VSG control method under grid voltage symmetrical drop fault
A grid voltage and control method technology, applied in the direction of AC network voltage adjustment, wind power generation, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of less attention to the control of rapid and stable recovery to normal operation status, threats to system stability and reliability, difficult grid supply Issues such as voltage and frequency support
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
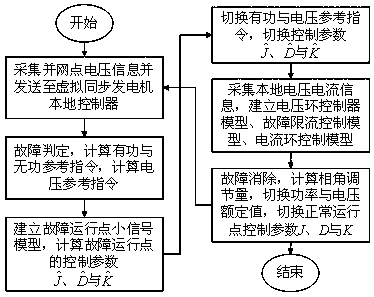
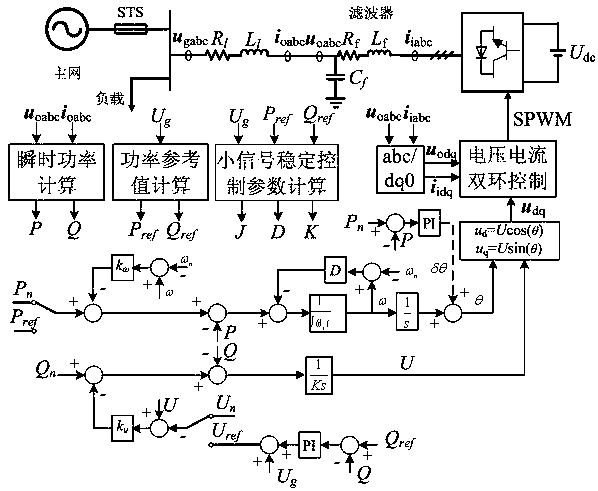
[0061] A VSG control strategy under grid voltage symmetric sag fault, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0062] Step 10) The microgrid energy management layer collects the grid voltage information at the tie line, and transmits it to the local controller of the VSG in the microgrid;
[0063] Step 20) When a grid voltage symmetrical drop fault is detected, the VSG local controller calculates active and reactive power reference commands according to the received grid voltage information;
[0064]
[0065] Among them, Q ref with P ref are the reference commands of reactive power and active power of VSG during the fault period, U G is the per unit value of grid voltage amplitude, S N is the rated installed capacity of VSG, S max Transfer active power capacity for the line.
[0066] Calculate the voltage reference order from the reactive power reference order:
[0067] u ref =U g +k Qp (Q ref -Q)+k Qi ∫(Q ref -Q) (2)
[0068] where U ref is t...
Embodiment 2
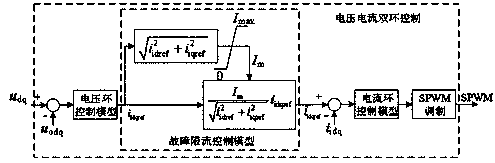
[0106] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: the failure operating point (U s0 ∠θ 0 ,U g0 ∠0) It is determined by setting VSG to provide different output active power and reactive power according to the grid voltage drops to different degrees in step 20). At operating point (U s0 ∠θ 0 ,U g0 ∠0), the primary frequency modulation coefficient and the primary voltage regulation coefficient are k ω with k u , and when the VSG grid-connected line reactance is X, the control parameters that meet the required dynamic performance and stability performance and It may not exist. If this happens, you can adjust the operating point or change the frequency modulation coefficient k once ω , primary pressure regulation coefficient k u , VSG grid-connected line reactance X, damping ratio ζ, stable adjustment time t s One or more variables in , to obtain a feasible and value, so as to continue the steps and realize the smooth and fast transition of the virt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com