Medicine carrying injectable implanted in-situ hydrogel
A hydrogel, in situ technology, used in anti-tumor drugs, drug combinations, drug delivery, etc., can solve the problems of slow speed and low gelation speed, and achieve increased residence time, less physical trauma, and tumor prevention. effect of recurrence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1. Isoniazid injectable implantation in situ hydrogel
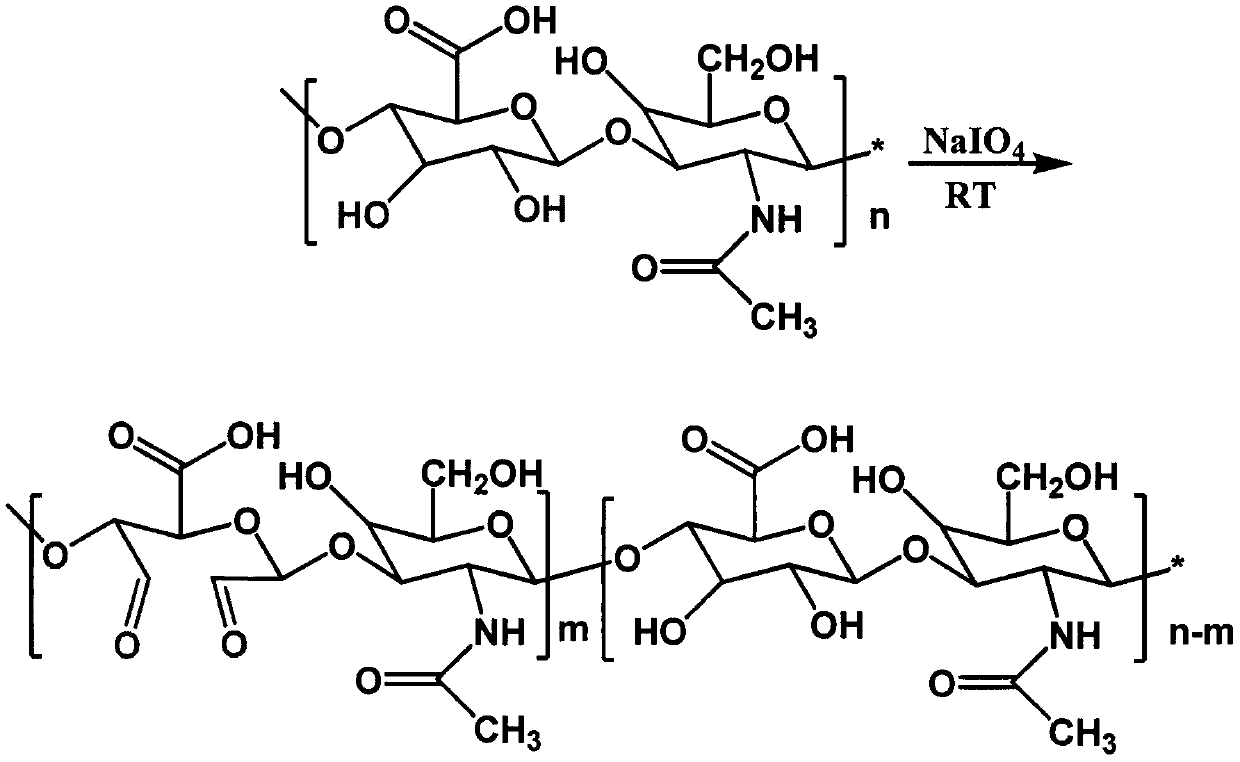
[0036] Dissolve 1 g of sodium hyaluronate with a molecular weight of 500 kDa in 100 mL of water, add an equimolar amount of sodium periodate, keep away from light, stir at room temperature for 2 h, then add 1 mL of ethylene glycol, continue stirring for 1 h, and dialyze the reaction solution with water for 3 h. Day, after freeze-drying to obtain aldylated hyaluronic acid, dissolved in phosphate buffer to obtain 20mg / mL aldylated hyaluronic acid, added 1g of isoniazid, stirred evenly as the aldylated precursor material, an equal volume of 20mg / mL carboxymethyl chitosan solution was used as the amination precursor material. After the two precursor materials were mixed, they were quickly injected into the cavity of the body to obtain isoniazid injectable implantable in situ hydrogel.
