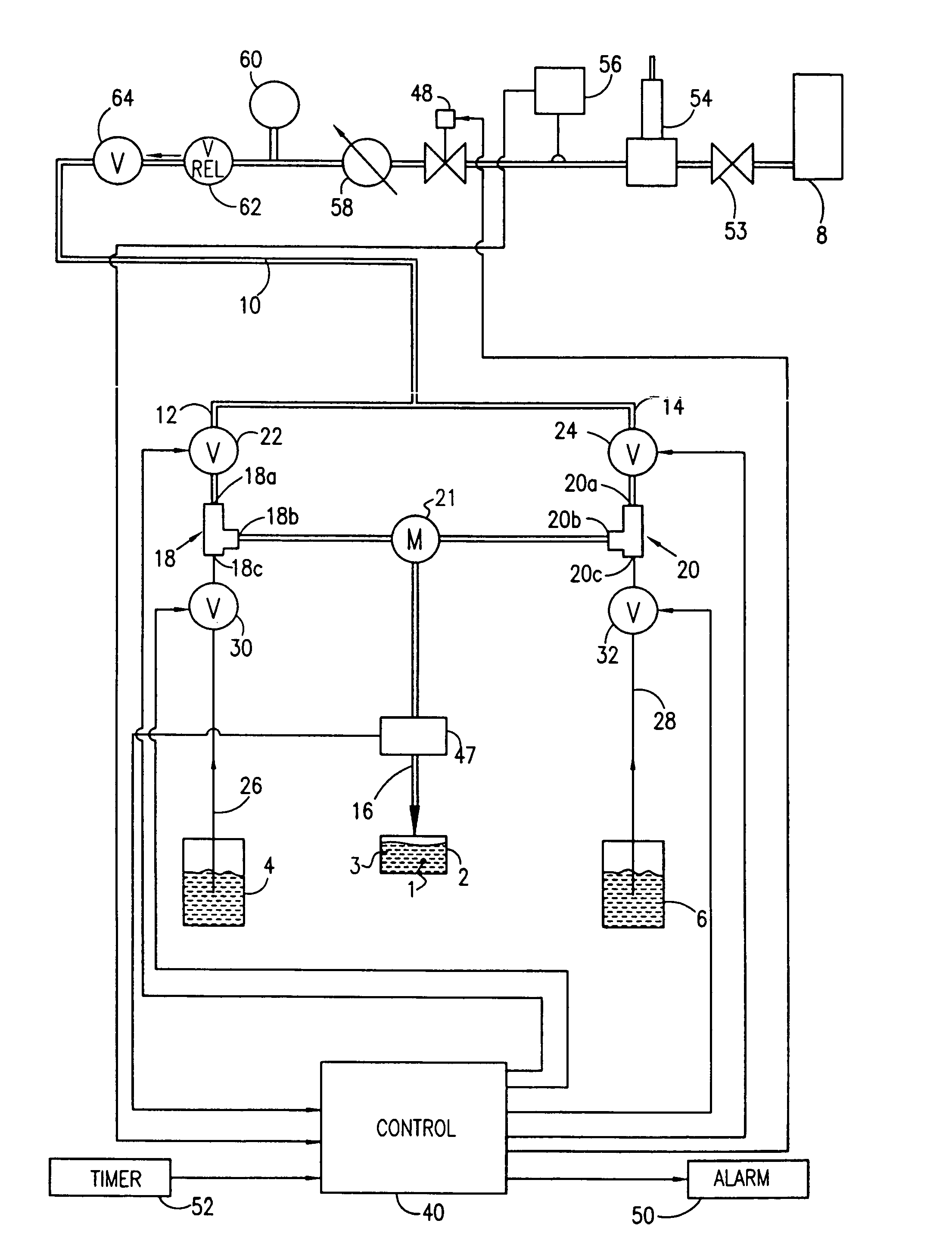
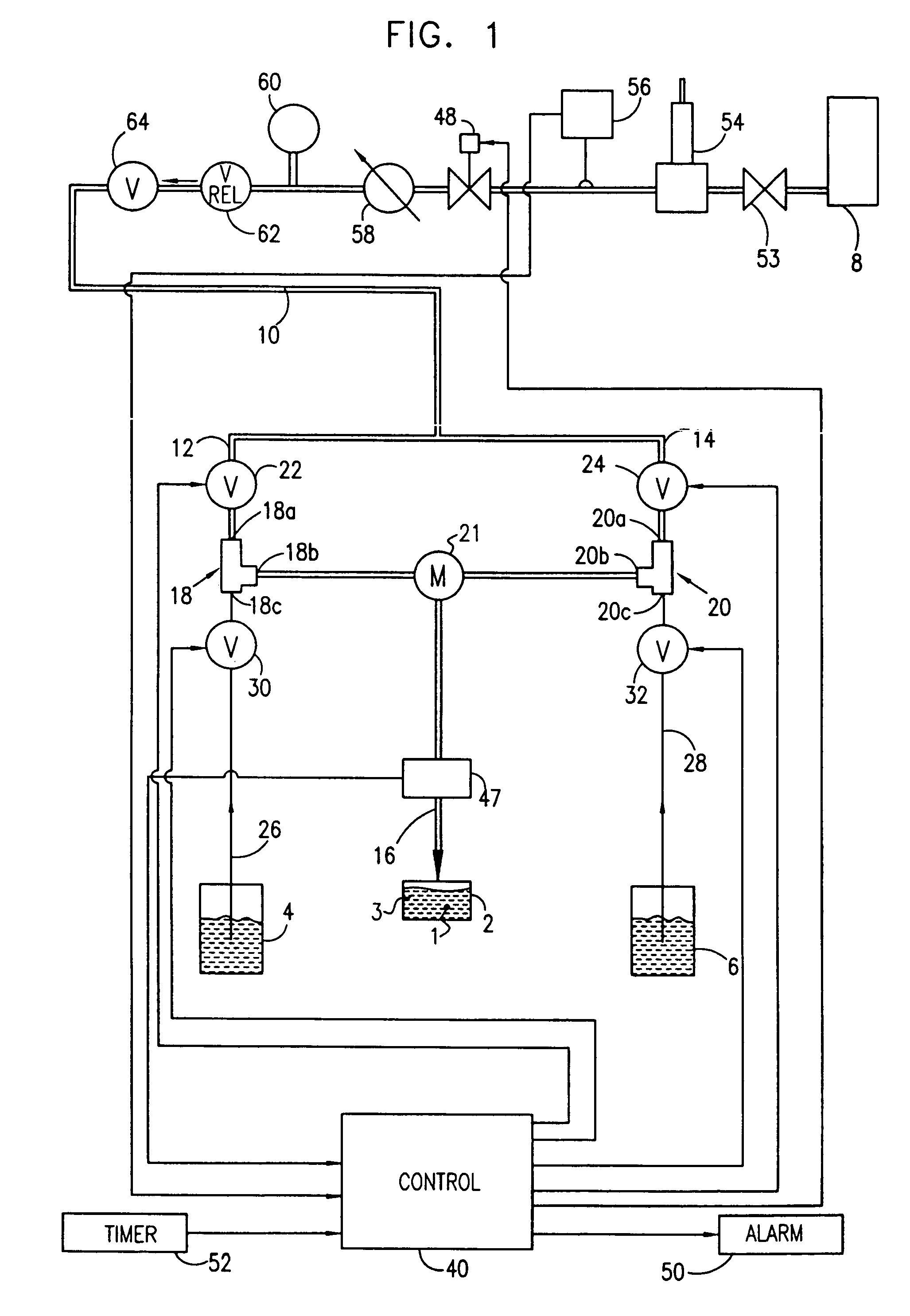
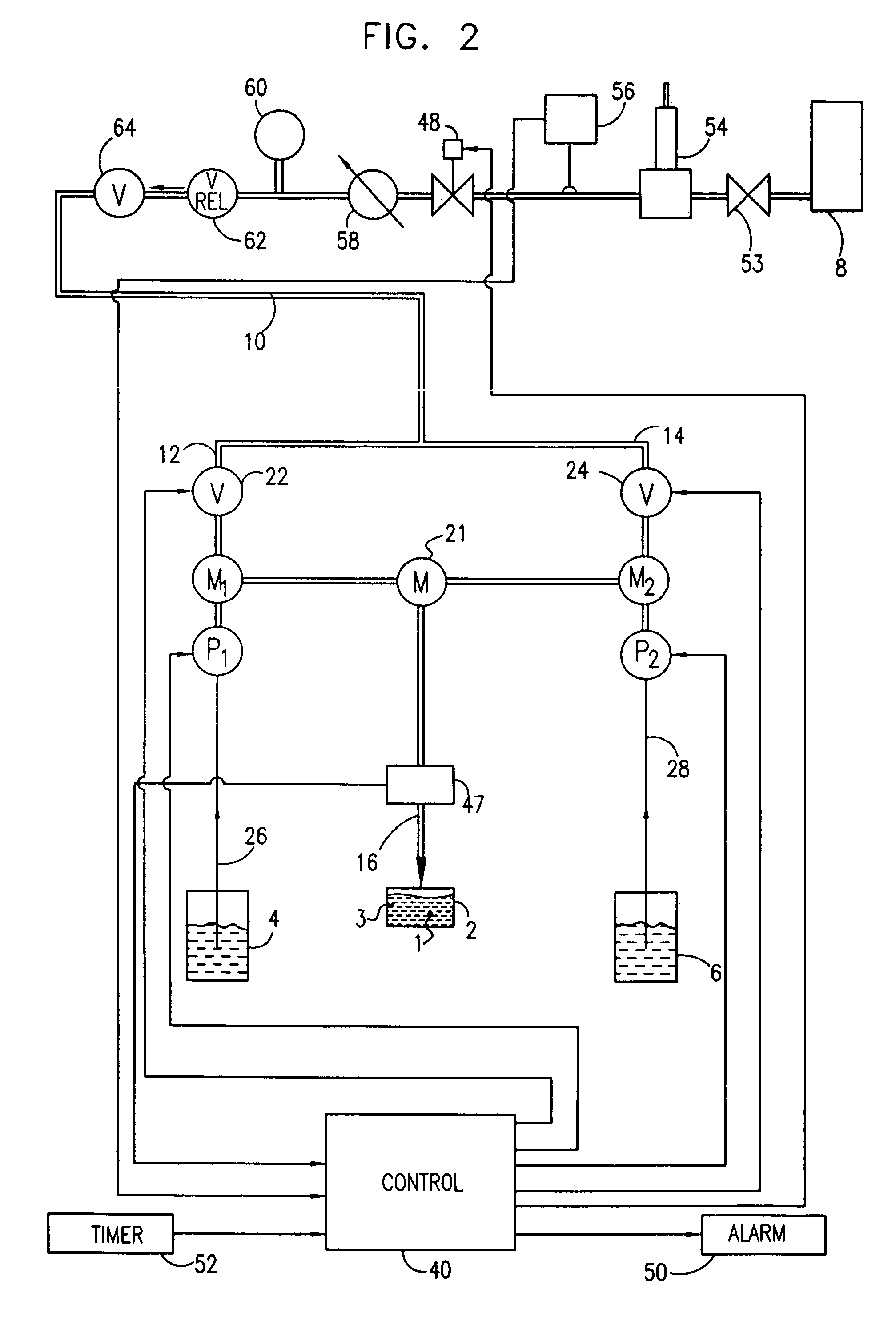
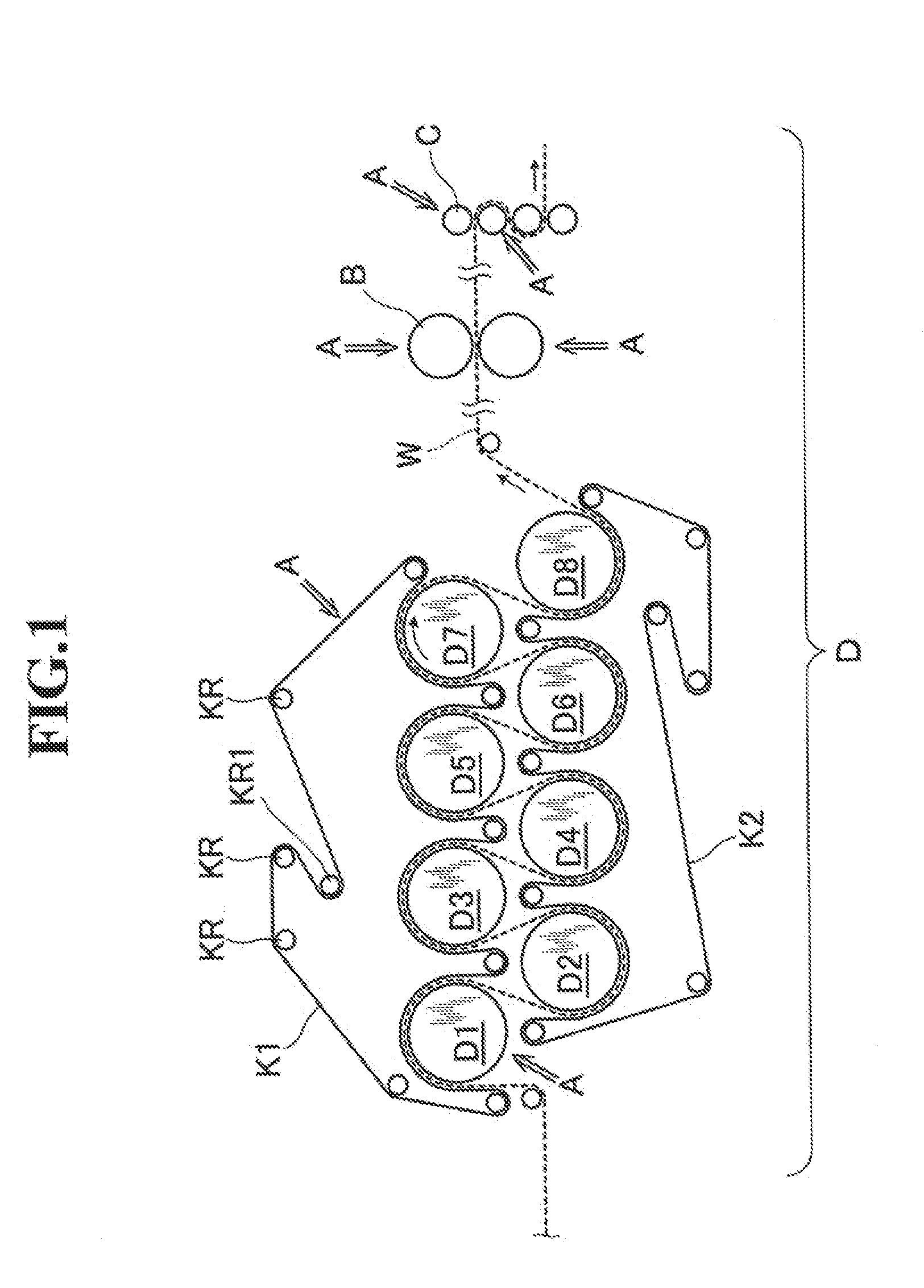
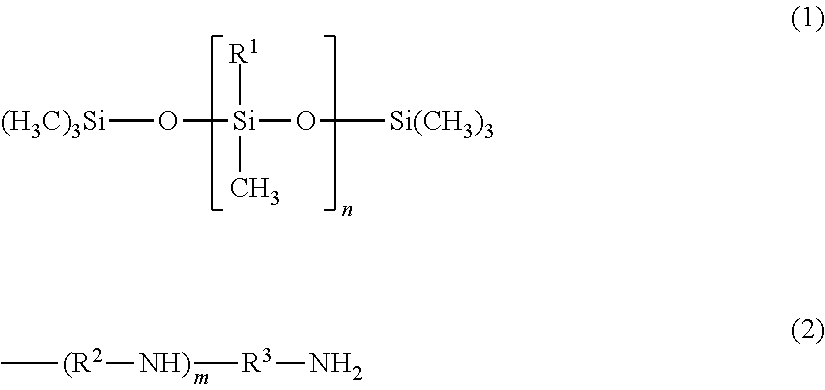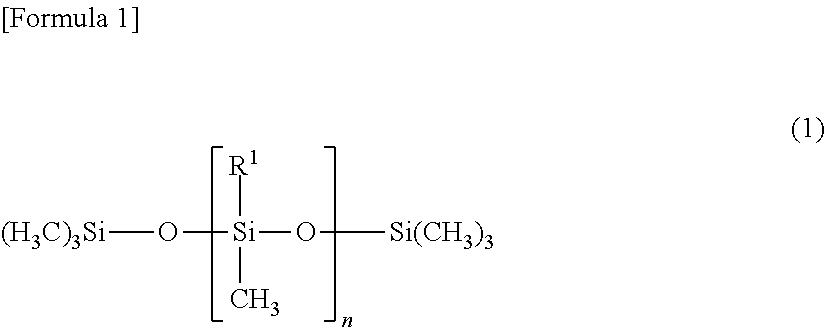Patents
Literature
77results about "Slime-control agents addition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process for the preparation of peroxy acids
ActiveUS20090221704A1Easy to controlIncrease powerBiocideOrganic compound preparationPeroxy acidCarboxylic acid
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of a solution comprising a first peroxy acid comprising performic acid and a second peroxy acid, said process comprising forming a carboxylic acid solution comprising a first carboxylic acid comprising formic acid, a second carboxylic acid and hydrogen peroxide, wherein the amount of formic acid is from 0.5 to 20% by weight of the amount of the second carboxylic acid, and allowing the components to react to form a solution comprising performic acid and said second peroxy acid, the amount of peroxy acids being at least 5% by weight. The invention also relates to a storable solution comprising performic acid and said second peroxy acid. The solution can be used as a disinfecting agent for controlling micro-organisms.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
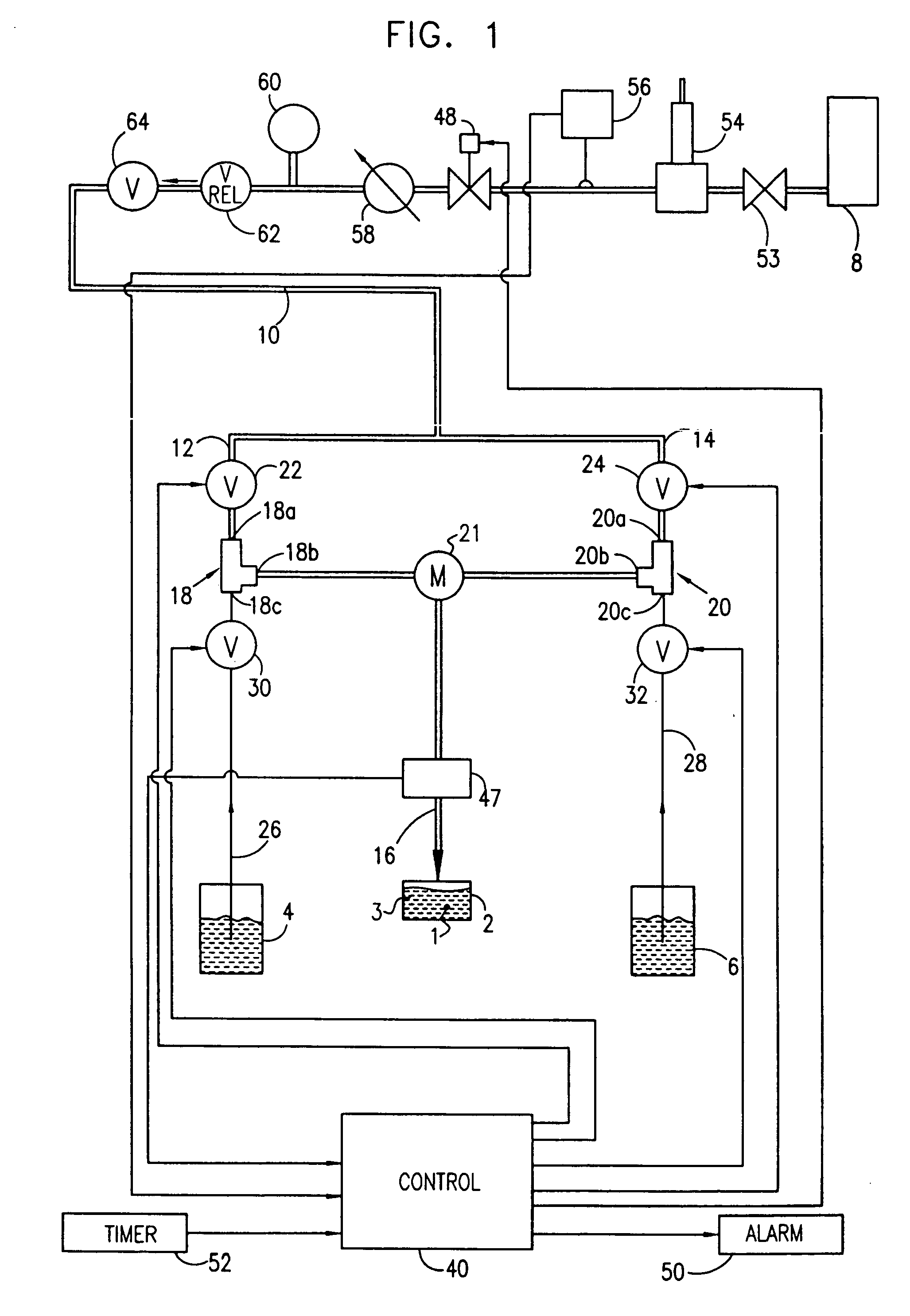
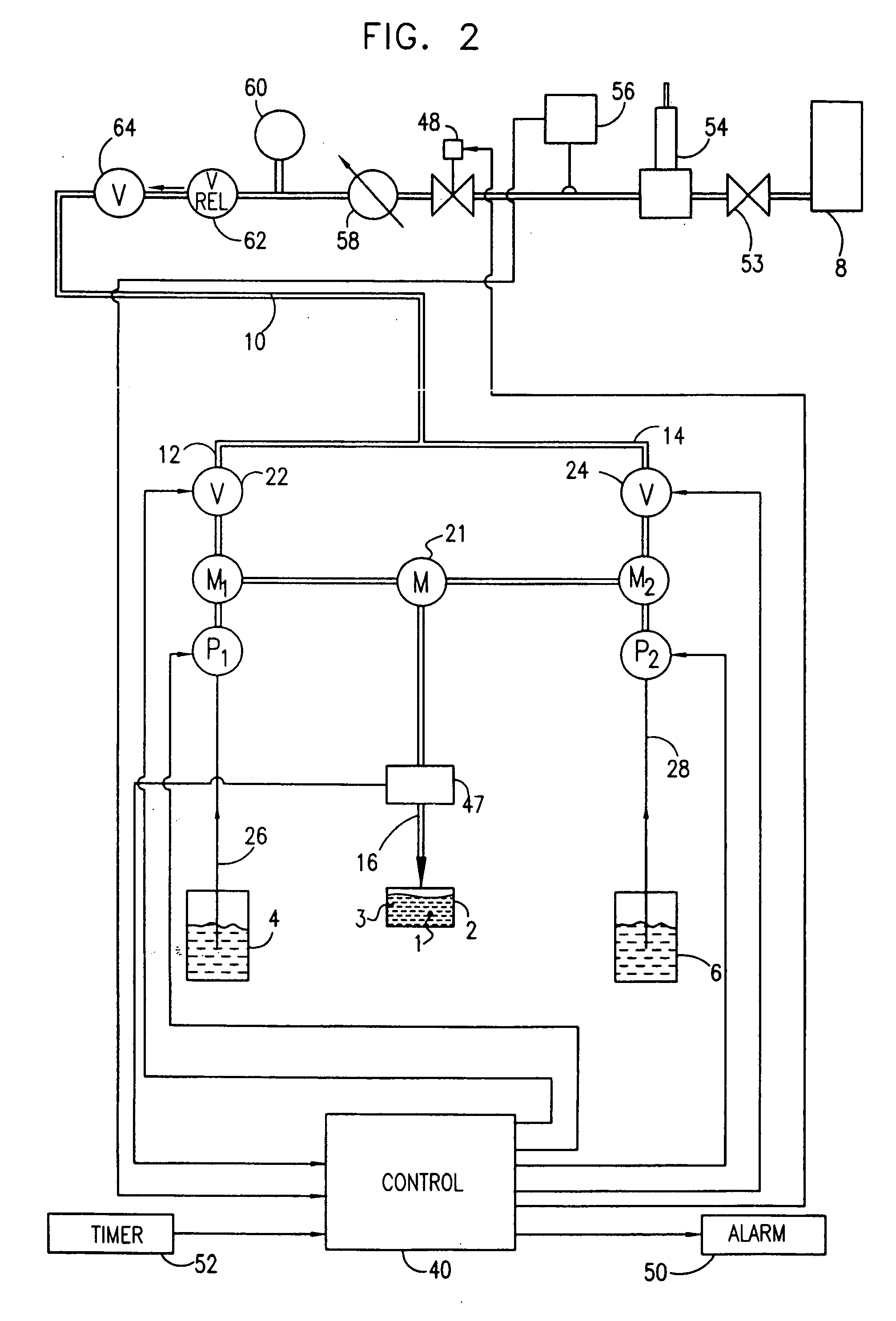
Control of development of biofilms in industrial process water
There is provided a method of inhibiting the development of a biofilm adjacent a surface, the method comprising intermittently applying a biofilm inhibiting substance to a collection of microorganisms having biofilm developing potential. There is also provided a method of inhibiting the development of a biofilm adjacent a surface, the method comprising inhibiting the biofilm developing potential of a collection of microorganisms without completely eradicating said collection of microorganisms. Also provided are a system for inhibiting the development of a biofilm, and a method and system for inhibiting the production of an enzyme by a collection of microorganisms.
Owner:A Y LAB
Process for the preparation of peroxy acids
ActiveUS8828910B2Easy to controlIncrease powerBiocideOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acidPeroxy acid
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of a solution comprising a first peroxy acid comprising performic acid and a second peroxy acid, said process comprising forming a carboxylic acid solution comprising a first carboxylic acid comprising formic acid, a second carboxylic acid and hydrogen peroxide, wherein the amount of formic acid is from 0.5 to 20% by weight of the amount of the second carboxylic acid, and allowing the components to react to form a solution comprising performic acid and said second peroxy acid, the amount of peroxy acids being at least 5% by weight. The invention also relates to a storable solution comprising performic acid and said second peroxy acid. The solution can be used as a disinfecting agent for controlling micro-organisms.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Method for monitoring the presence of biofilmforming microorganisms in paper industry
InactiveUS20070134649A1Save time and efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCardboardProduction line
