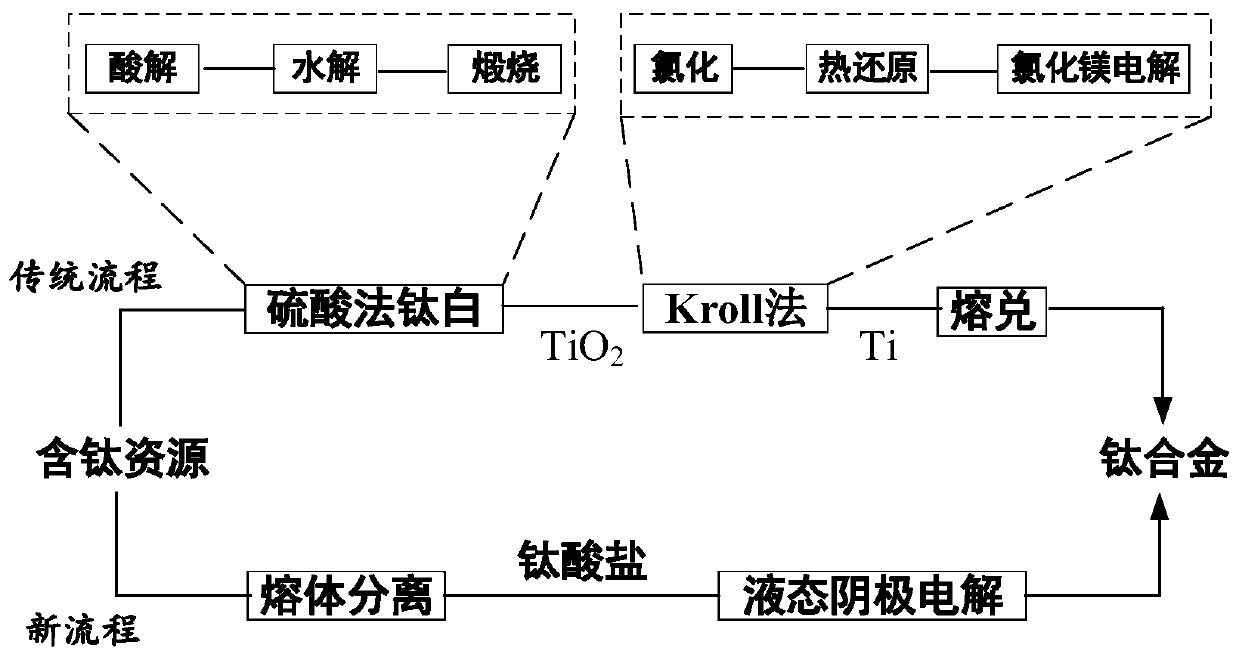
Method for preparing titanium alloy by carrying out molten salt electrolysis on soluble titanate through liquid metallic cathode
A liquid metal and molten salt electrolysis technology, applied in the electrolysis process, electrolysis components, electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of poor controllability and difficulty in continuous operation of the electrolysis process, achieve low equipment material requirements, shorten the process, and improve the working environment. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Aluminum metal was placed in a silicon nitride crucible and placed in a graphite crucible. Use cryolite and aluminum fluoride as molten salt, add 5% calcium titanate, and add the molten salt into the graphite crucible. The graphite crucible is placed in a closed steel reactor, heated to 300°C in an argon atmosphere, and kept at constant temperature for 24 hours to remove the moisture in the molten salt, and then heated to 800°C, with graphite as the anode and liquid metal aluminum as the cathode, at a constant temperature of 2.5V Voltage electrolysis for 24 hours; after electrolysis, take out the silicon nitride crucible containing the liquid metal cathode from the molten salt, continue to keep constant temperature for 1 hour, cool to room temperature, separate the cathode surface product, and obtain a titanium alloy with a titanium content of 3%.
Embodiment 2
[0025] Aluminum metal was placed in a silicon nitride crucible and placed in a graphite crucible. Use cryolite, aluminum fluoride and sodium fluoride as molten salt, add 10% sodium titanate, and add the molten salt into the graphite crucible. The graphite crucible is placed in a closed steel reactor, heated to 300°C in an argon atmosphere, kept at a constant temperature for 24 hours to remove moisture in the molten salt, and heated to 1000°C, with graphite as the anode and liquid metal aluminum as the cathode, at 4.5V constant Voltage electrolysis for 20 hours; after electrolysis, remove the silicon nitride crucible containing the liquid metal cathode from the molten salt, continue to keep the temperature constant for 5 hours, cool to room temperature, separate the cathode surface products, and obtain a titanium alloy with a titanium content of 7%.
Embodiment 3
[0027] Metal tin is placed in a silicon nitride crucible and placed in a graphite crucible. Sodium fluoride, potassium fluoride, and calcium fluoride are used as molten salt, and 1% potassium titanate is added, and the molten salt is added into the graphite crucible. The graphite crucible is placed in a closed steel reactor, heated to 300°C in an argon atmosphere, kept at constant temperature for 24 hours to remove moisture in the molten salt, and then heated to 900°C, with graphite as the anode and liquid metal tin as the cathode, at 4.2V constant Voltage electrolysis for 5 hours; after electrolysis, take out the silicon nitride crucible containing the liquid metal cathode from the molten salt, continue to keep constant temperature for 0.5 hours, cool to room temperature, separate the cathode surface product, and obtain a titanium alloy with a titanium content of 1.5%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com