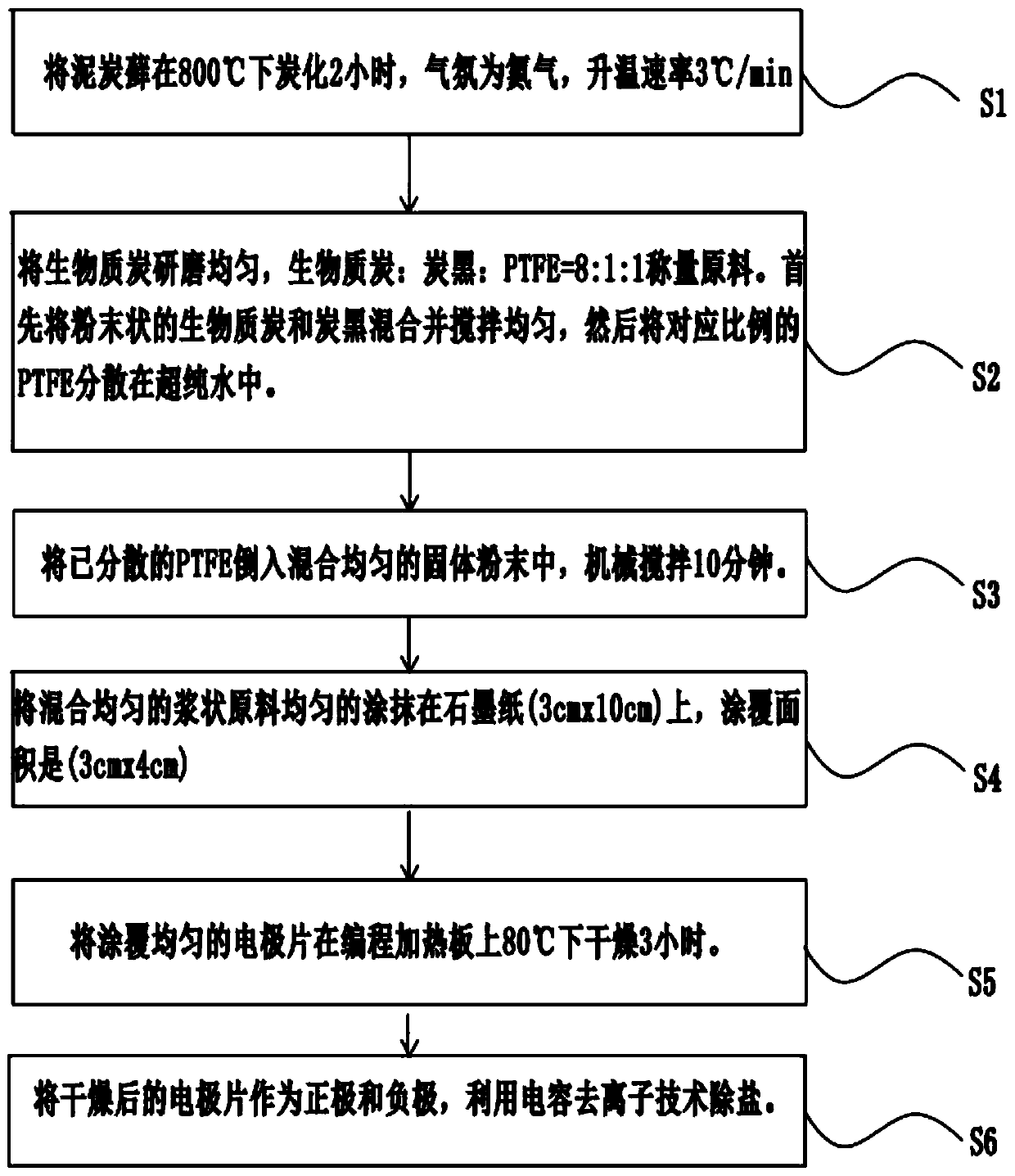
[0043] The embodiment is basically as attached figure 2 Shown: A method for desalination with a sphagnum-derived biomass carbon electrode divided into the following stages:
[0044] One, making material selection and equipment: choose fresh sphagnum moss as the basic material, test with saline (NaCl aqueous solution, 250mgL -1 ), the auxiliary materials are ultrapure water, nitrogen tank, graphite paper, carbon black and PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), and the selected equipment is tube furnace, mortar, programming heating plate, electronic balance, mechanical stirring tool, scissors, Medicine spoon, beaker and power supply.
[0045] 2. Carbonization stage: put the sphagnum moss into the tube furnace in a vacuum state, the operator continuously feeds nitrogen into the tube furnace to make the nitrogen serve as the atmosphere, and then the operator sets the heating rate of the preset tube furnace to 3 °C / min, the peat moss was carbonized at a temperature of 800 °C for two ho...