The invention is directed to a method for detecting the presence of biofilm-forming microorganisms in a paper or board making process for determining the need of an anti-biofilm agent in the process. The method comprises the steps: (a) subjecting a sampler device in the process line for a period of time to enable said microorganisms to form a biofilm in situ in said process on the surface of the sampler, (b) optionally treating said formed biofilm in a solution of a test anti-biofilm agent for a period of time, then (c) contacting said biofilm with a liquid growth medium in a recession of a culturing device for a period of time, and (d) removing the growth solution from the recession of said device and detecting qualitatively and / or quantitatively the presence or absence of a biofilm adhered on the walls of the recession. An assembly kit is also provided.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Control of development of biofilms in industrial process water
InactiveUS7189329B2Avoid developmentBiocideWater/sewage treatment by substance additionMicroorganismBiochemical engineering
Owner:A Y LAB LTD
Method for removal of biofilm
The present invention provides a method for the removal of biofilm, flocculent bulked sludge or bulked biologically active sludge from an aqueous system. The method involves adding one or more chlorinated hydantoins, such as dichloro- or monochlorodialkylhydantoin, to the aqueous system. Alternatively, the chlorinated hydantoin may be formed in situ by adding a chlorine source and an alkylated hydantoin separately to the aqueous system. The invention is particularly advantageous because of the outstanding photostability of the chlorinated hydantoin solutions even when exposed to sunlight.
Owner:ARXADA LLC
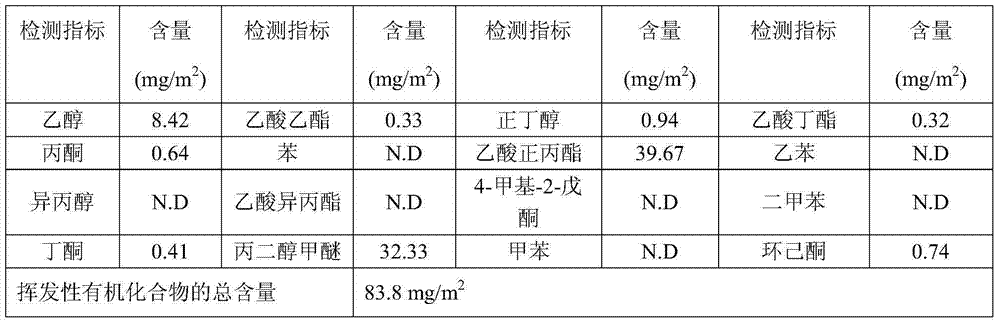
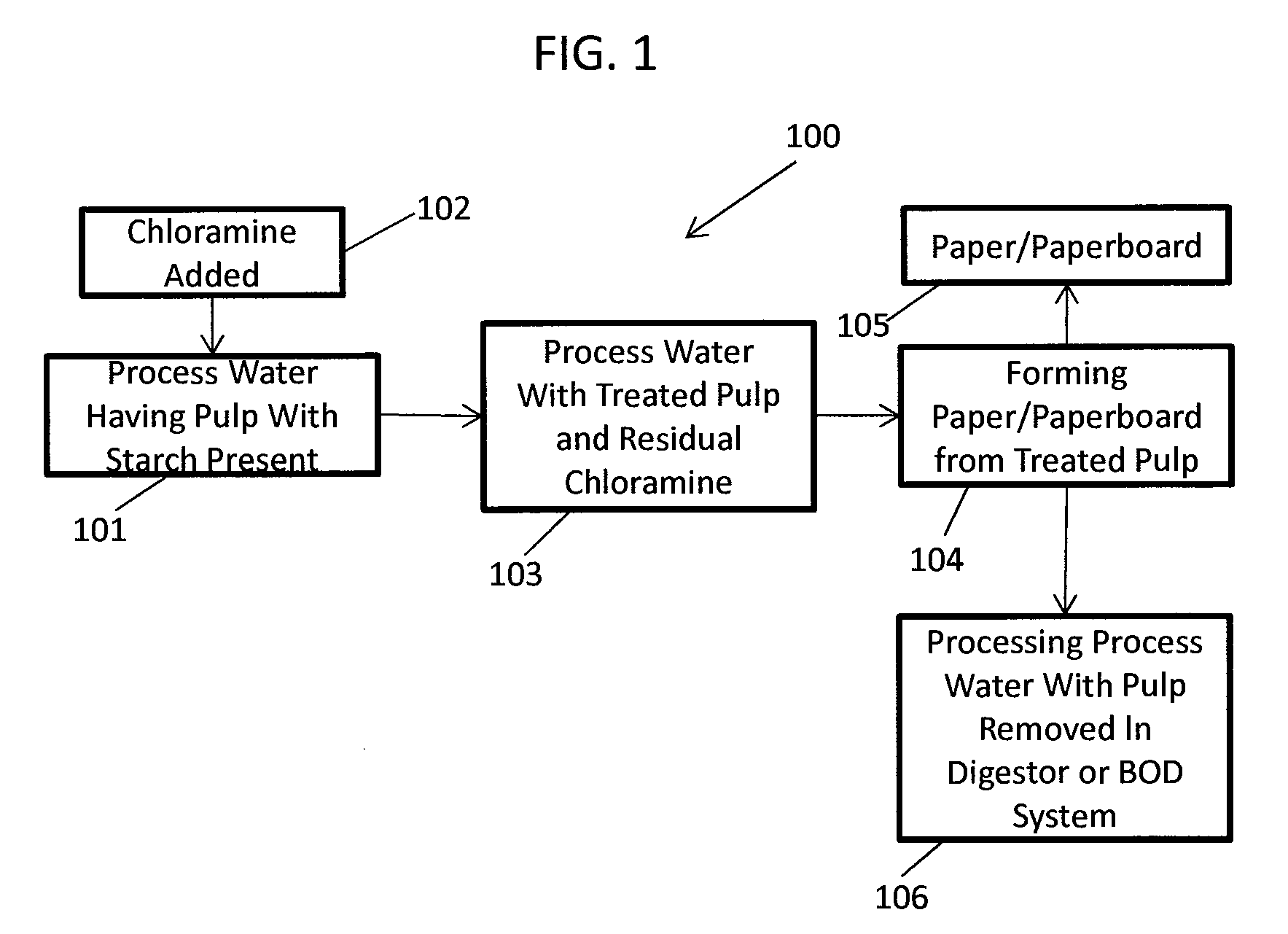
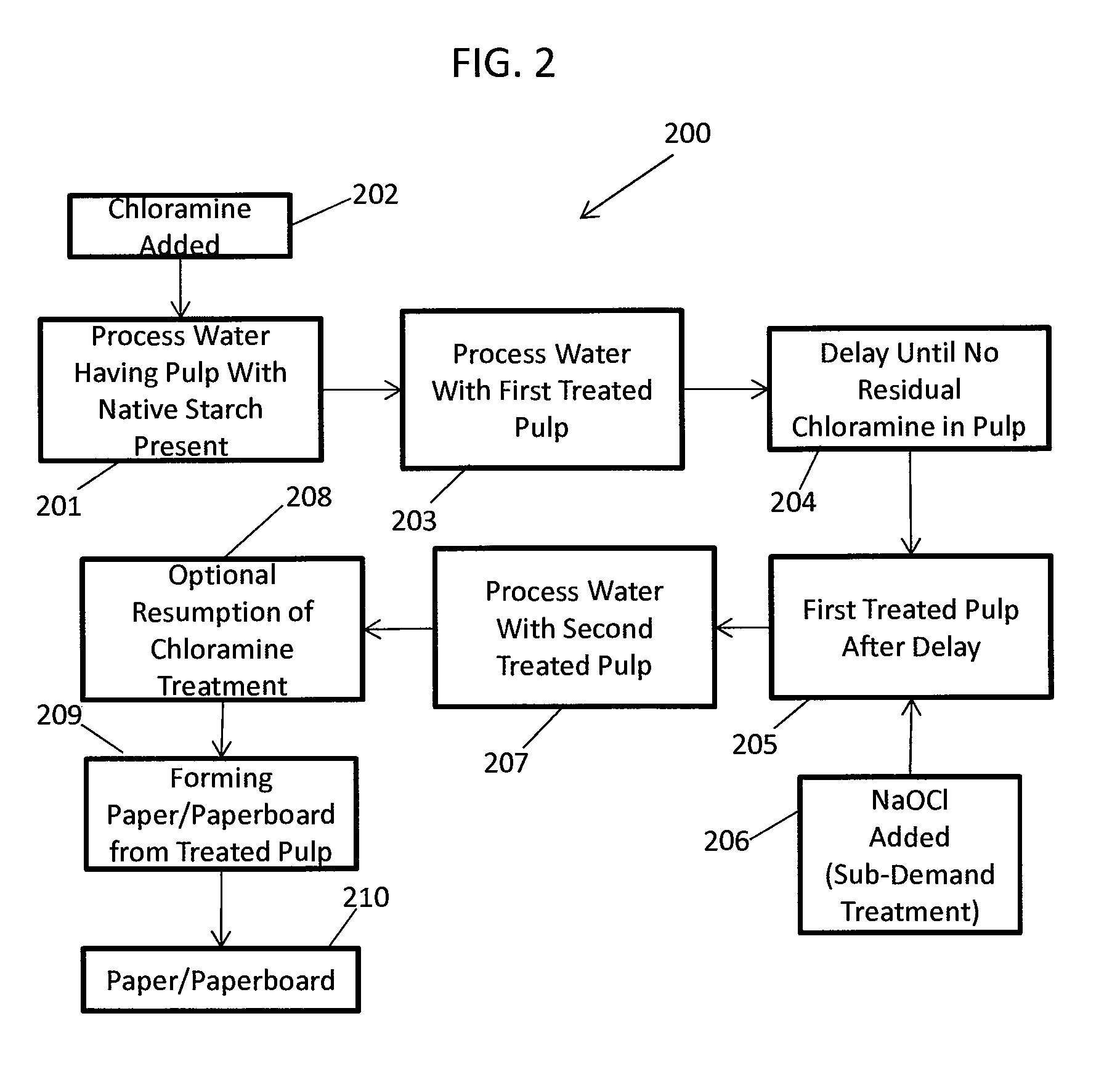
Methods Of Preserving Starch In Pulp And Controlling Calcium Precipitation And/Or Scaling
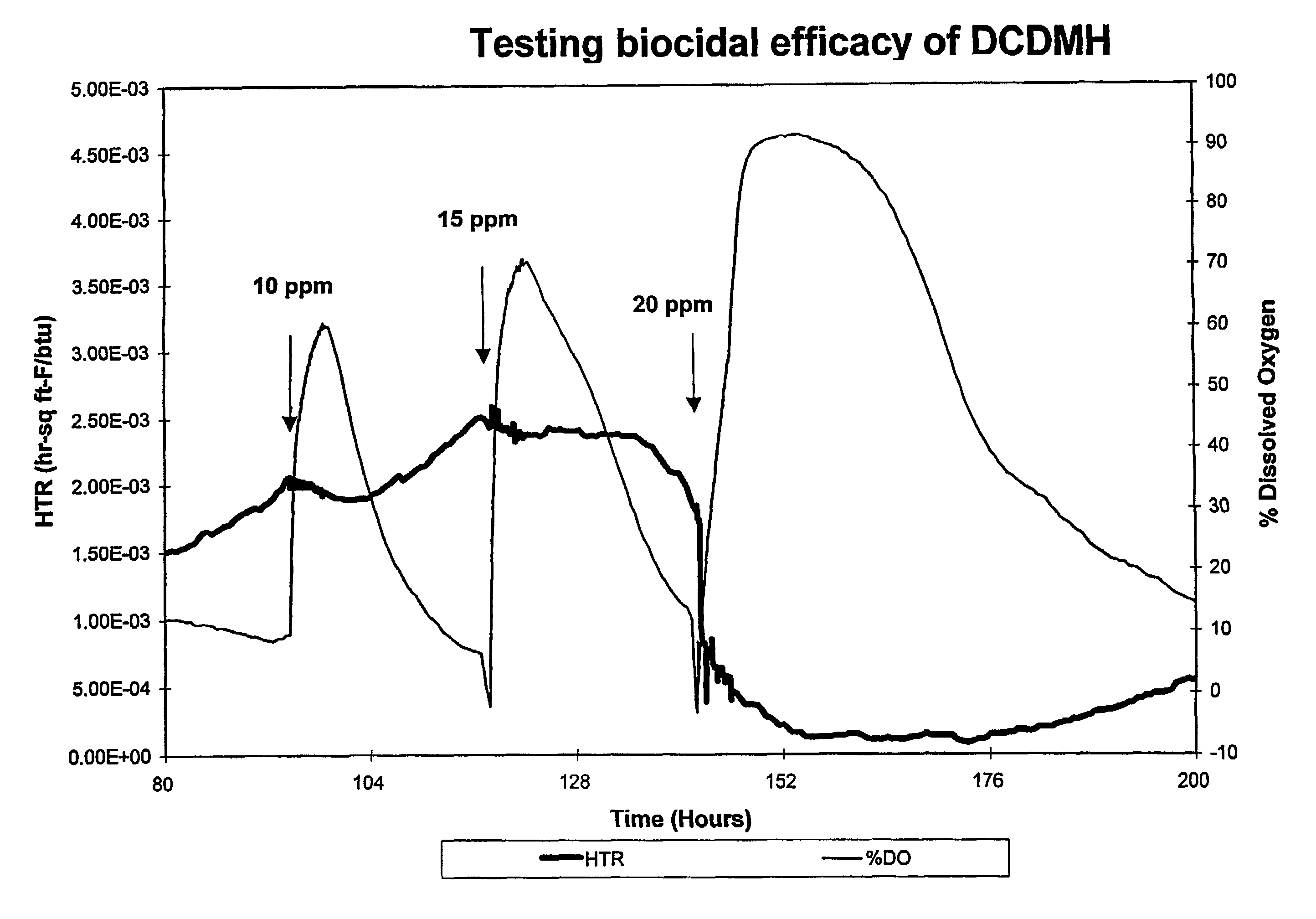
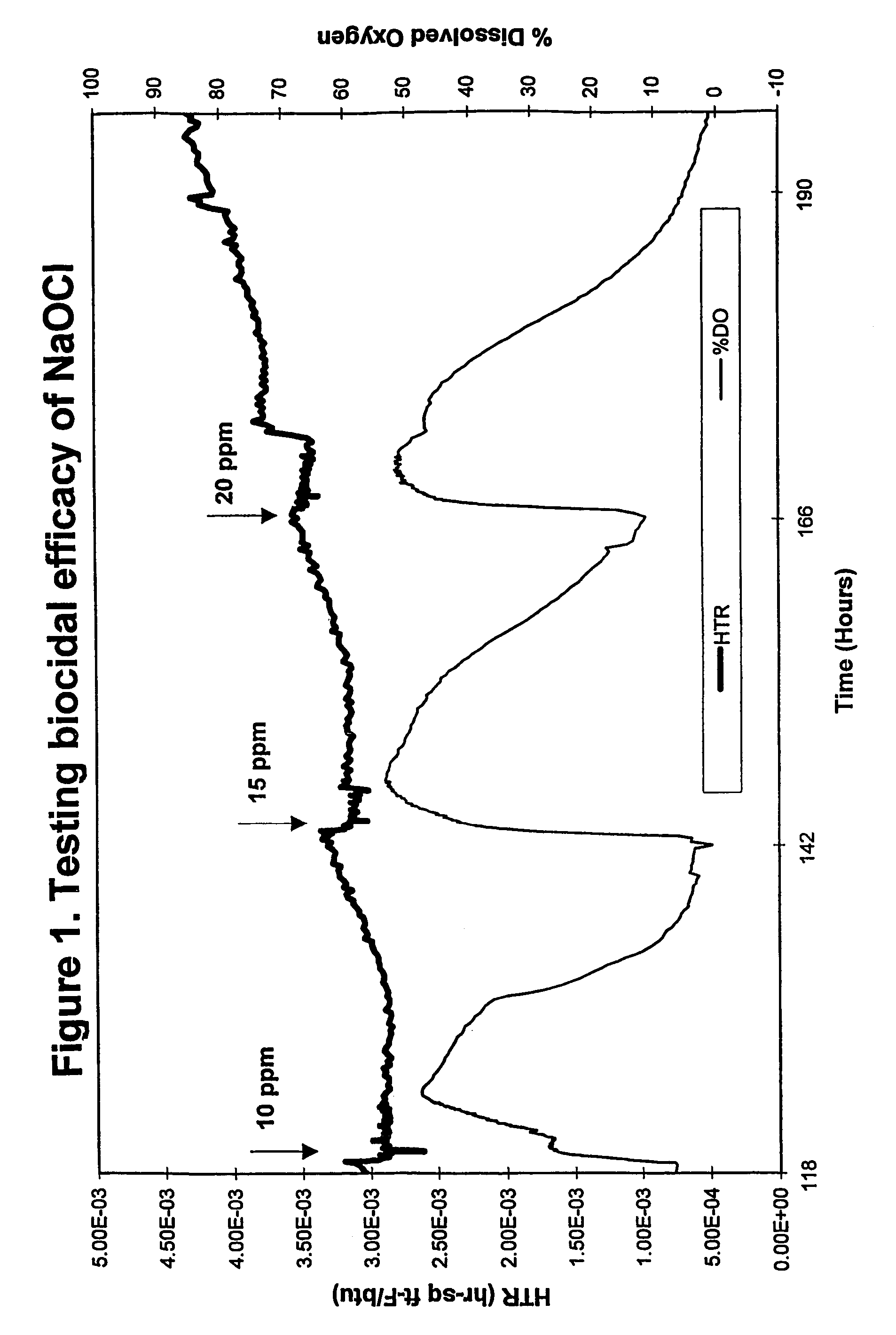
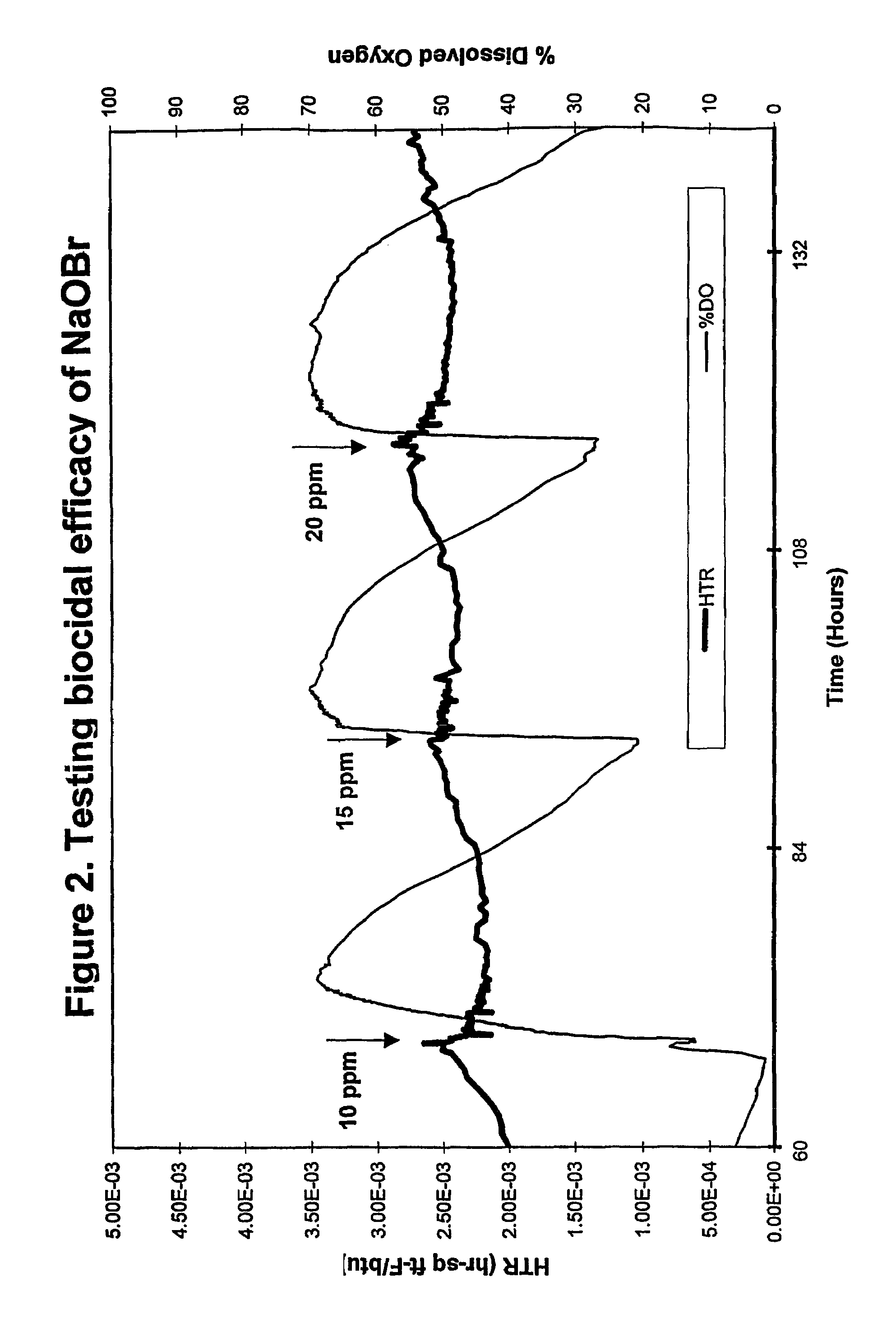
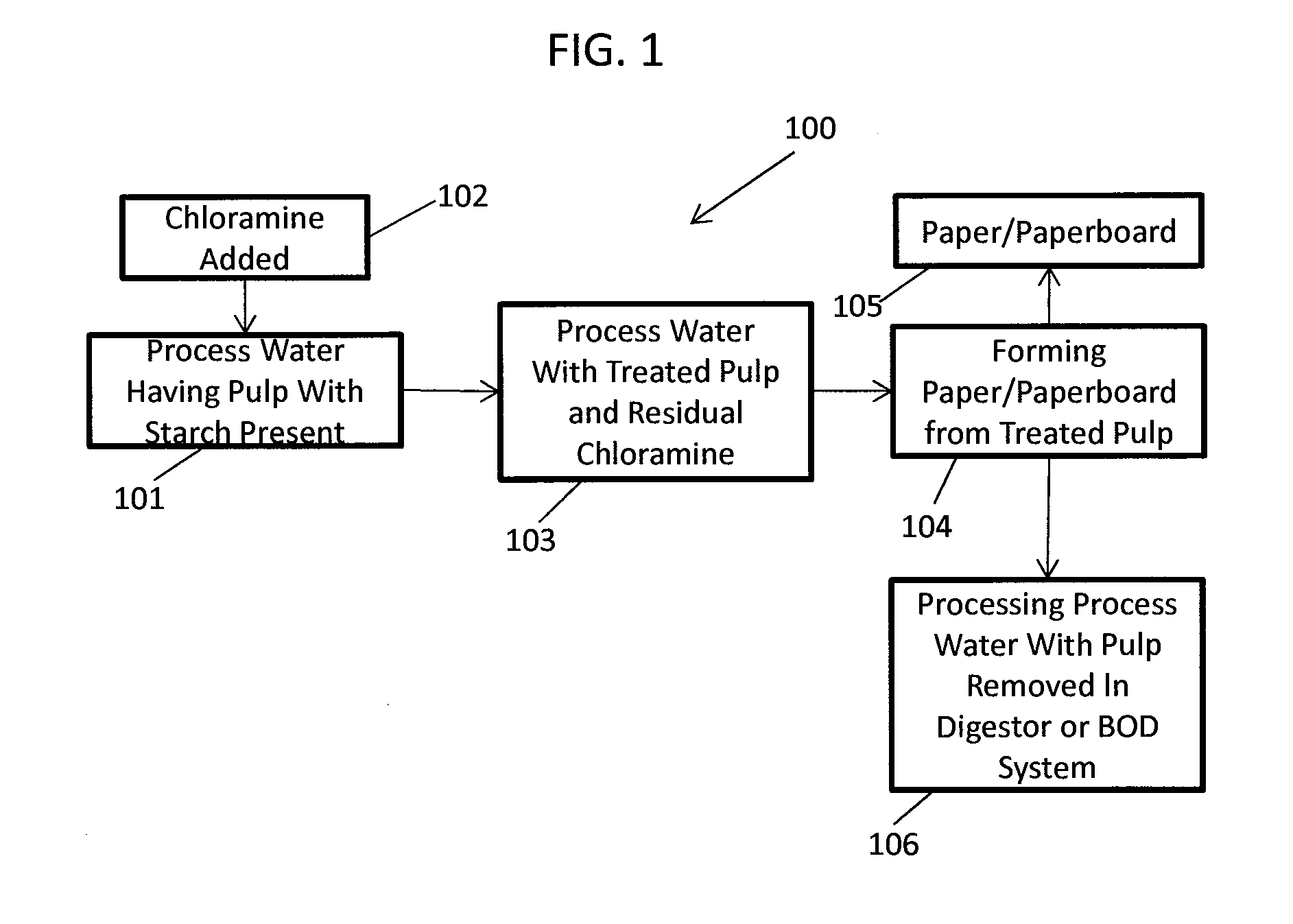
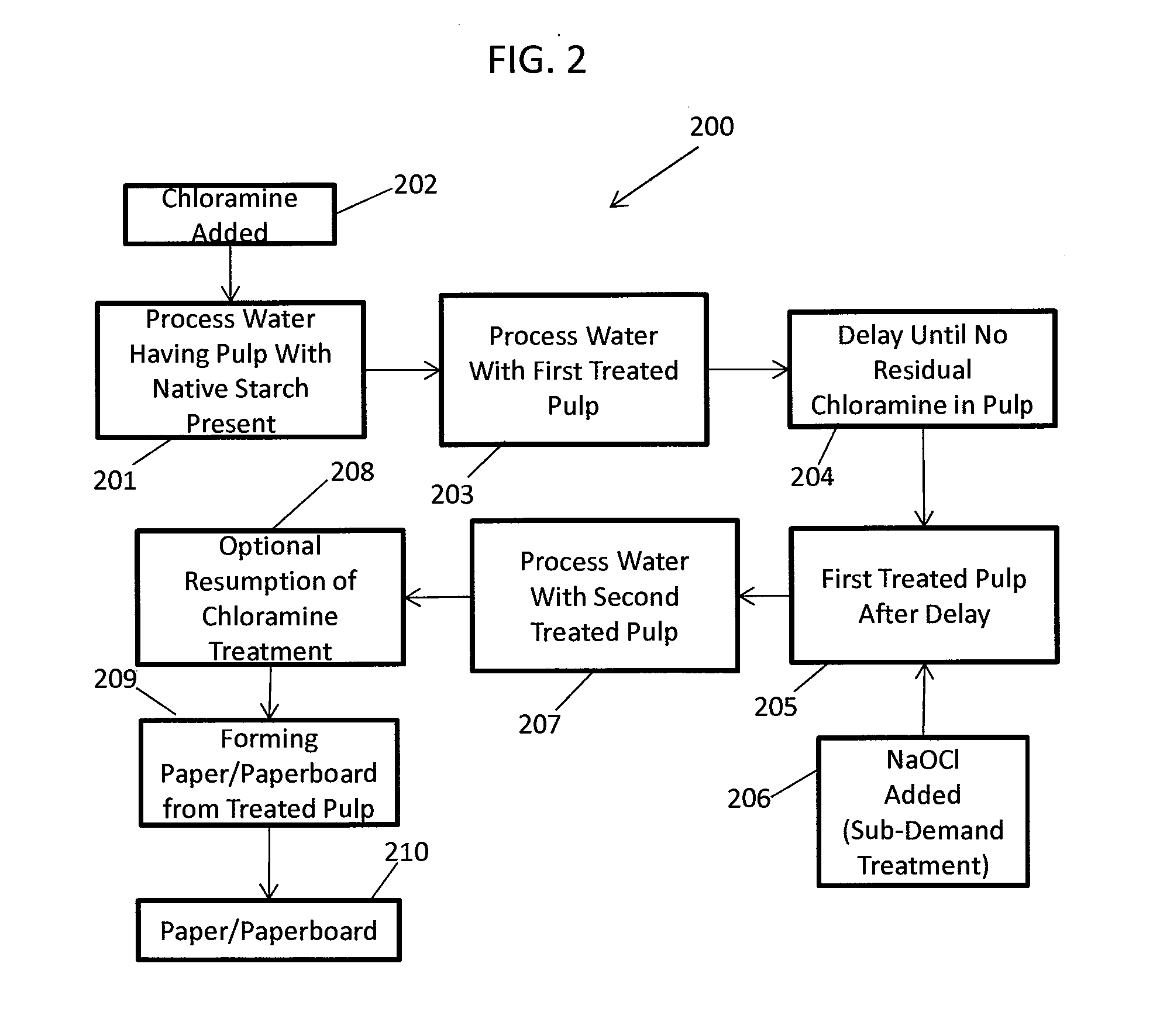
ActiveUS20130319627A1Improve the level ofHigh strengthBiocideNatural cellulose pulp/paperChloramine BChloramine
Methods to preserve starch present in pulp are provided and also methods to control calcium precipitation and / or scaling in digesters or BOD systems. The methods can be performed as part of a papermaking process. Process water containing pulp can be treated with a chloramine. Process water containing pulp with native starch can receive a double treatment with at least one biocide, such as chloramine, and at least one oxidant, such as sodium hypochlorite. The treatment can be performed in any suitable manner. The treatment can be performed at one or more stages or locations in a papermaking system. A target residual chloramine value or range can be achieved by the treatment. Packaging sheets / boards and other paper products manufactured using the methods provided exhibit superior strength and other desirable characteristics.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
Method for removal of biofilm
