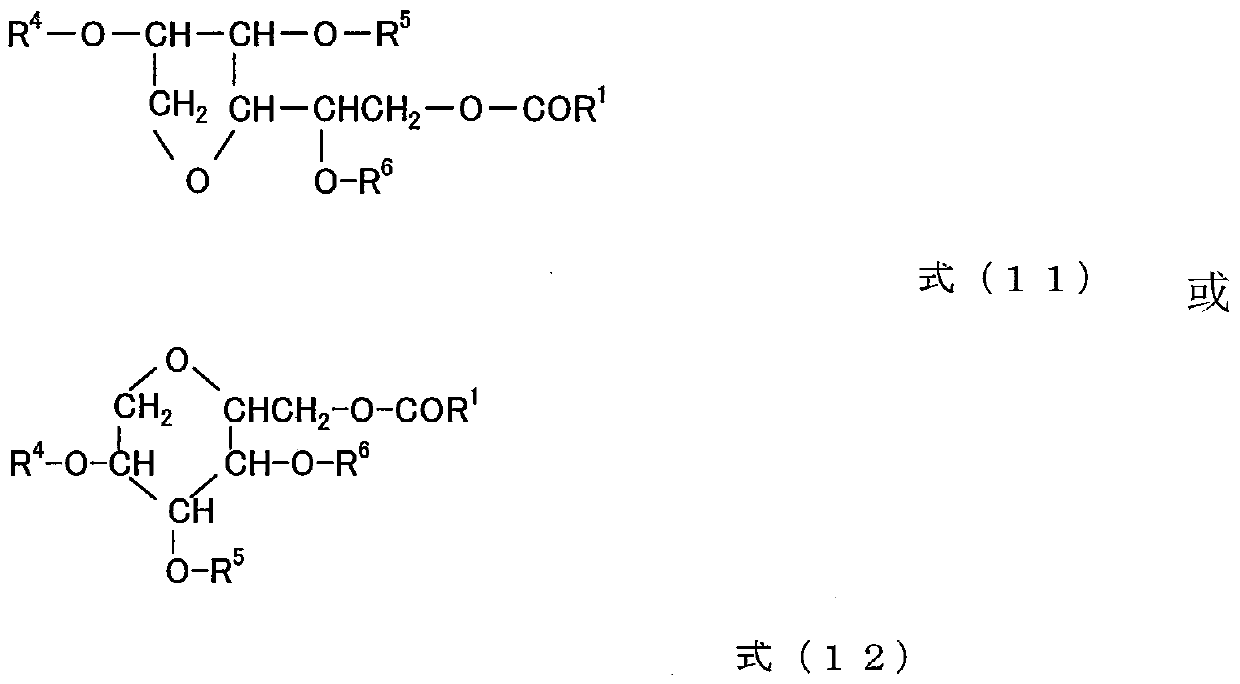
Surface treatment agent
An emulsifier, water-repellent oil-repellent technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0213] Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail with examples, but the present invention is not limited to these examples.
[0214] In the following, as long as there is no special mark, parts or% or ratio means parts by weight,% by weight or ratio by weight.
[0215] The test procedure is as follows.
[0216] Spray water repellency test
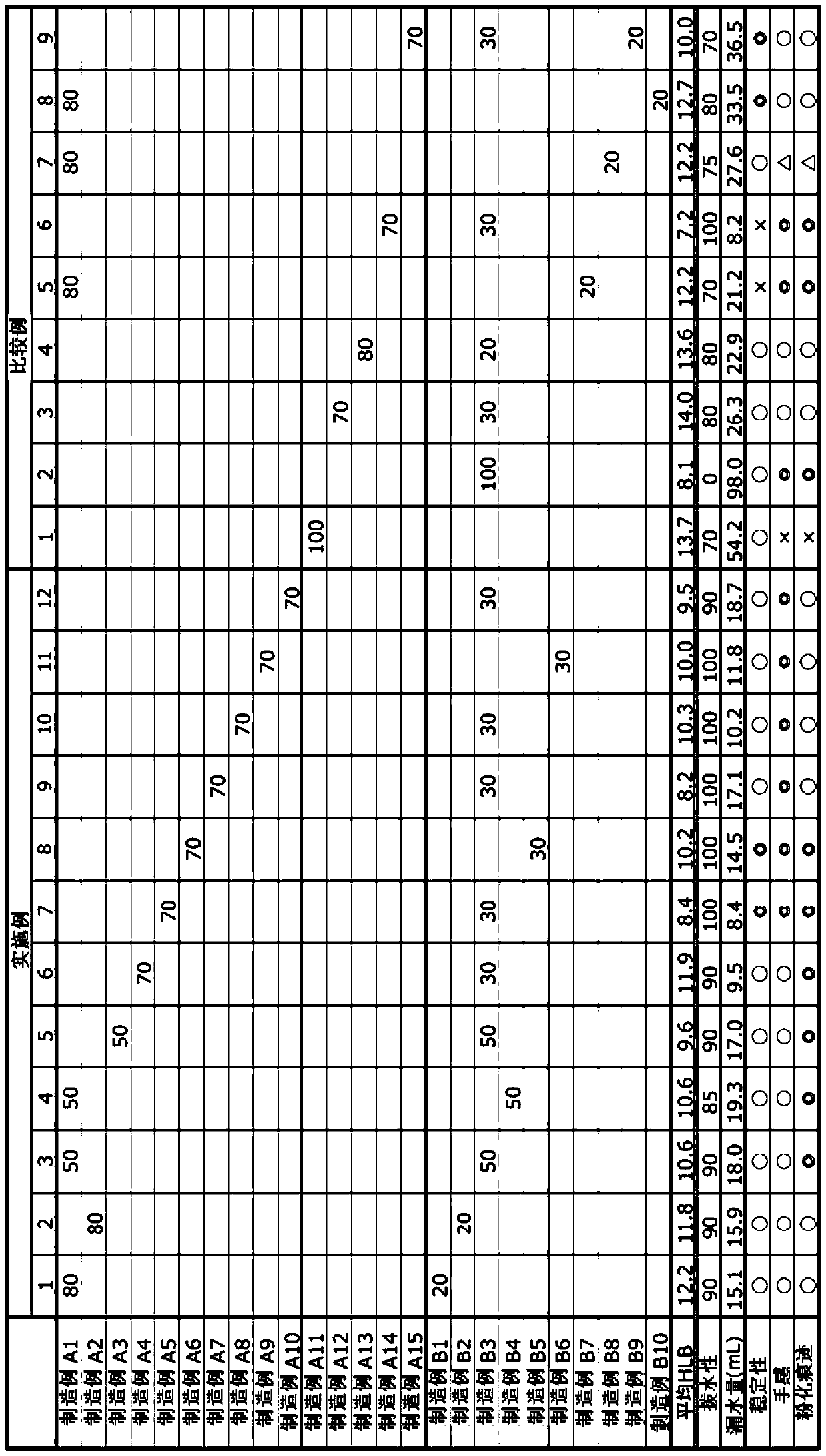
[0217] The treatment agent dispersion was diluted with tap water to a solid content concentration of 1.5% by weight to prepare a test solution. After immersing a twill cloth in the test solution, it was passed through a roller and heat-treated at 160°C for 2 minutes. The test cloth was evaluated Water-based. The water repellency of the treated cloth was evaluated in accordance with the spray method of JIS-L-1092 (AATCC-22). As shown in Table 1 described below, it is represented by the water repellency No. The larger the score, the better the water repellency. According to the state, the middle value (95, 85, 75) is taken.
...
manufacture example A1
[0242] A 1L autoclave was charged with stearyl acrylate=150g, pure water=360g, tripropylene glycol=60g, polyoxyethylene tridecyl ether (EO3) (HLB 8.0)=7.5g, polyoxyethylene Ethyl tridecyl ether (EO20) (HLB 16.3) = 12.5 g, lauryl mercaptan = 1.0 g, emulsified