Embodiment 2
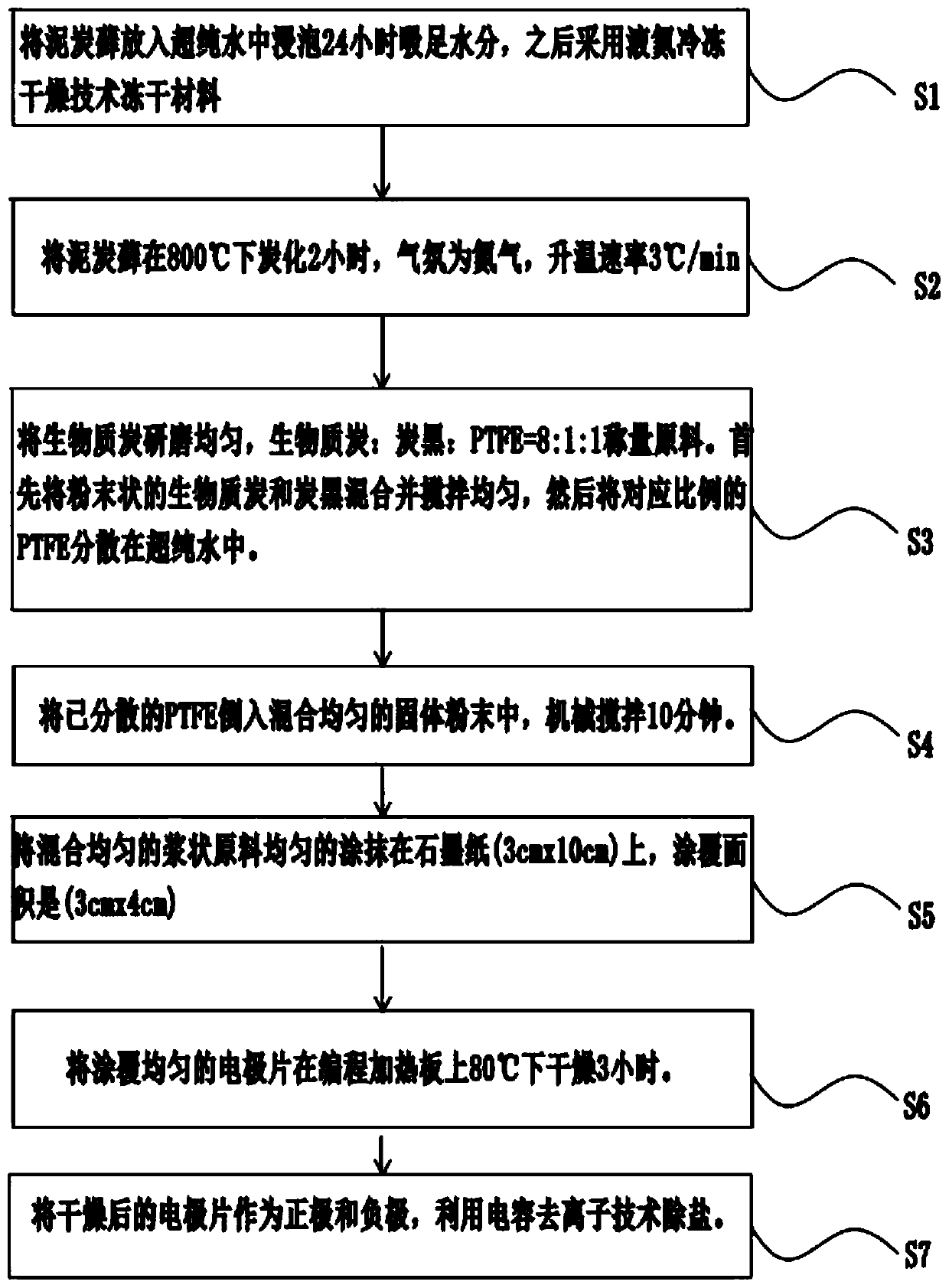
[0050] as attached image 3 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 lies in two points, the first point is to add liquid nitrogen and tweezers to the selected equipment, and the second point is to pretreat the peat moss before carbonization treatment, put the peat moss into Soak in ultra-pure water for 24 hours to absorb enough water, and then use liquid nitrogen freeze-drying technology to freeze-dry the material.
[0051] as attached Figure 4 As shown, freeze-dried carbonized peat moss was observed under a scanning electron microscope. After absorbing ultrapure water, the surface of sphagnum moss is completely stretched, the pore size distribution is orderly, the structure does not collapse, and there is no obvious crack on the surface of sphagnum moss under the quick freezing effect of liquid nitrogen.
[0052] as attached Figure 5 As shown, the operator then put the freeze-dried and carbonized sphagnum moss into a transmission electron micros...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com