The present invention provides a method for the removal of biofilm, flocculent bulked sludge or bulked biologically active sludge from an aqueous system. The method involves adding one or more chlorinated hydantoins, such as dichloro- or monochlorodialkylhydantoin, to the aqueous system. Alternatively, the chlorinated hydantoin may be formed in situ by adding a chlorine source and an alkylated hydantoin separately to the aqueous system. The invention is particularly advantageous because of the outstanding photostability of the chlorinated hydantoin solutions even when exposed to sunlight
Owner:ARXADA LLC
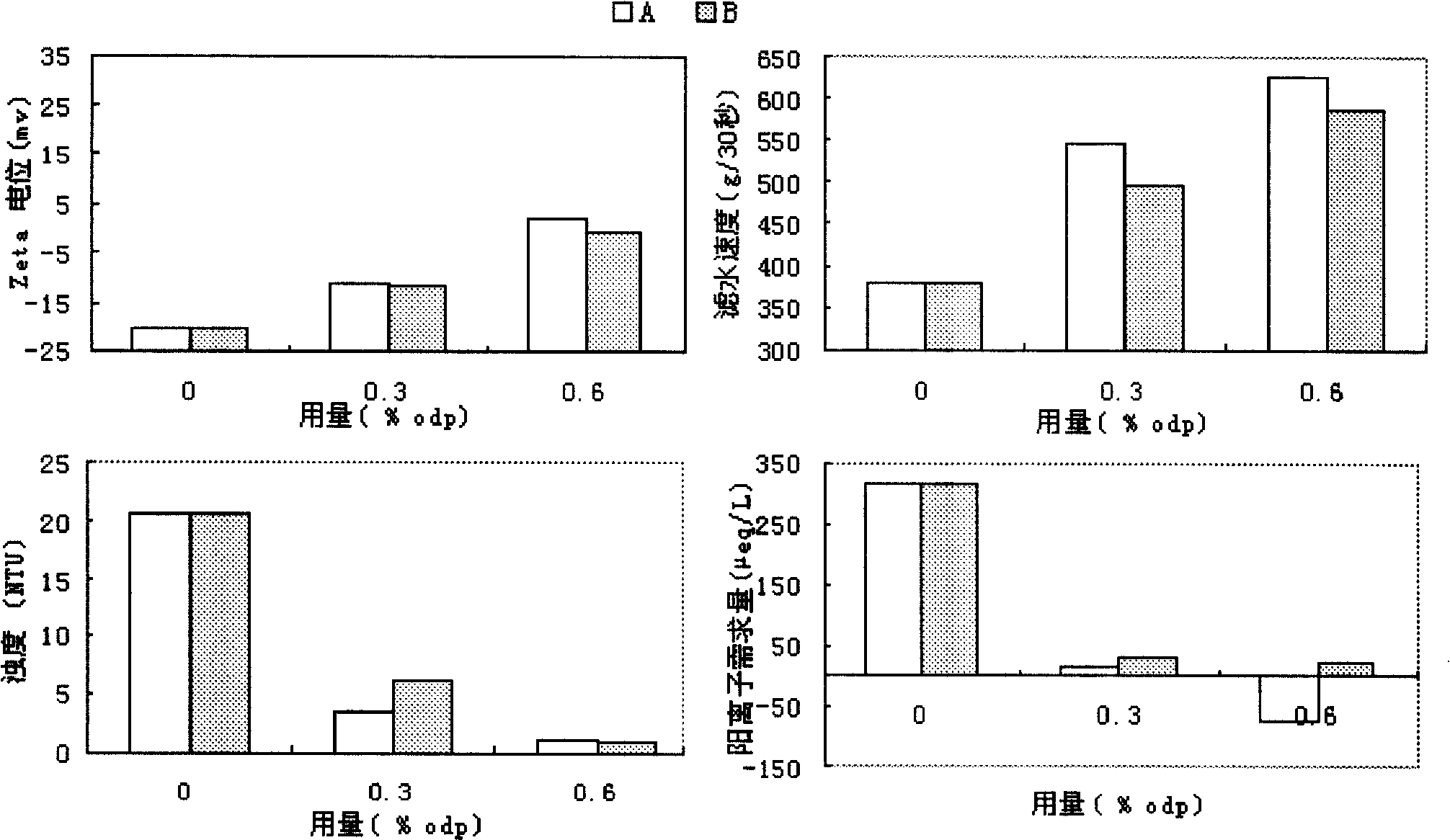
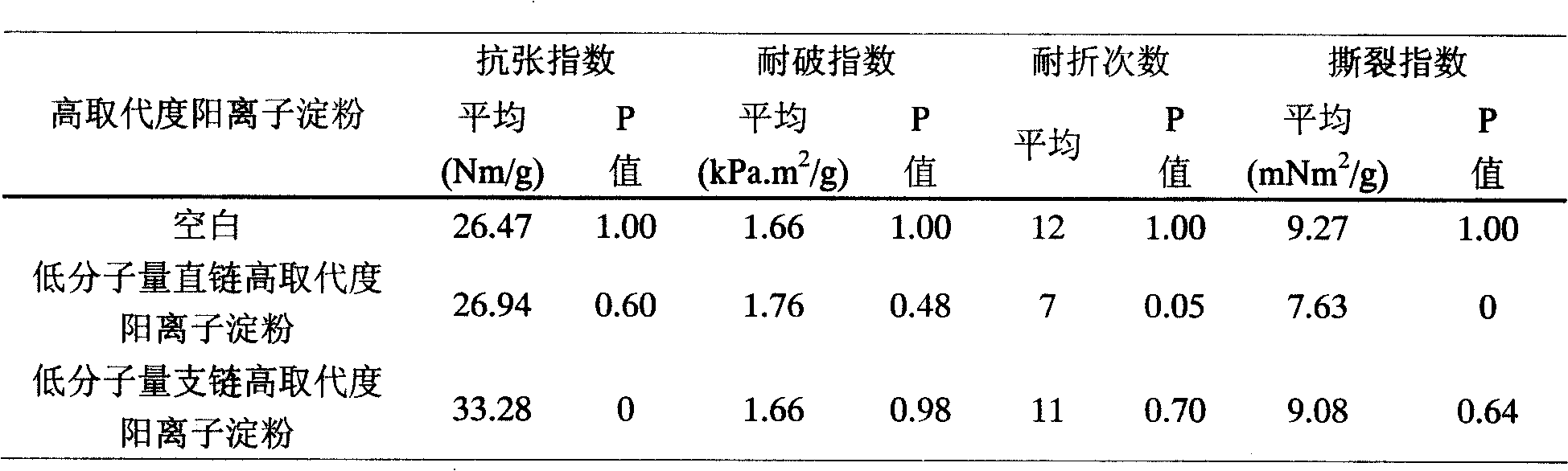
Control of waste paper stock micro-adhesive material by using low molecular weight and high cation substituted ratio starch
InactiveCN101525856AImprove control effectHigh strengthPaper/cardboardSlime-control agents additionElectronegativityColloid
The invention belongs to the field of chemical engineering, in particular to the industry of pulping and paper making, and relates to a novel method for controlling micro-adhesive material. The method comprises: when the electronegativity of sizing agent is stronger, low molecular weight branched-chain and high substituted ratio cationic starch is taken as control agent of the micro-adhesive material; when the strength of paper is needed to be considered, low molecular weight branched chain. The method has good controllability for the micro-adhesive materials with dissolved state and colloidal state, can effectively realize the control for the micro-adhesive material, and maintains and enhances the strength performance of the page.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
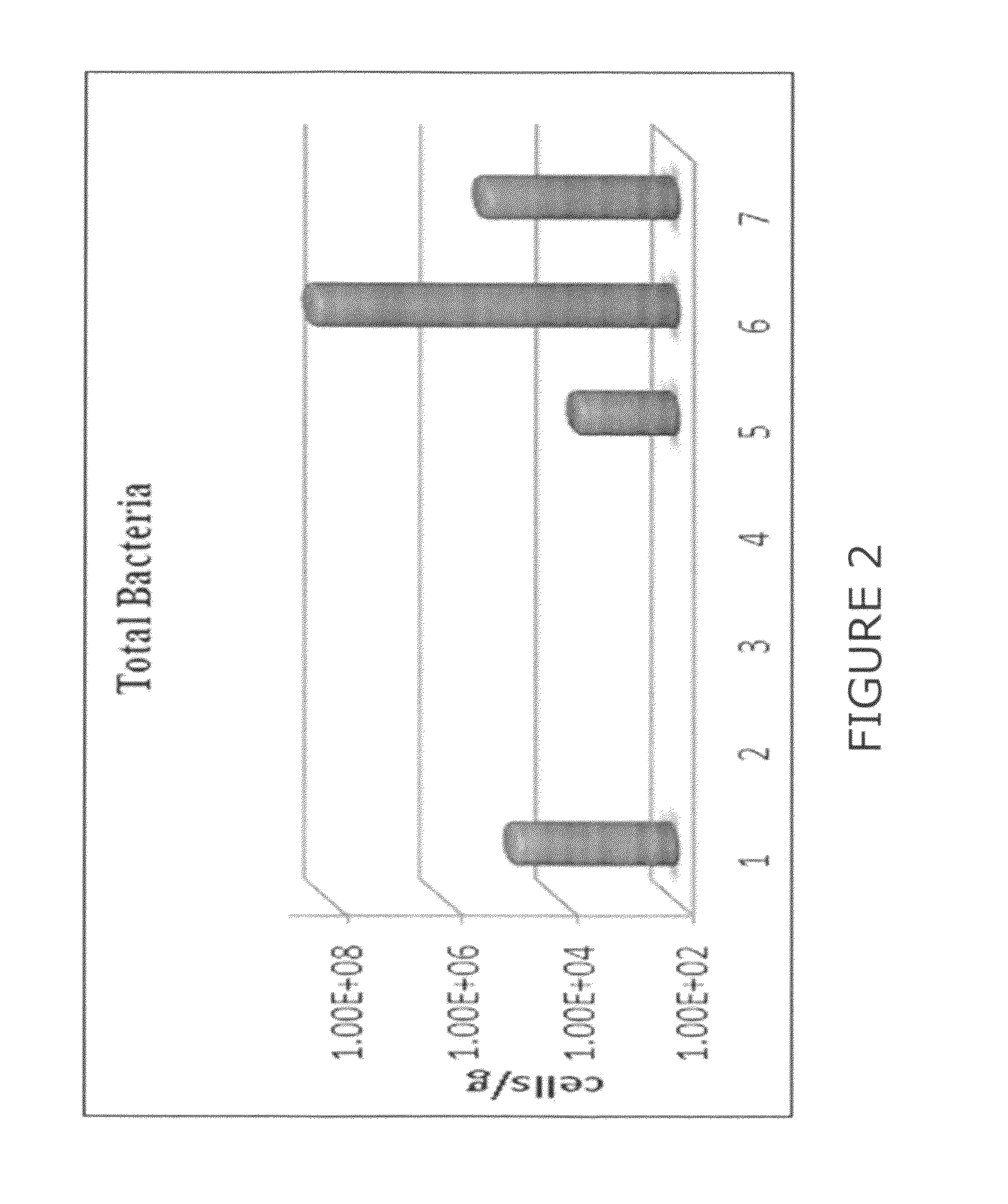
Detection and quantification of nucleic acid to assess microbial biomass in paper defects and machine felts
The invention is directed towards methods and compositions for identifying the specific microorganisms present in a particular potion of a papermaking processes. The method involves obtaining a sample from the process which is such that little or no live examples of the microorganism remain. However because DNA from the organisms is still present, an analysis which identifies portions of DNA specific to the particular organism will correctly identify the microorganism present. This allows for analysis of infestations present on felts or paper sheets which typically no longer have many live microorganisms on them when samples are taken for analysis.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Anti-soiling agent composition
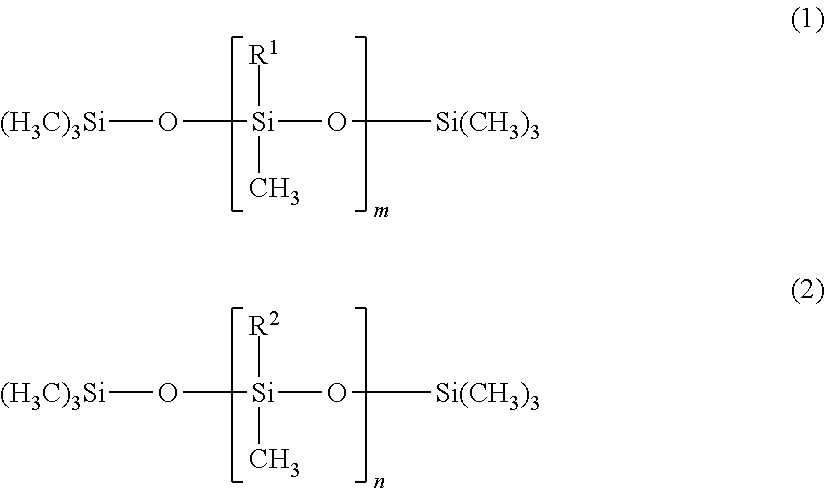
InactiveUS20140128521A1Improved pitch dispersing effectAchieving fixabilityGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsAntifouling/underwater paintsMethyl groupChemistry
[Object] To provide an anti-soiling agent compound that can sufficiently prevents adhesion of pitch to a dry part region.[Solution] The present invention provides an anti-soiling agent composition is provided with: a low molecular polysiloxane compound represented by the following formula (1); and a high molecular polysiloxane compound represented by the following formula (2), and characterized in that the number of modified groups per low molecular polysiloxane compound is in a range from 0.1 to 3, the number of modified groups per high molecular polysiloxane compound is in a range from 1.0 to 10, and the number m of repeating polysiloxane units in the low molecular polysiloxane compound and the number n of repeating polysiloxane units in the high molecular polysiloxane compound have the following relationship: 2 m≦n,[in formula (1), substituent R1 represents a methyl group or a modified group, with the repeating number m being set to an integer from 20 to 200], and[in formula (2), substituent R2 represents a methyl group or a modified group, with the repeating number n representing an integer].
