Fluorinated phosphate sodium iron pyrophosphate@c@rgo composite material and its preparation and application in sodium-ion batteries
A technology of fluorinated sodium ferric phosphate pyrophosphate and fluorinated sodium ferric phosphate pyrophosphate, which is applied in the field of sodium ion battery materials, can solve problems affecting practical applications, improve capacity performance, improve thermal stability and chemical stability, and improve The effect of cycle stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
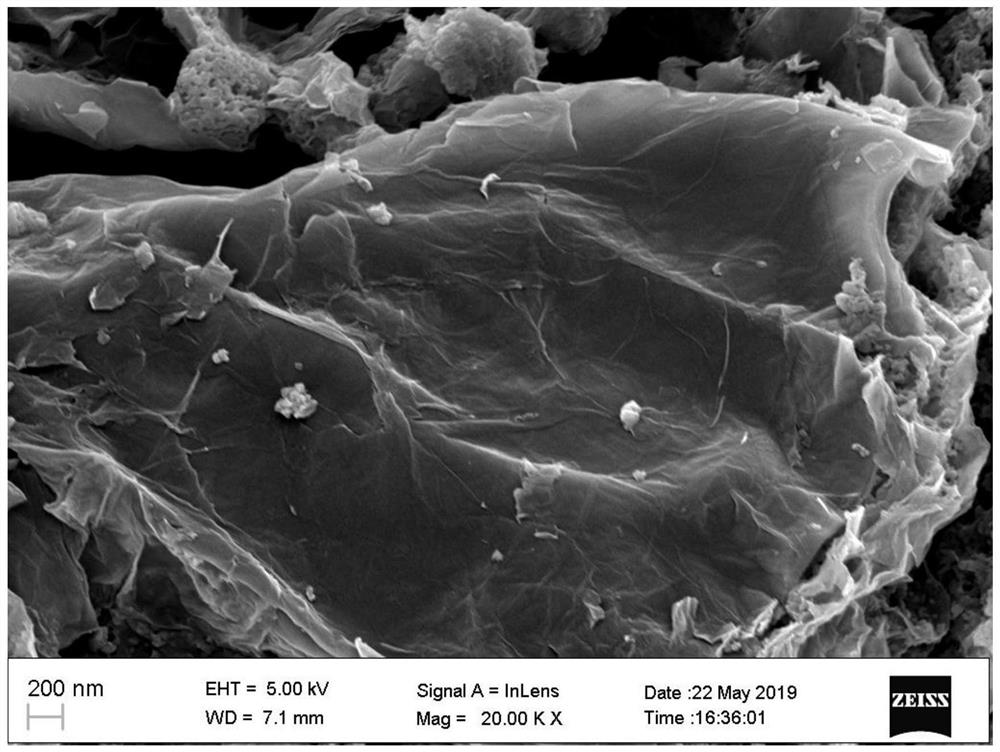
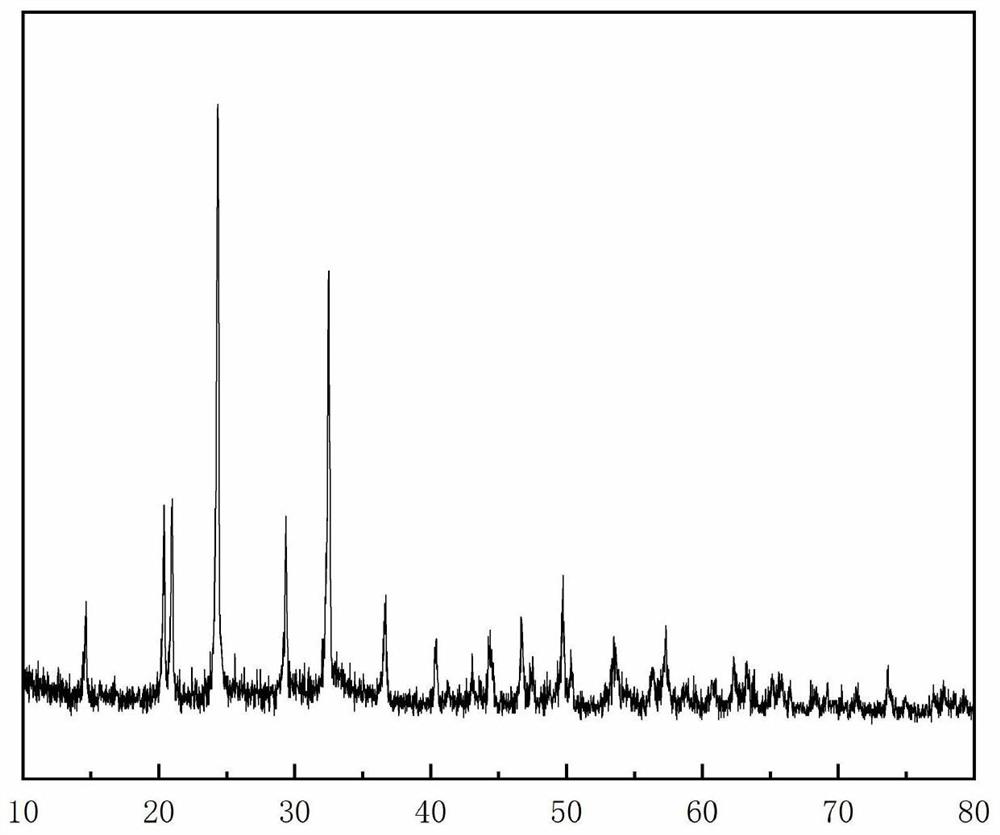
[0062] First take 0.015mol ferric nitrate nonahydrate, 0.015mol ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.02mol anhydrous sodium carbonate, 0.015mol ammonium fluoride and 0.03mol (molar ratio to iron 2:1) of ascorbic acid, and then weigh 0.15g of RGO ( Equivalent to 5% of the theoretical active substance), dissolved in deionized water, and adjusted to pH 3 to 4 by sulfurous acid. Evaporated water at 80 degrees, dried in vacuum at 100 degrees for 4 hours, and put the powder into a porcelain boat. Under an atmosphere of argon, 550 ℃ sintering 12h. i.e. get Na 4 Fe 3 PO 4 P 2 o 7 f 3 @C@RGO. See XRD diagram figure 1 , a material with high crystal phase purity was obtained. see SEM figure 2 .
[0063] The sodium ion battery composite positive electrode material prepared in this example is assembled into a button battery with sodium sheets, and the voltage of the material can reach 3.6V; at 1C rate, the discharge specific capacity reaches 95mAh / g after 100 cycles, and the capacit...
Embodiment 2