and dispersed with ultrasonic waves at 60°C for 15 minutes while stirring. After replacing the interior of the autoclave with nitrogen, 50 g of vinyl chloride was charged under pressure, 2,2-azobis(2-amidinopropane) 2 hydrochloride=2.0 g was added, and the reaction was carried out at 60°C for 3 hours to obtain polymerization Aqueous dispersion of material (average HLB 13.2). Furthermore, the solid content concentration was adjusted to 30% with pure water. The monomer composition of the resulting polymer is basically the same as the composition of the charged monomer.
manufacture example A2
[0244] Fill a 1L autoclave with stearyl acrylate=150g, pure water=360g, tripropylene glycol=60g, polyoxyethylene lauryl ether (EO2) (HLB 6.4)=7.5g, polyoxyethylene laurel Ether (EO20) (HLB 16.5) = 12.5 g, lauryl mercaptan = 1.0 g, emulsified and dispersed with ultrasonic waves at 60°C for 15 minutes while stirring. After replacing the interior of the autoclave with nitrogen, 50 g of vinyl chloride was charged under pressure, 2,2-azobis(2-amidinopropane) 2 hydrochloride=2.0 g was added, and the reaction was carried out at 60°C for 3 hours to obtain polymerization Aqueous dispersion of material (average HLB 12.7). Furthermore, the solid content concentration was adjusted to 30% with pure water. The monomer composition of the resulting polymer is basically the same as the composition of the charged monomer.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com