Owner:MAINTECH
Anti-soiling agent composition
ActiveUS20140206805A1Prevent pitchWell formedFouling preventionOther chemical processesMethyl groupOrganic chemistry
[Object] To provide an anti-soiling agent compound that can sufficiently prevents adhesion of pitch to a dry part region.[Solution] The present invention provides an anti-soiling agent composition for preventing pitch contamination in a dry part of a paper-making process, and the composition has a polysiloxane compound represented by the following formula (1), wherein the number of amino-modified groups per molecule of the polysiloxane compound is in a range from 0.5 to 5.[wherein, a substituent R1 represents a methyl group or an amino-modified group represented by the following formula (2), and the number n of repeating siloxane units represents an integer in a range from 50 to 1000, andwherein, each of a substituent R2 and a substituent R3 independently represents an alkylene group having carbon atoms of 1 to 6, and the number m of repeating amino-alkylene units represents an integer in a range from 0 to 2].
Owner:MAINTECH
Detection and quantification of nucleic acid to assess microbial biomass in paper defects and machine felts
ActiveUS20140141443A1Microbiological testing/measurementSlime-control agents additionBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention is directed towards methods and compositions for identifying the specific microorganisms present in a particular potion of a papermaking processes. The method involves obtaining a sample from the process which is such that little or no live examples of the microorganism remain. However because DNA from the organisms is still present, an analysis which identifies portions of DNA specific to the particular organism will correctly identify the microorganism present. This allows for analysis of infestations present on felts or paper sheets which typically no longer have many live microorganisms on them when samples are taken for analysis.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Manufacturing method of waterproof and fireproof paper
InactiveCN102808362AWith waterproof functionWith fire performanceDefoamers additionSpecial paperFiberDodecylsulfonic acid
The invention belongs to the field of fine chemical engineering, and particularly relates to a manufacturing method of waterproof and fireproof paper. The manufacturing method is characterized in that 50 to 65 parts of fibrous raw materials, 5 to 9 parts of anthraquinone, 6 to 10 parts of xylitol, 3 to 5 parts of silicone oil, 2 to 4 parts of p-chloro-m-cresol, 2 to 4 parts of rosin size, 5 parts of pigments, 5 to 7 parts of polyacrylamide, 2 to 4 parts of sodium dodecyl sulfonate, 2 to 4 parts of polyethyleneimine, 2 to 4 parts of polyacrylate, 2 to 4 parts of polyethylene, 5 to 7 parts of hydrous zinc borate and 5 to 7 parts of waterproof agents are adopted. The waterproof and fireproof paper can be manufactured after the steps of steam cooking, paper making and coating are conducted. The waterproof and fireproof paper produced by using the manufacturing method not only has waterproof and fireproof functions, but also has better flexibility and tear resistance.