[0065] First take 0.015mol ferric nitrate nonahydrate, 0.015mol ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.02mol anhydrous sodium carbonate, 0.015mol ammonium fluoride and 0.045mol (molar ratio to iron 3:1) ascorbic acid, then weigh 0.15g of RGO , dissolved in deionized water, and adjusted to pH 3-4 with sulfurous acid. Evaporate water at 80°C, dry in vacuum at 100°C for 4 hours, put the powder into a porcelain boat, and sinter at 550°C for 12 hours in an argon atmosphere. i.e. get Na 4 Fe 3 PO 4 P 2 o 7 f 3 @C@RGO.
[0066] The sodium-ion battery composite positive electrode material prepared in this example and the sodium sheet were assembled into a button battery. Under the rate of 1C, the discharge specific capacity reached 92mAh / g after 100 cycles, and the capacity retention rate reached more than 90%.
Embodiment 3
[0068] First take 0.015mol ferric nitrate nonahydrate, 0.015mol ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.02mol anhydrous sodium carbonate, 0.015mol ammonium fluoride and 0.03mol (molar ratio to iron 2:1) of ascorbic acid, and then weigh 0.15g of RGO , dissolved in deionized water, and adjusted to pH 3-4 with sulfurous acid. Evaporate water at 80°C, dry in vacuum at 100°C for 4 hours, put the powder into a porcelain boat, and sinter at 650°C for 16 hours in an argon atmosphere. i.e. get Na 4 Fe 3 PO 4 P 2 o 7 f 3 @C@RGO.
[0069] The sodium-ion battery composite positive electrode material prepared in this example and the sodium sheet were assembled into a button battery. Under the rate of 1C, the discharge specific capacity reached 87mAh / g after 100 cycles, and the capacity retention rate reached more than 90%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com