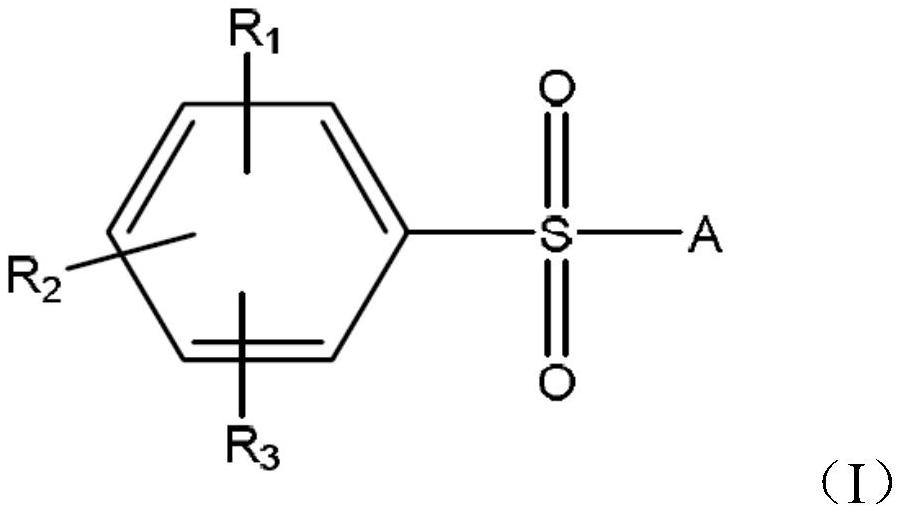
Methods for controlling the growth of microorganisms and/or biofilms in industrial processes
A biofilm and microbial technology, applied in the direction of adding anti-biological reagents, adding sludge control agents, preventing corrosion/sediment formation of pulping equipment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] Example 1 (reference)
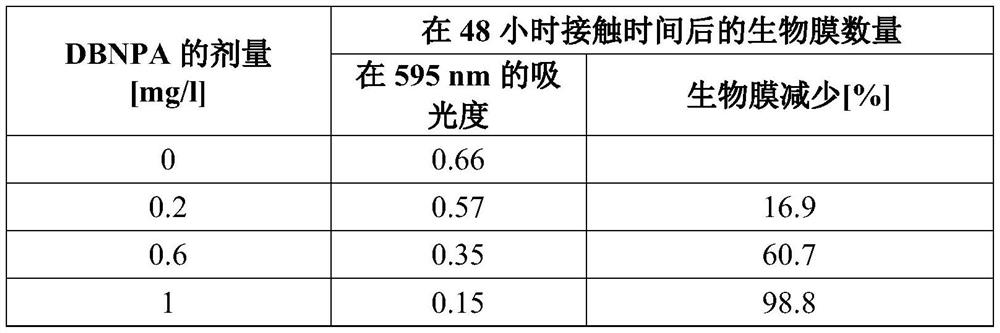
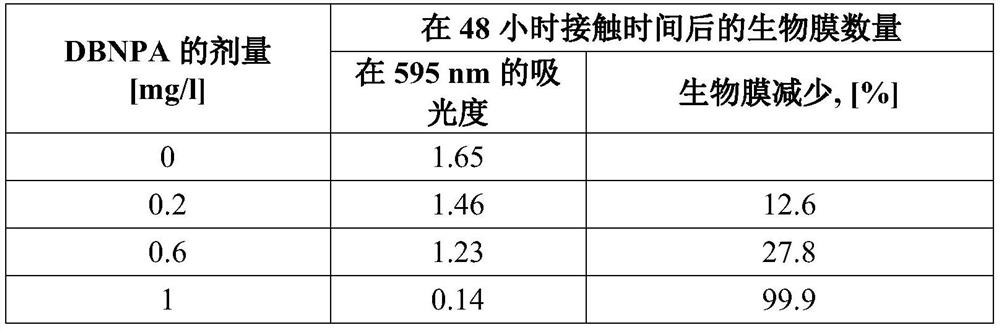
[0083] Tables 1 and 2 demonstrate the ability of the conventional antimicrobial agent DBNPA to prevent biofilm formation by Meiothermussilvanus and Pseudoxanthomonas taiwanensis. Test conditions were simulated paper or board manufacturing process conditions (synthetic paper machine water, high temperature, presence of fibers, high flow). The conventional antimicrobial DBNPA requires an active compound dose of 1 mg / l to achieve acceptable or significant biofilm reduction efficacy. The results of DBNPA are given in Tables 1 and 2.
[0084] Table 1 shows the effect of DPNPA dose in SPW on the biofilm of Thermus silvanus at 45°C and 150 rpm (high mixing). Biofilms were stained and quantified by absorbance measurements. Dosages are given in active ingredient form.
[0085] Table 1
[0086]
[0087] Table 2 shows the effect of DPNPA dosage in SPW on Pseudoxanthomonas taiwanensis biofilm at 45°C and 150 rpm (high mixing). Biofilms were stained ...
Embodiment 2
[0090] Example 2 (reference)
[0091] Tables 3 and 4 show the effect of the well-known antibiotic gramicidin on biofilm formation of Meiothermussilvanus and Pseudoxanthomonas taiwanensis. In synthetic growth medium R2-broth, gramicidin was able to protect against biological activity at significantly lower concentrations compared to conditions simulating a paper or board production process (synthetic paper machine water, high temperature, presence of fibers, high fluidity). film formation.
[0092] The results in Tables 3 and 4 demonstrate the expected behavior of clinical antibacterial compounds with reduced performance when exposed to non-clinical conditions.
[0093] Table 3 shows the effect of gramicidin doses on Meiothermussilvanus biofilms in R2-broth and SPW. Biofilms were stained and quantified by absorbance measurements. Dosages are given in active ingredient form.
[0094] table 3
[0095]
[0096] Table 4 shows the effect of gramicidin doses on Pseudoxanthomo...
Embodiment 3
[0100] Tables 5 and 6 demonstrate the ability of Compound C and Compound E to prevent biofilm formation by Meiothermus silvanus and Pseudoxanthomonas taiwanensis. The test conditions were the same as those of Example 1. Compound C and Compound E were observed to be able to control biofilms at very low concentrations. The biofilm reduction effect of active compound C or compound E at a dose of 0.2 mg / l has exceeded 90%.
[0101] Table 5 shows the effect of compound C dosage on the biofilm of Thermus rubrum (Meiothermus silvanus) in SPW at 45°C and 150 rpm (high mixing). Biofilms were stained and quantified by absorbance measurements. Compound C doses are given as the active compound.
[0102] table 5
[0103]
[0104] Table 6 shows the effect of Compound E dosage on Meiothermus silvanus biofilm at 45°C and 150 rpm (high mixing). Biofilms were stained and quantified by absorbance measurements. Compound E doses are given as the active compound.
[0105] Table 6
[0106...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com