Owner:师文
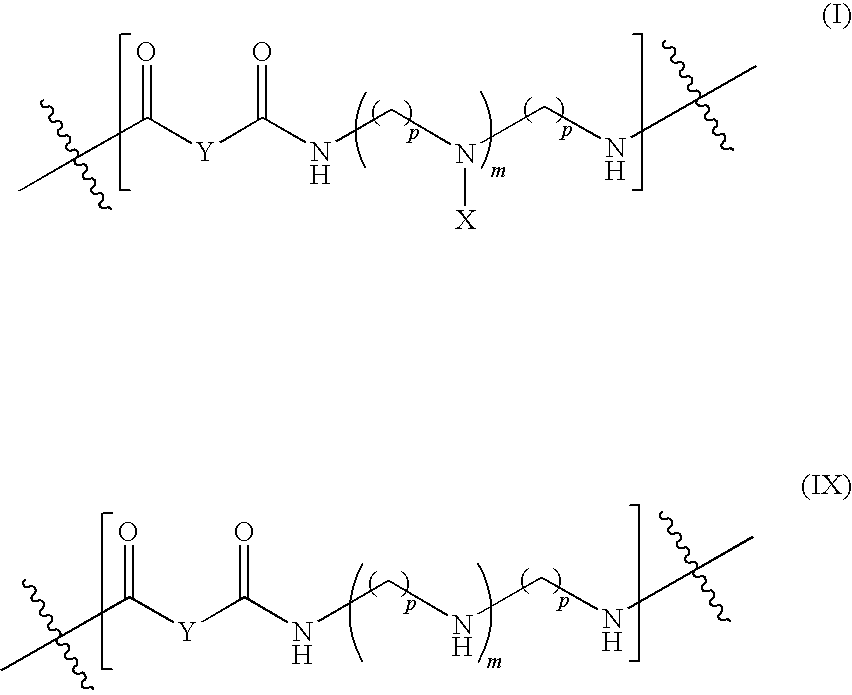
Hydrophobically Modified Poly(aminoamides)
Disclosed herein are hydrophobically-modified poly(aminoamides) useful as fixative detackifiers for stickies and pitch control in papermaking processes. These polymers are prepared via modification of amine-containing water-soluble poly(aminoamides) with reactive functional group-containing hydrophobic compounds. In particular, poly(aminoamides) may be modified, under appropriate reaction conditions, with long chain alkyl glycidyl ether, AKD (alkyl ketene dimer), ASA (alkyl succinyl anhydride), or Quab (3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl-N,N,N-dimethylalkyl ammonium chloride). These novel polymers are effective in inhibiting deposition of organic contaminants in pulp and papermaking systems.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Methods To Control Organic Contaminants In Fibers
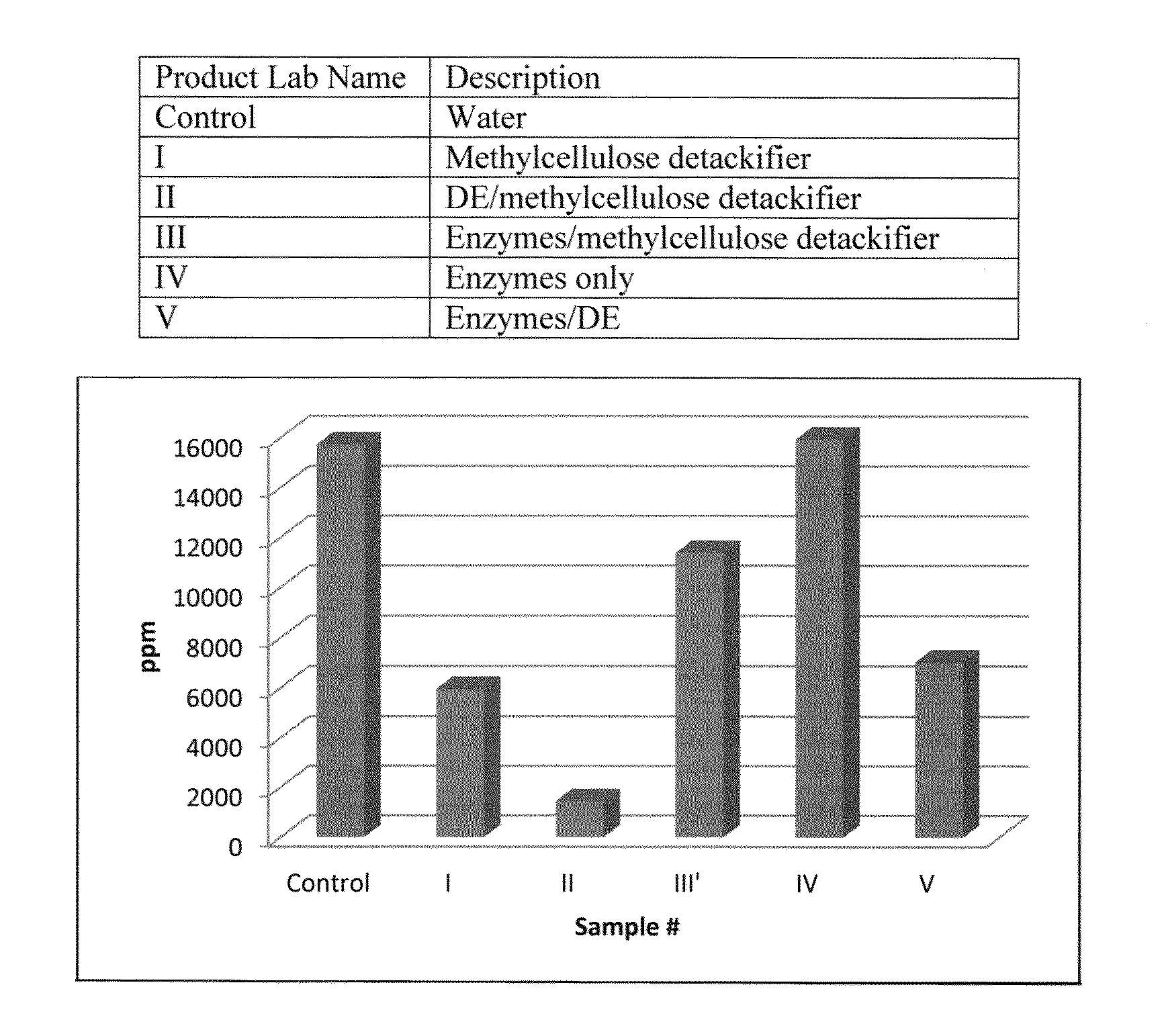
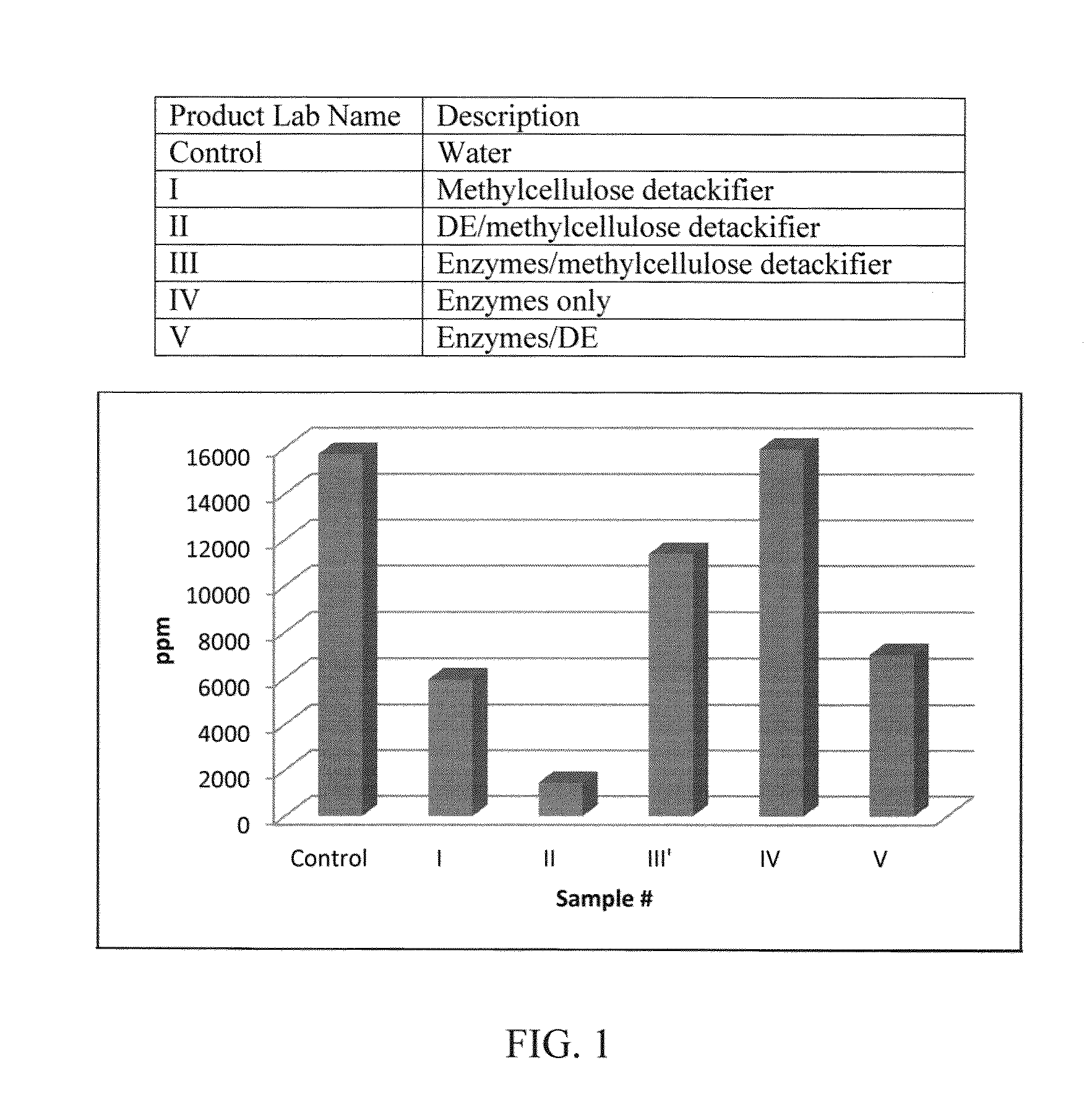
InactiveUS20130180677A1Easy to controlReduce viscosityNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperFiberSufficient time
Methods to control organic contaminants in fibers are described. One method involves contacting the fibers with a) diatomaceous earth and b) detackifier, or an ester hydrolyzing enzyme, or both, for a sufficient time and in a sufficient amount to control the organic contaminants present in the fibers. This method is effective to reduce stickies in paper mill furnish formed with recycled fibers. A method for pitch control in paper mill furnish formed with virgin fibers is also provided. Resulting paper products formed from the processed fibers are also described as well as methods to make them.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
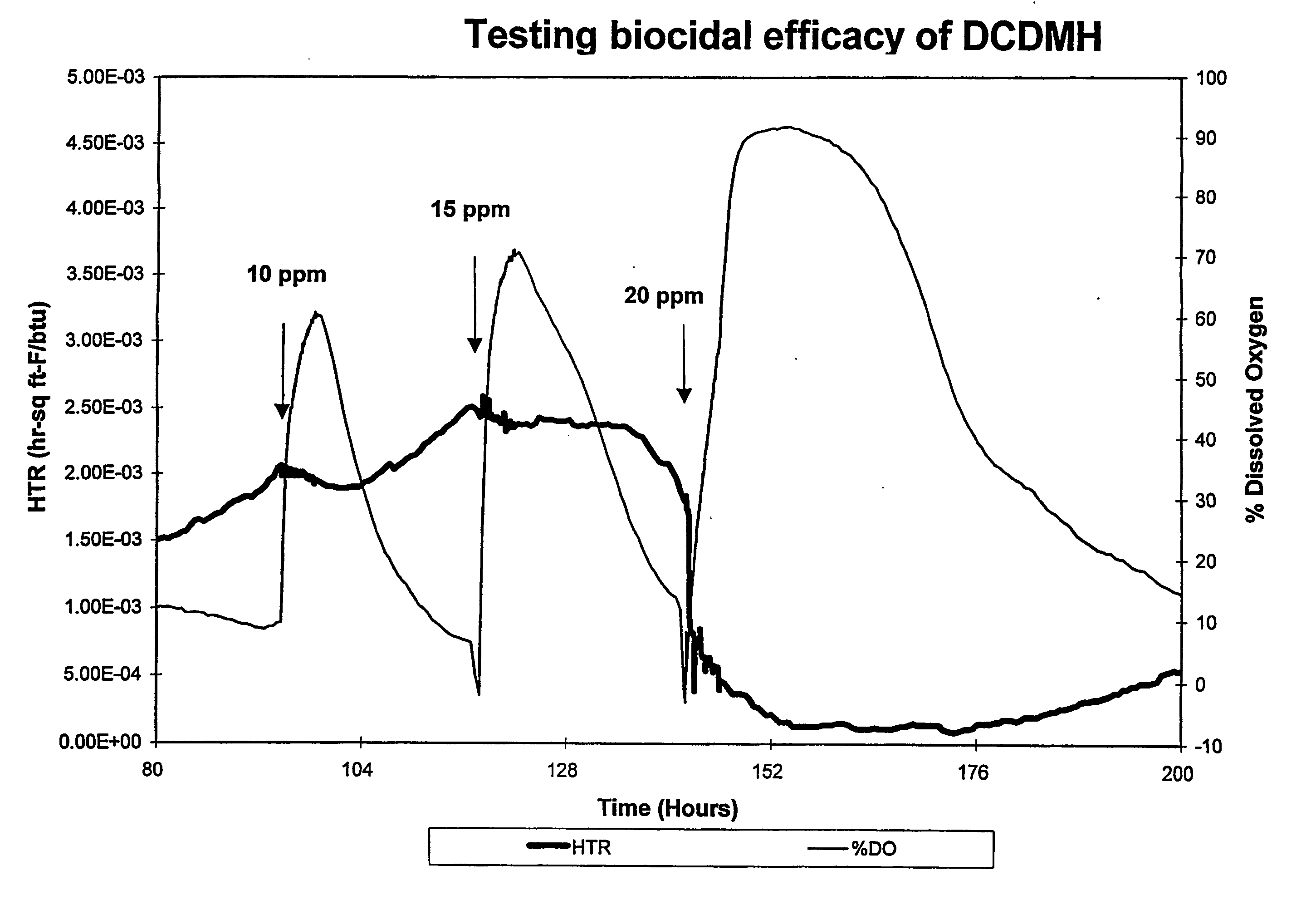
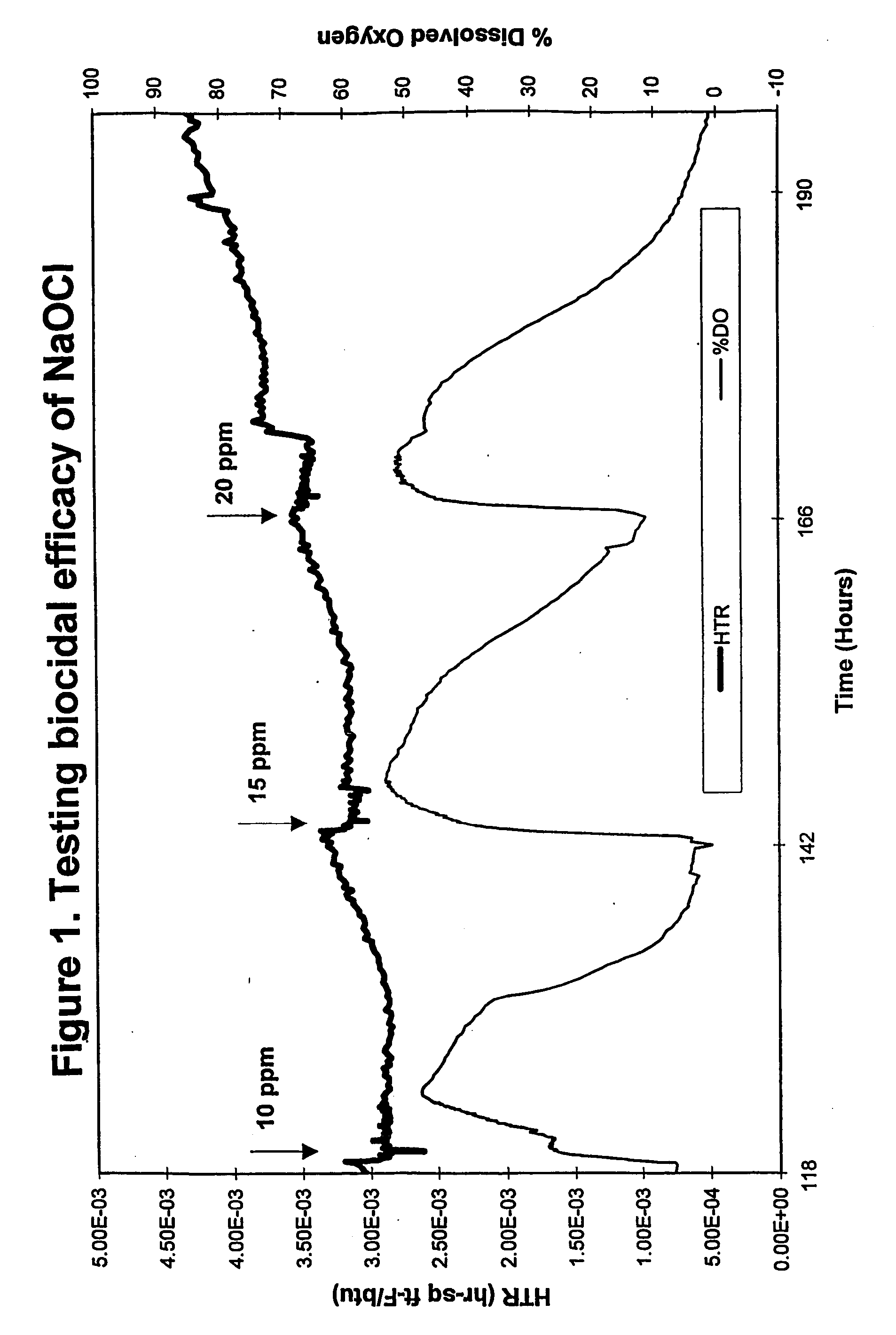
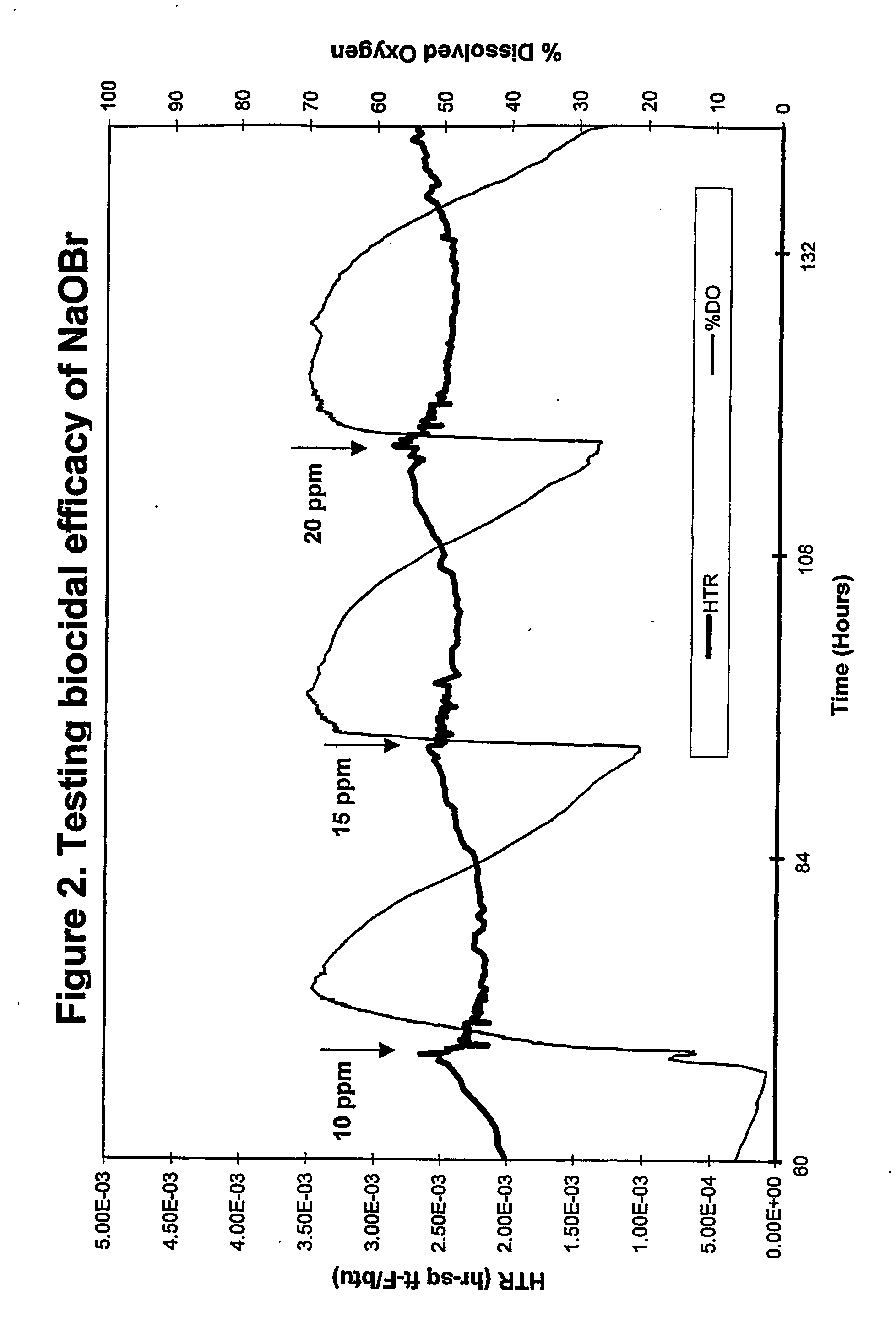
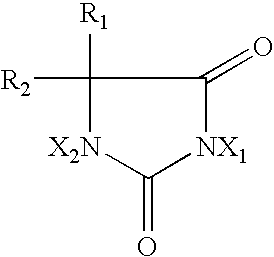
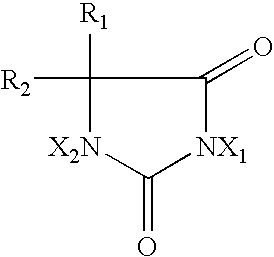
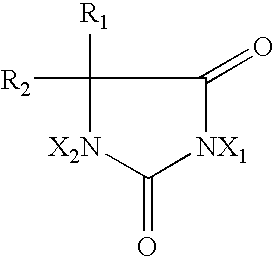
Hydantoin-enhanced halogen efficacy in pulp and paper applications
InactiveUSRE39021E1Improve bactericidal efficacyReduce the amount requiredBiocideNatural cellulose pulp/paperHydantoinSuccinimide
Free halogen sources (e.g., sodium hypochlorite and chlorine) added as slimicides in high organic component process streams such as pulp and paper processing are rendered more efficacious by the addition of selected N-hydrogen compounds (namely, 5,5-dimethylhydantoin, 5-ethyl-5-methylhydantoin, cyanuric acid, succinimide, urea, 4,4-dimethyl-2-oxazolidinone, and glycouril) to the process stream. The latter compounds may be added to the process stream before or after the slimicide is added or combined with the slimicide and added directly thereto. The direct use of halogenated hydantoins has also been found to provide improved efficacy relative to free halogen sources. In addition, absorbable organic halogen by-products are reduced.
Owner:LONZA INC
Ketone-removing additive for removing ketone substances from packaging card paper and application of additive
ActiveCN103882766AEasy to removeExcellent selective elimination effectDefoamers additionNon-macromolecular organic additionPropanoic acidPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a ketone-removing additive for removing ketone substances from packaging card paper, and application of the additive. The ketone-removing additive comprises organic amine and a catalyst, wherein the organic amine is one or more of ethanediamine, propane diamine, butanediamine, ethanolamine, guanidine and dimethyl biguanide; the catalyst is one or more of acetic acid, propionic acid, citric acid and malic acid; the mass ratio