A method for feeding back and rebuilding the lithium cobalt oxide structure of the positive electrode of the lithium battery
A lithium cobalt oxide and lithium battery technology, which is applied in the field of recycling waste lithium batteries, can solve the problems that the original form and size distribution of lithium cobalt oxide cannot be restored, the performance of new batteries cannot be compared, and the electrochemical performance is limited. Achieve the effects of relieving ecological pressure, increasing electrochemical specific capacity, and easy migration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] (1) First, disassemble the waste lithium-ion battery, immerse it in sodium chloride solution, and discharge it to obtain positive aluminum foil, which is cut into pieces with a size of 3-5cm. The positive electrode sheet was placed in a solution of DMF and NMP=1:3 (volume ratio), and immersed in ultrasonic immersion at a constant temperature of 80°C with a power of 100W for 2 hours. The positive electrode active material fell off, the aluminum foil was separated, the positive electrode active material was filtered out, and dried in a vacuum at 100°C to obtain a crude positive electrode active material product.
[0029] (2) Since some binders and carbon powders remain in the crude positive active material product, the crude active material obtained in step (1) is processed as follows: heating at 700° C. for 5 hours, Grind after cooling. A treated positive electrode active material was obtained.
[0030] (3) Weigh 5g (about 0.05mol cobalt ion) treated lithium cobalt oxi...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) The process of obtaining the treated positive active material is the same as in Example 1
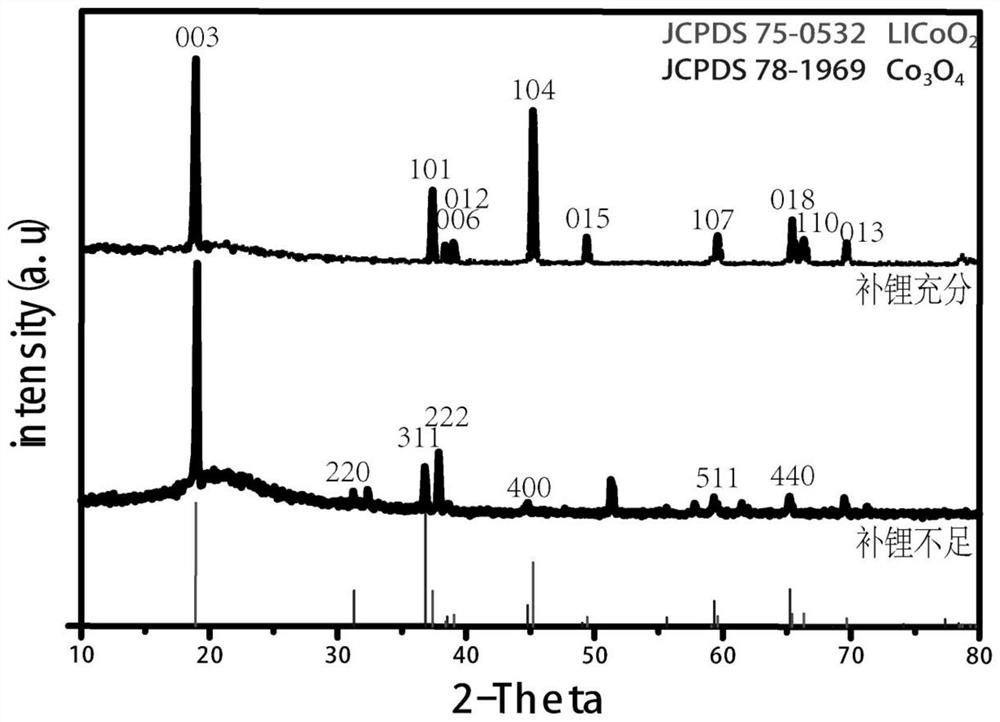
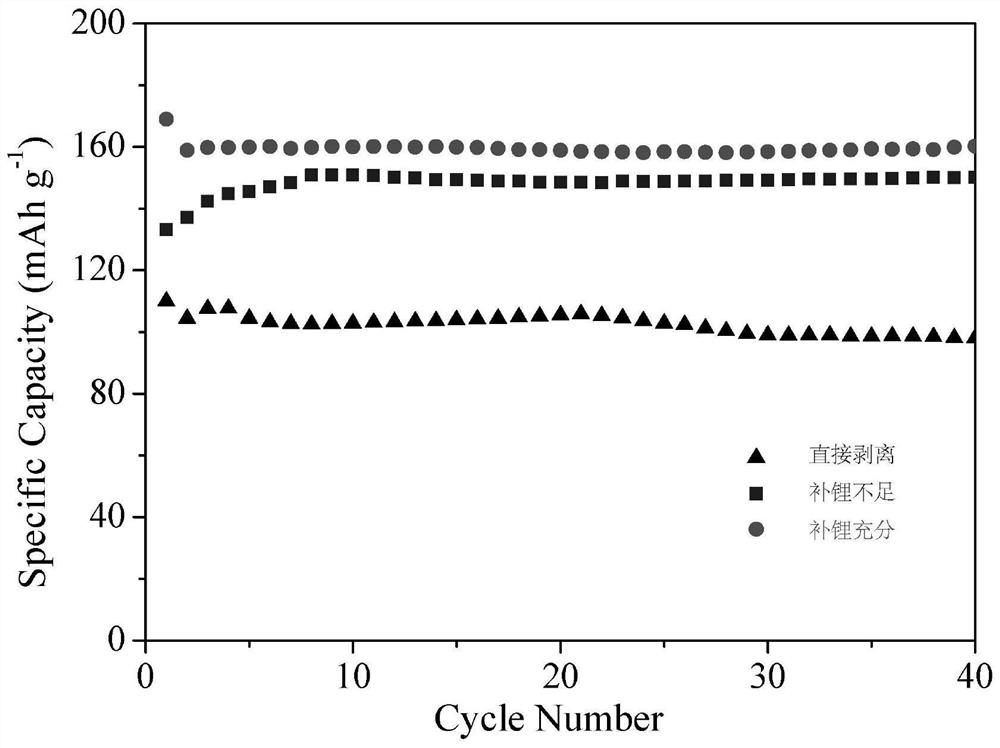
[0040] (2) The positive active material was directly assembled into a button battery for testing. correspond figure 2 directly peeled off.
[0041] The preparation method and charge-discharge experiment of the button battery are the same as those in Example 1, and the results are shown in figure 2 .
Embodiment 3
[0043] (1) The process of obtaining the treated positive active material is the same as in Example 1
[0044] (2) Weigh 5g (about 0.05mol cobalt ion) treated lithium cobalt oxide positive active material into 20ml 8mol / L sulfuric acid solution, add 2.5ml 30% hydrogen peroxide to dissolve. The insoluble impurities are removed, and the filtrate contains cobalt ions and lithium ions and is ready for use.
[0045] To the filtrate obtained in (2), 12 g of solid lithium hydroxide was added to control Li / Co=10:1. 2.5ml of 30% hydrogen peroxide was added into a 50ml polytetrafluoroethylene reaction kettle, the filling amount was 0.8, and the reaction kettle was placed in an oven at 200° C. for reaction for 24h.
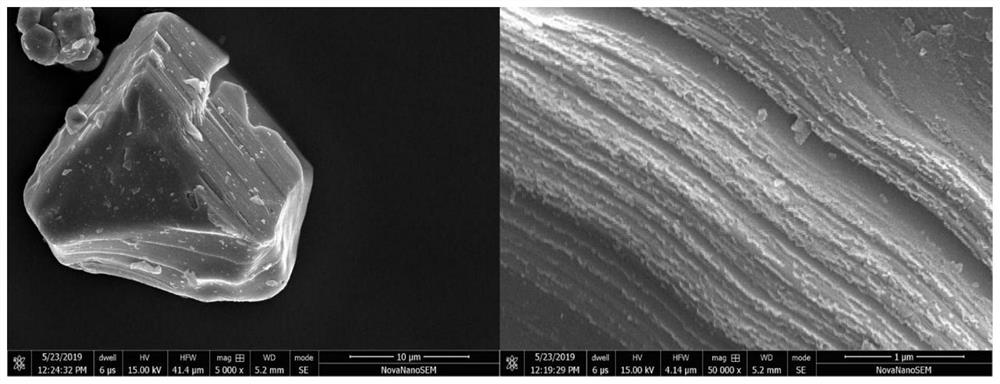
[0046] After the reaction is stopped, it is taken out by filtration, centrifuged with water and ethanol, and the obtained lithium cobalt oxide crystals are dried for 12 hours, and finally the lithium cobalt oxide cathode material after hydrothermal feed-feed reconstruction is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com