of the organic amine to the catalyst is 1.5: 1 to 2.5: 1. The ketone-removing additive is added into a water dispersible coating solution containing acrylic resin at room temperature to obtain a water-based coating solution, wherein the mass percent of the ketone-removing additive in the coating solution is 0.5%-5.0%. The water-based coating solution is used for removing the ketone substances from the packaging card paper. An experiment shows that the water-based coating solution can be used for effectively removing the ketone substances from the packaging card paper. The water-based coating solution is low in production cost, cannot change the structure and the characteristics of the paper in a ketone removing process, and cannot influence the subsequent processing process of the packaging card paper.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO HUNAN INDAL CORP +1
Methods of preserving starch in pulp and controlling calcium precipitation and/or scaling
Methods to preserve starch present in pulp are provided and also methods to control calcium precipitation and / or scaling in digesters or BOD systems. The methods can be performed as part of a papermaking process. Process water containing pulp can be treated with a chloramine. Process water containing pulp with native starch can receive a double treatment with at least one biocide, such as chloramine, and at least one oxidant, such as sodium hypochlorite. The treatment can be performed in any suitable manner. The treatment can be performed at one or more stages or locations in a papermaking system. A target residual chloramine value or range can be achieved by the treatment. Packaging sheets / boards and other paper products manufactured using the methods provided exhibit superior strength and other desirable characteristics.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
Sterilizing and deodorizing method for paper making water and slime pulp controlling agent used thereby
InactiveCN1702236AWater treatment parameter controlSpecific water treatment objectivesHigh concentrationPapermaking
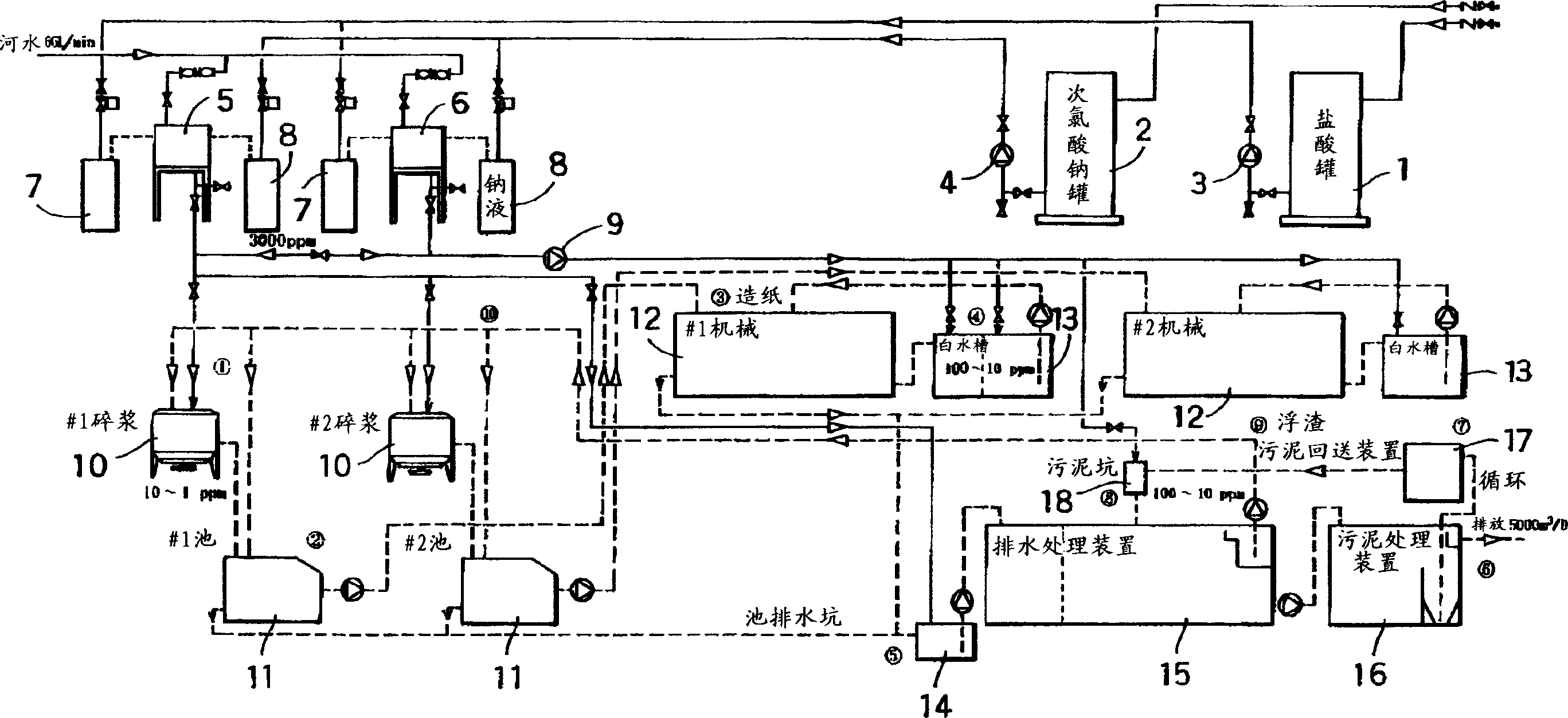
This invention provides an economical slime-controlling and deodorizing method in a papermaking process. The method for sterilizing and deodorizing water for the papermaking comprises adding a high-concentration aqueous solution of sodium hypochlorite in a hydrochloric acid condition, having pH>=4 and 1,000-10,000 ppm, preferably 2,000-8,000 ppm effective chlorine concentration to a water tank for a white water system or a recovered scum system, and regulating the effective chlorine concentration of the water so as to be 100-10 ppm. The method enables the reduction of the papermaking slime or deodorization to be achieved at an economical cost. The water for the papermaking after addition is effective even in a neutral region but is preferably used in a weak acidic region.
Owner:イーエステクノロジー
Microorganism control system and use thereof
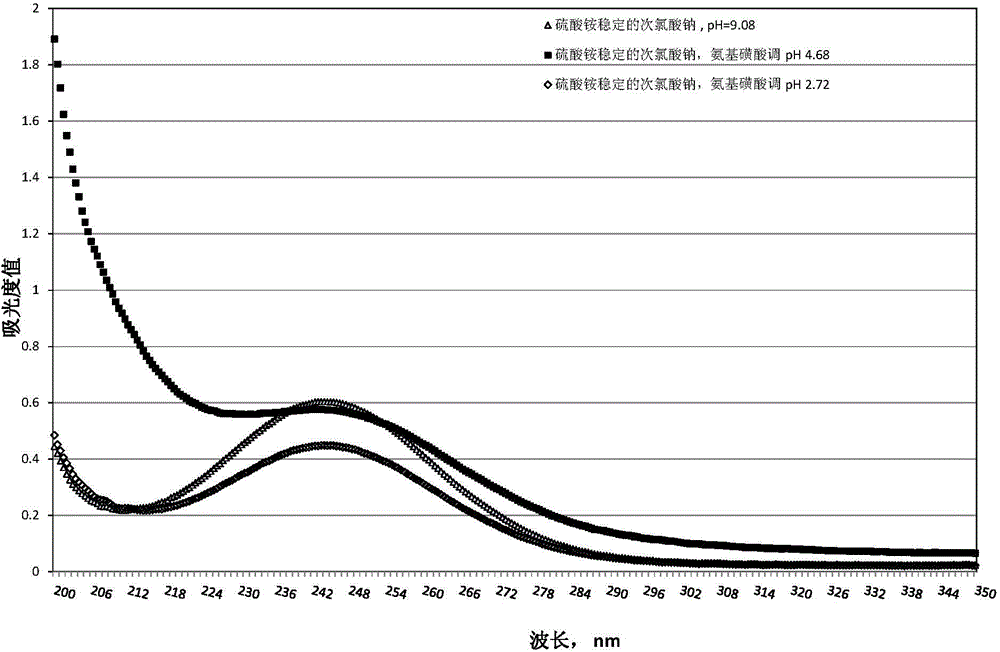
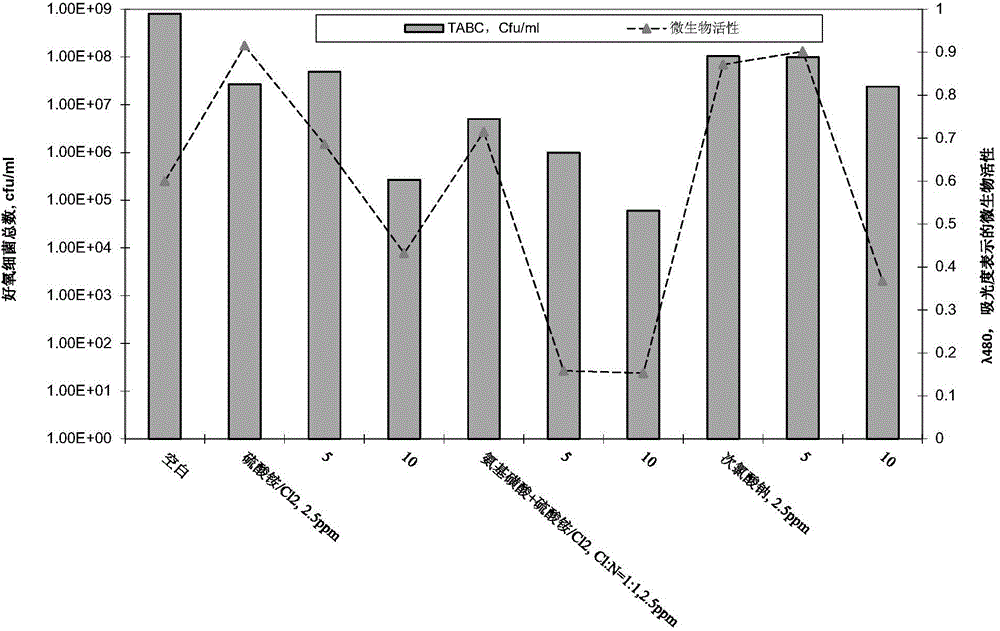
The invention relates to the field of microorganism control in the paper pulp and / or water treatment process in a papermaking technology, and concretely provides a microorganism control system. The system includes a first component and a second component which are separate, the first component comprises a stabilized halogen-containing bactericide (such as stabilized hypochlorite), and the second component includes a sulfamic acid reagent (such as sulfamic acid). The invention also provides a method for controlling microorganisms in the paper pulp and / or water treatment process in the papermaking technology. The microorganism control system is used in the method.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
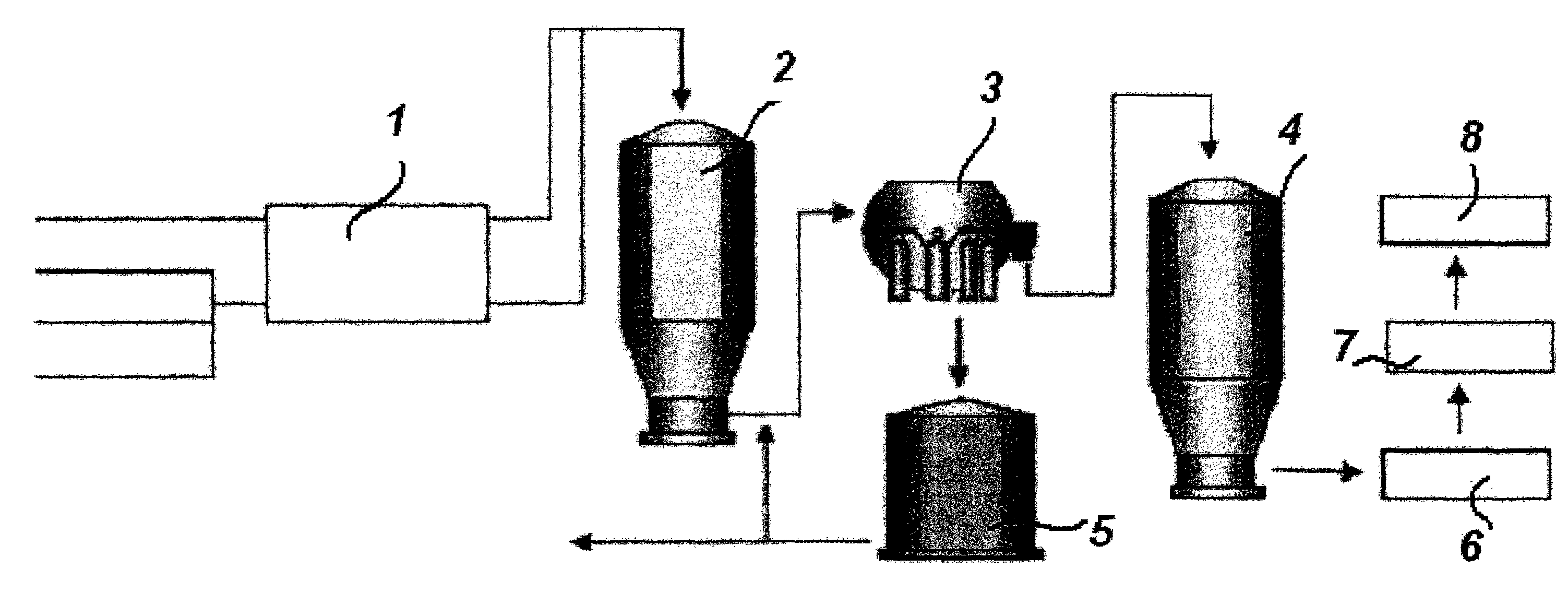
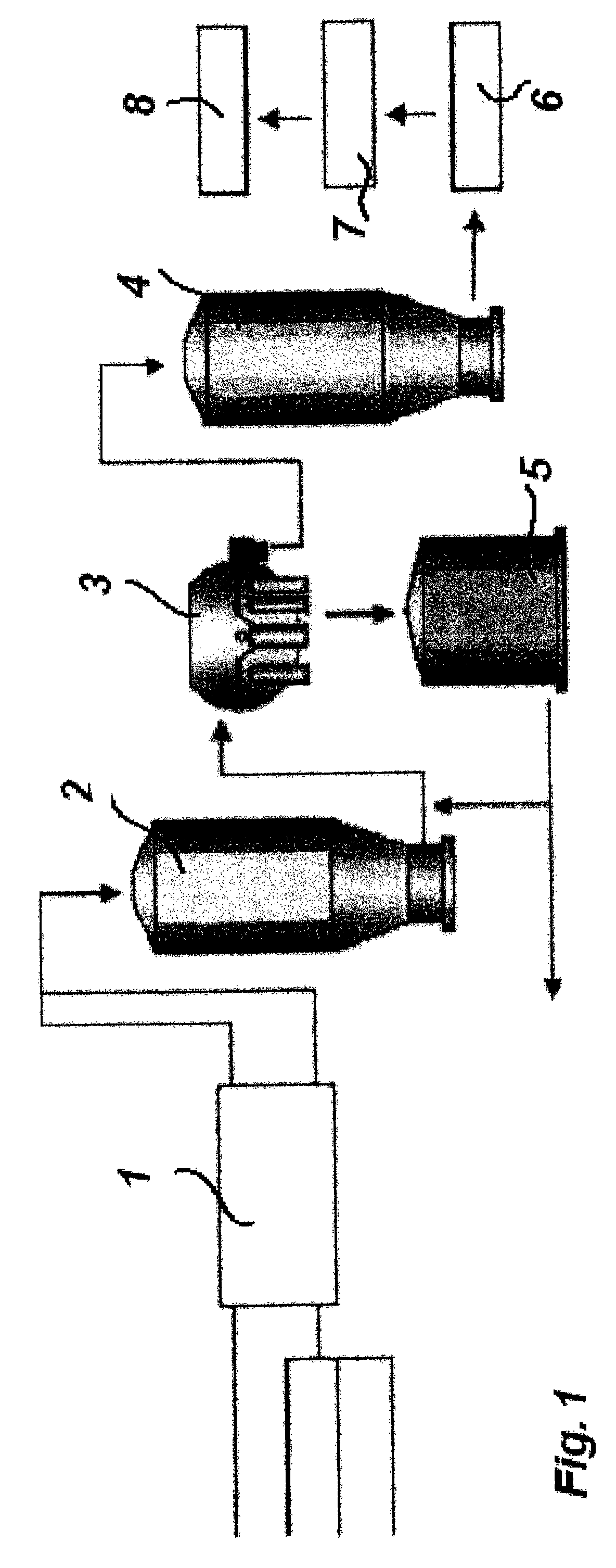
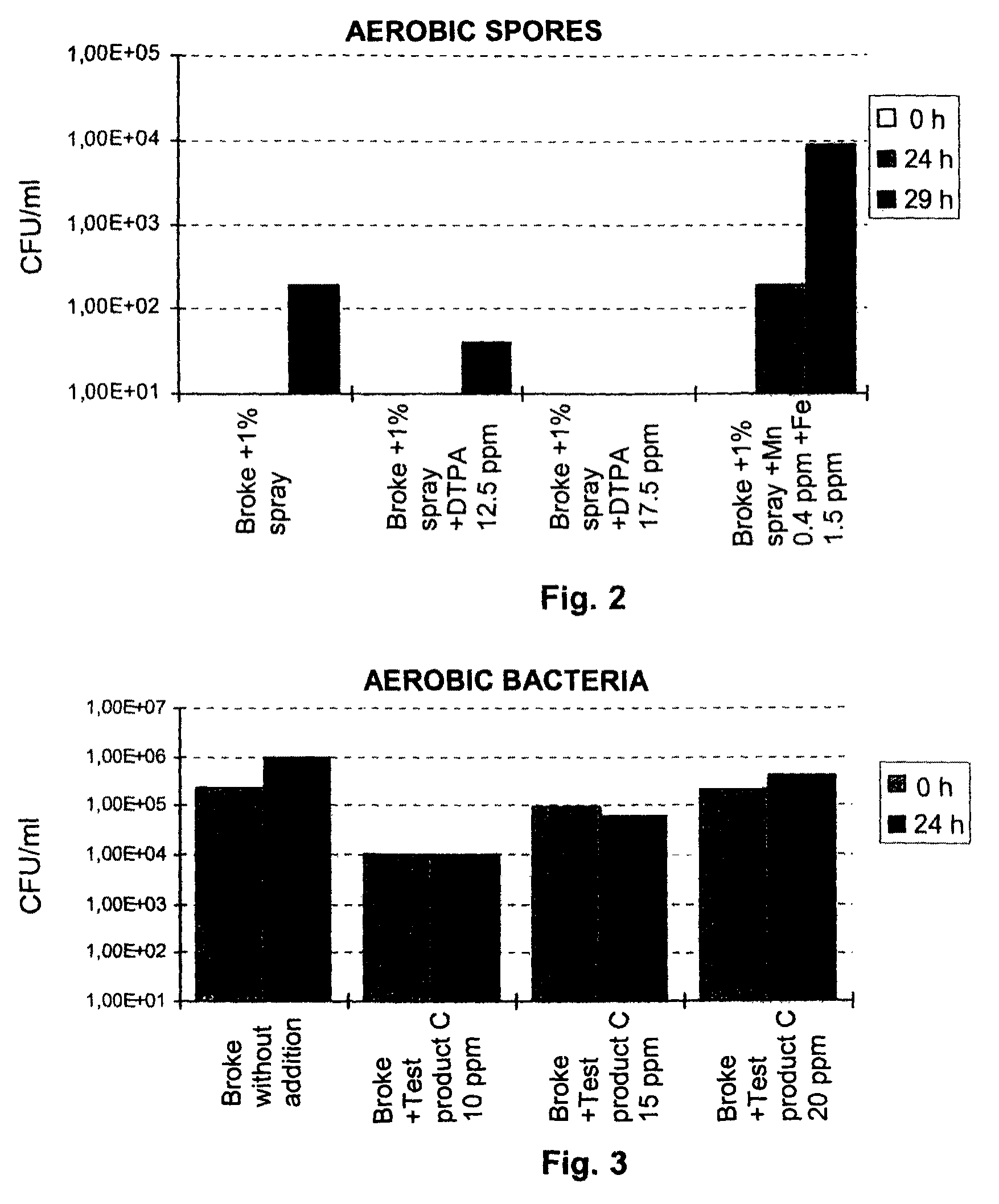
Prevention of bacterial spore formation in a broke system of a board machine
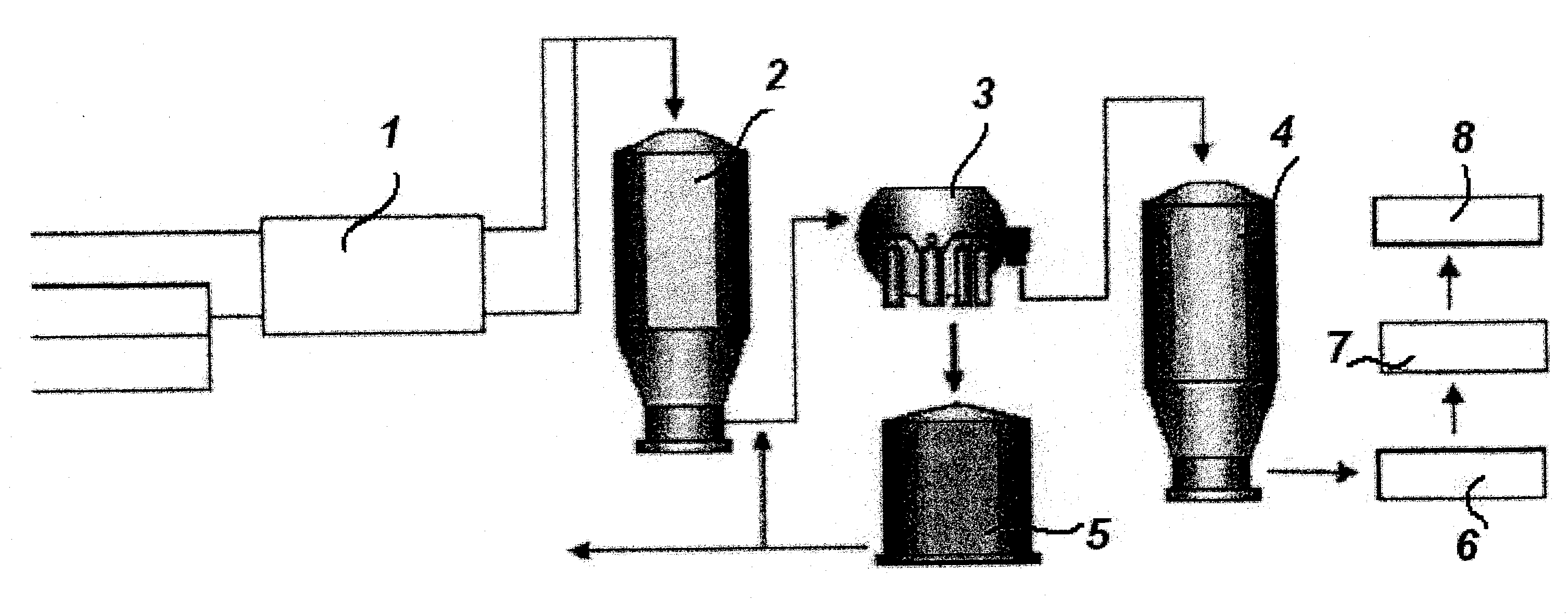
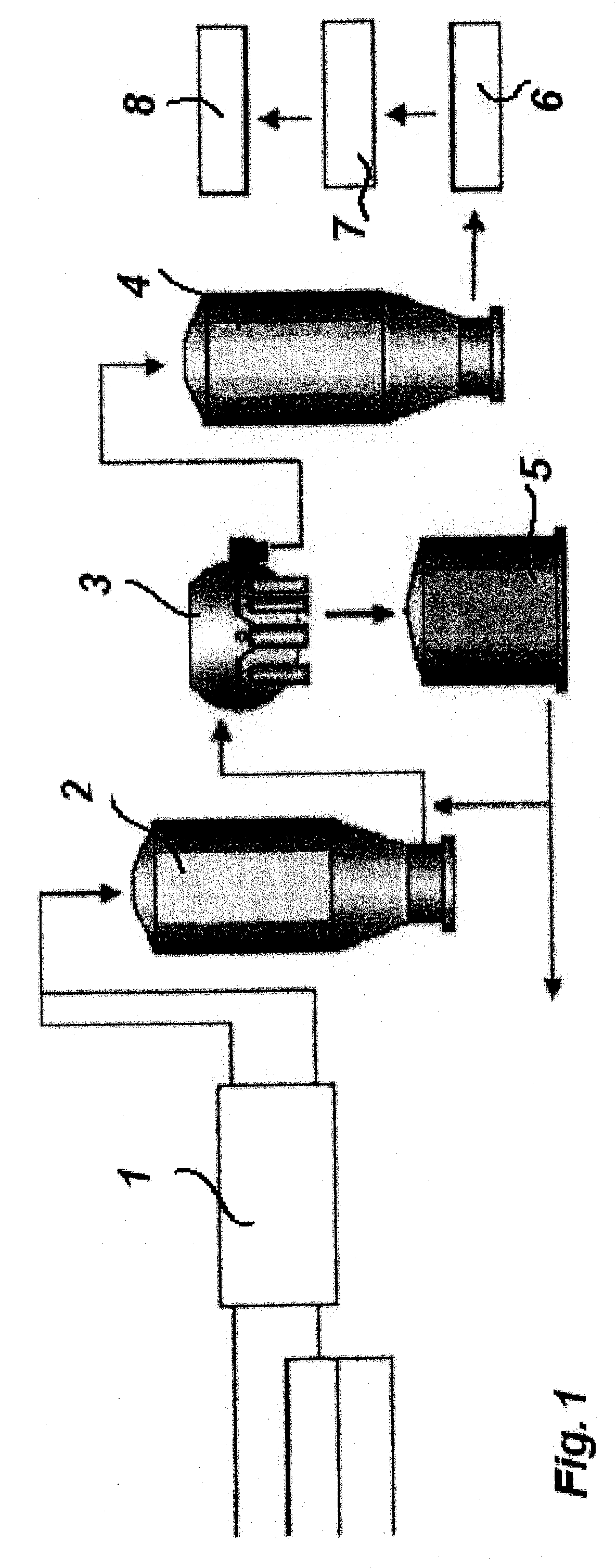
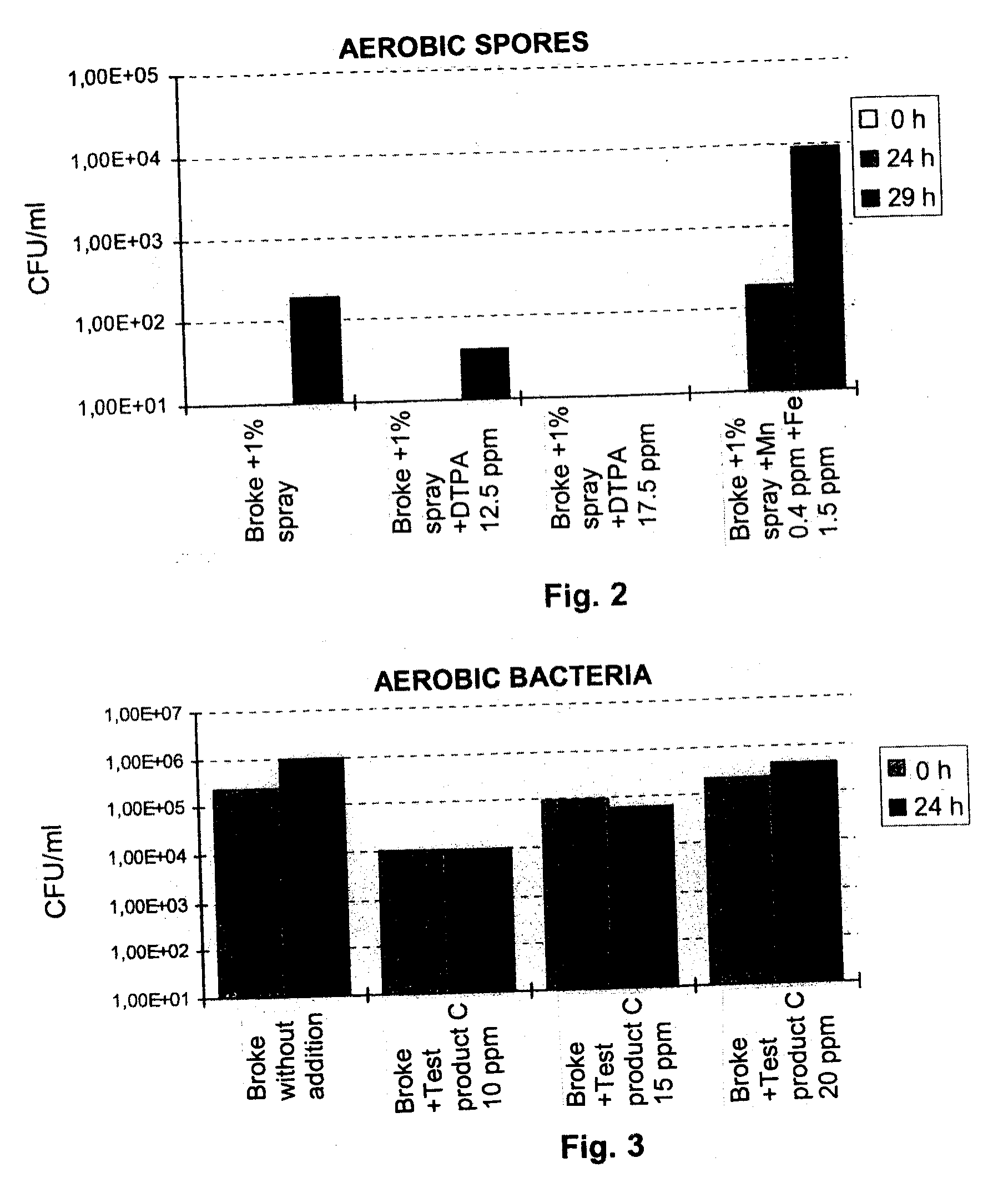
The invention relates to a method for preventing or delaying bacterial sporulation in the broke system of a board or paper machine by lowering the content of transition metals in the broke to a level unfavorable for sporulation. Preferably bacterial cells present in the broke system of the board or paper machine are not substantially killed by the procedure used for lowering the content of the transition metals. The invention further relates to a method for producing packaging board or packaging paper having a low bacterial spore content.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Control of development of biofilms in industrial process water
InactiveUS20060138058A1Improve durabilityPulp deposit formation/corrosion preventionBiocideMicroorganismBiochemical engineering
Owner:A Y LAB LTD
Detection and quantification of nucleic acid to assess microbial biomass in paper defects and machine felts
The invention is directed towards methods and compositions for identifying the specific microorganisms present in a particular potion of a papermaking processes. The method involves obtaining a sample from the process which is such that little or no live examples of the microorganism remain. However because DNA from the organisms is still present, an analysis which identifies portions of DNA specific to the particular organism will correctly identify the microorganism present. This allows for analysis of infestations present on felts or paper sheets which typically no longer have many live microorganisms on them when samples are taken for analysis.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Methods For Inhibiting The Deposition Of Organic Contaminates In Pulp And Papermaking Systems
ActiveUS20170009100A1Preventing and cleaning and inhibiting depositionPreventing and inhibiting organic depositFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPolyether coatingsPapermakingOrganopónicos
The current method relates to compositions and methods for inhibiting the deposition of organic contaminants in pulp and papermaking systems. The current method also relates to controlling the deposition of organic contaminants on equipment in the pulp and papermaking systems, which can cause both quality and efficiency problems. In particular it relates to the use of non-sulfonated or slightly sulfonated lignin dispersions and solutions for inhibiting deposition of contaminants in pulp and paper making system.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Prevention of bacterial spore formation in a broke system of a board machine
ActiveUS8282778B2Inhibition formationIncrease volumeCellulosic pulp after-treatmentBiocideCardboardMetal
The invention relates to a method for preventing or delaying bacterial sporulation in the broke system of a board or paper machine by lowering the content of transition metals in the broke to a level unfavorable for sporulation. Preferably bacterial cells present in the broke system of the board or paper machine are not substantially killed by the procedure used for lowering the content of the transition metals. The invention further relates to a method for producing packaging board or packaging paper having a low bacterial spore content.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Method of slime control in paper pulp manufacturing process
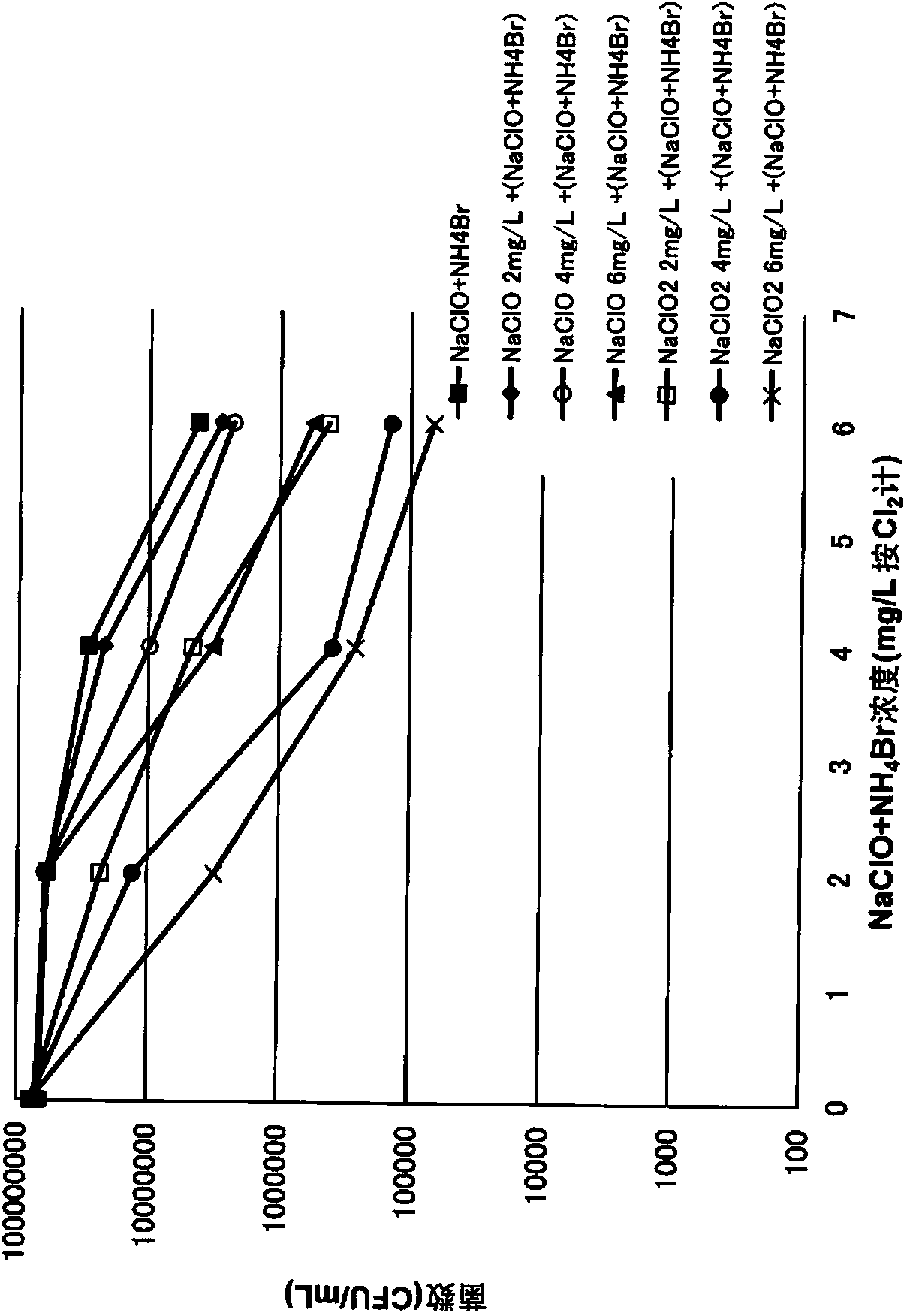
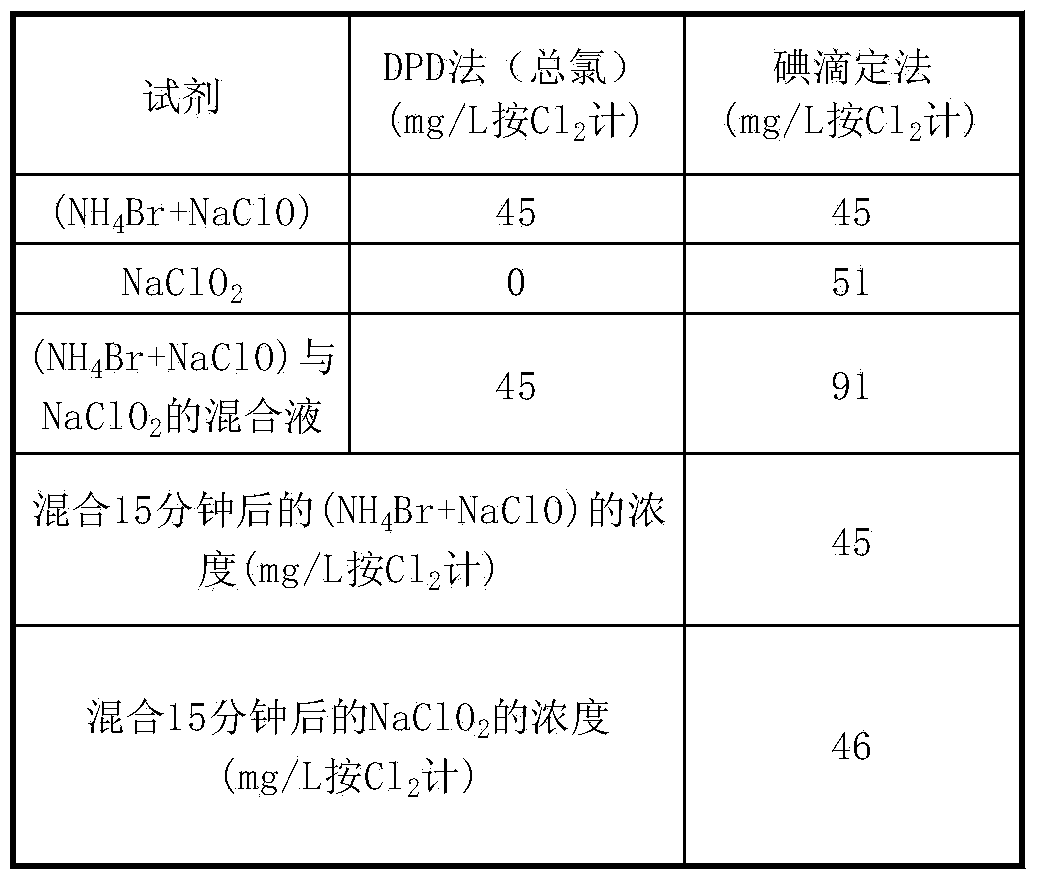
InactiveCN104204352AAvoid decompositionAdd lessSpecific water treatment objectivesNon-macromolecular organic additionDecompositionChlorous acid
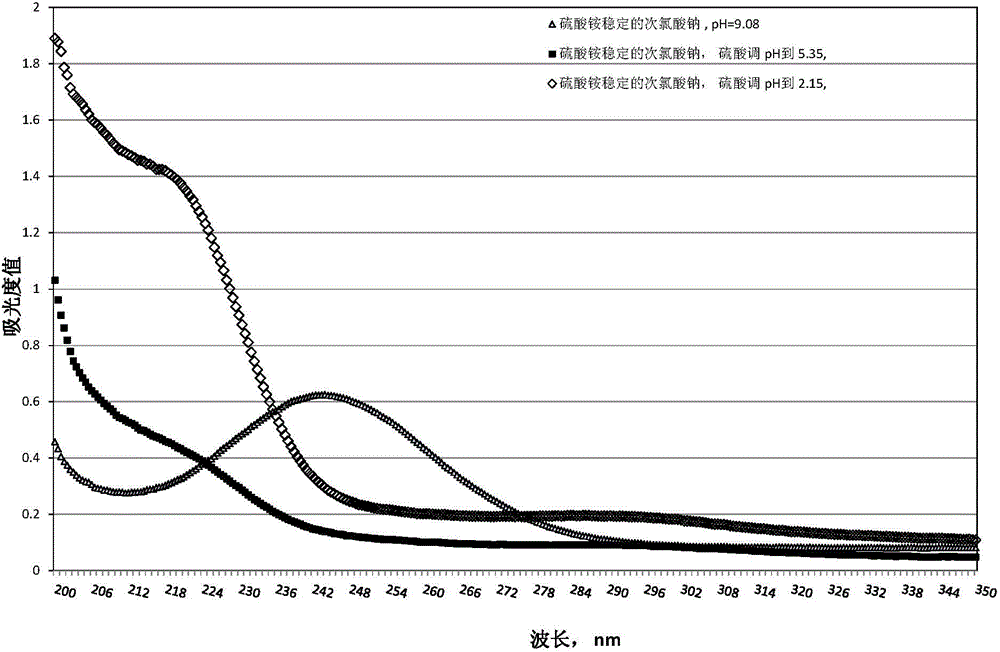
The present invention enables slime control by adding an optimal oxidant in a paper pulp manufacturing process for which the stock material is used paper, which includes a considerable amount of reducing substances and dissolved organic matter, thus preventing decomposition of inorganic chlorine bactericide and exerting high bactericidal efficacy with less of the inorganic bactericide added. An inorganic bactericide generated from hypochlorous acid (salt) and ammonium salt and chlorous acid (salt) are added to an aqueous system for a paper pulp manufacturing process for which the stock material is used paper. The inorganic bactericide generated from hypochlorous acid (salt) and ammonium salt is added after the chlorous acid (salt) has been added. Alternatively, the chlorous acid (salt) is added further upstream in the manufacturing process than the addition of the inorganic bactericide generated from hypochlorous acid (salt) and ammonium salt.
Owner:KURITA WATER INDUSTRIES LTD
Method for monitoring the presence of biofilmforming microorganisms in paper industry
InactiveUS7829305B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismCardboard
The invention is directed to a method for detecting the presence of biofilm-forming microorganisms in a paper or board making process for determining the need of an anti-biofilm agent in the process. The method comprises the steps: (a) subjecting a sampler device in the process line for a period of time to enable said microorganisms to form a biofilm in situ in said process on the surface of the sampler, (b) optionally treating said formed biofilm in a solution of a test anti-biofilm agent for a period of time, then (c) contacting said biofilm with a liquid growth medium in a recession of a culturing device for a period of time, and (d) removing the growth solution from the recession of said device and detecting qualitatively and / or quantitatively the presence or absence of a biofilm adhered on the walls of the recession. An assembly kit is also provided.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Process for producing ketone-free transferring card paper
ActiveCN103866646AHigh viscosityEfficient removalDefoamers additionSpecial paperWater basedOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a process for producing ketone-free transferring card paper. According to the process, an aqueous coating with a ketone removing function is utilized and is fed by a feeding system; then processes of coating by an anilox roller, drying by a drying system and the like are carried out to prepare the ketone-free transferring card paper. The process is simple and can utilize a water-based coating to coat the card paper, so that the problems of personal safety, environmental pollution and high cost, caused by an organic solvent type coating used in the prior art are effectively solved; the obtained ketone-free transferring card paper has a uniform coating and has no remains of butanone.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO HUNAN INDAL CORP +1
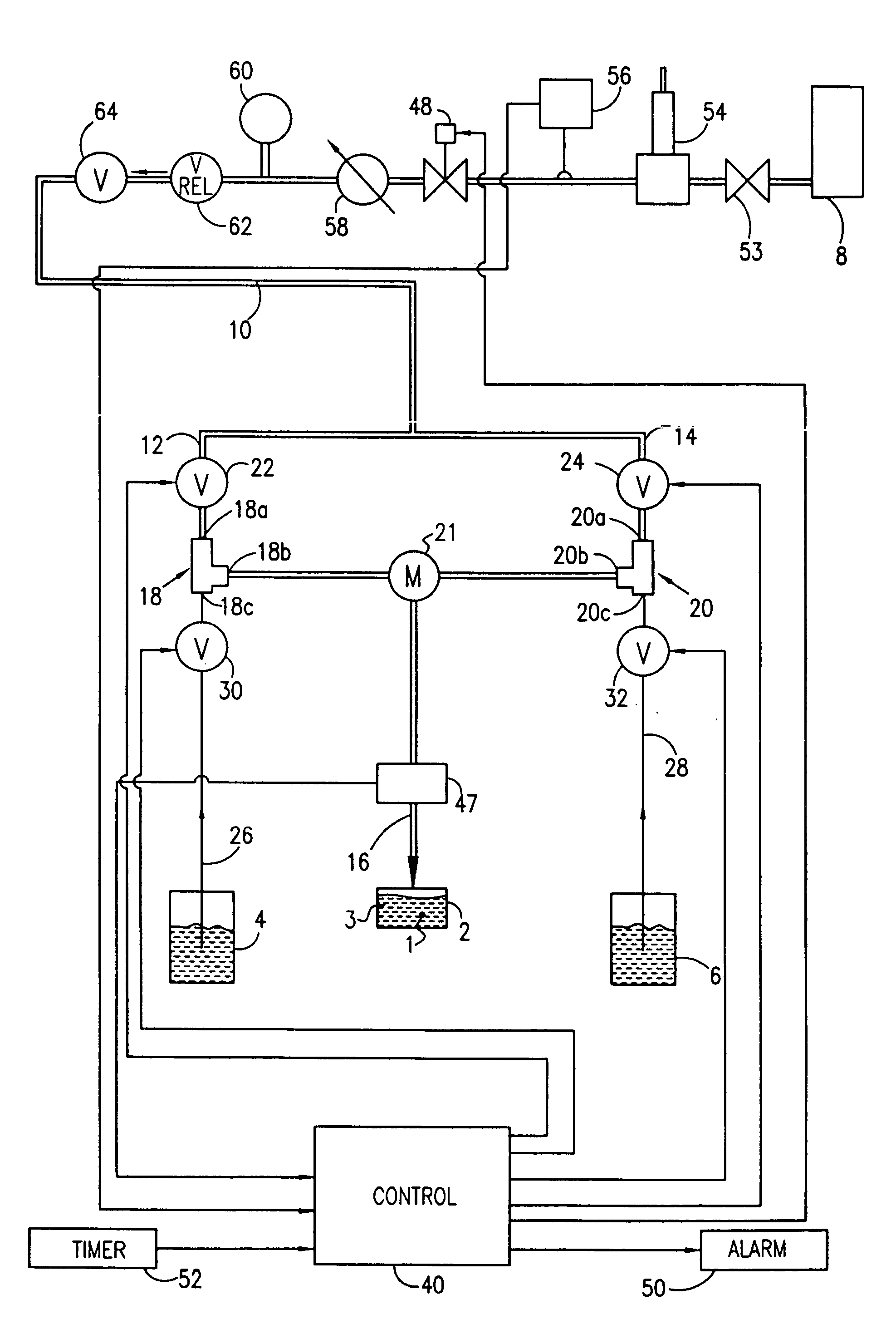
Device and method for monitoring biocide dosing in a machine
ActiveUS20150000853A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringVapor phase
Embodiments of the present disclosure include methods to control the quantity of vapor phase corrosion, devices, and the like.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com