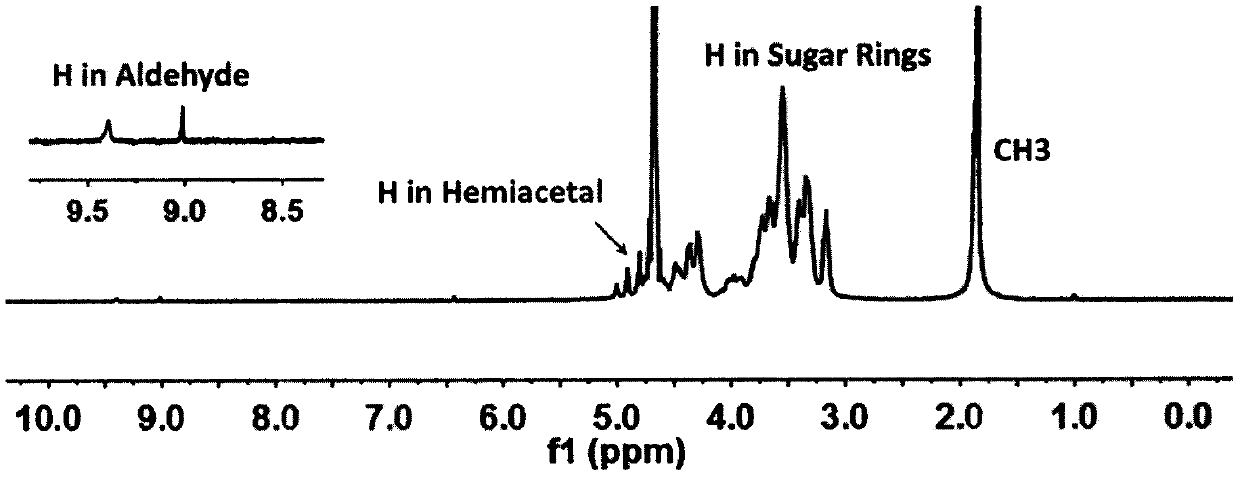
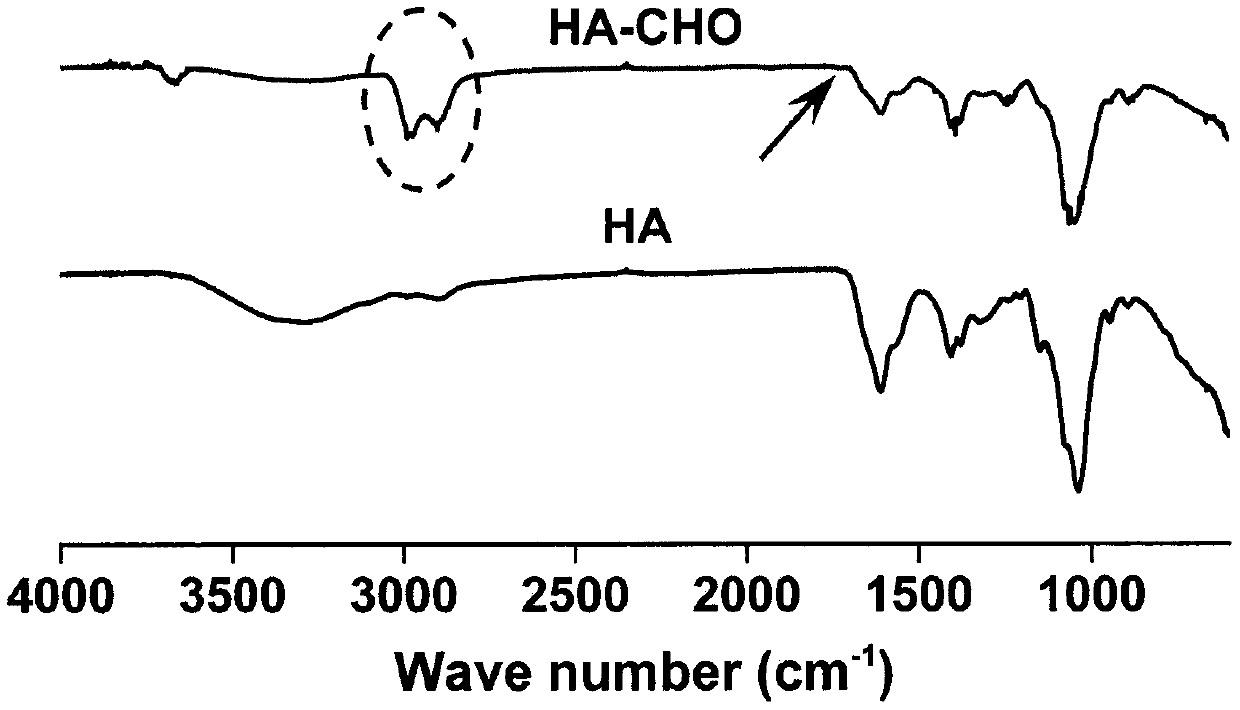
[0037] figure 1 is the synthetic route map of aldylated hyaluronic acid, figure 2 It is the H NMR spectrum of aldylated hy...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2, moxifloxacin injectable implantation in situ hydrogel
[0039] Using EDC / NHS catalysis, one end of adipic acid dihydrazide and hyaluronic acid are connected through an amide bond, purified by dialysis and freeze-dried to obtain aminated hyaluronic acid as an aminated precursor material, which is prepared by sodium periodate oxidation method Aldehydated hyaluronic acid was obtained as the aldhylated precursor material, and the phosphate buffer solution of the above-mentioned concentration of 20 mg / mL aldylated hyaluronic acid and aminated hyaluronic acid was mixed in equal volumes, and moxifloxacin was added , to obtain a mixed solution containing 10 mg / mL moxifloxacin, and quickly inject it into the cavity of the body to obtain an injectable implantable in situ hydrogel of moxifloxacin.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3, Paclitaxel injectable implantation in situ hydrogel
[0041] Prepare aldylated sodium alginate by sodium periodate oxidation method as the aldylated precursor material, lyophilize after dialysis purification, add phosphate buffer to prepare a 30mg / mL alginated sodium alginate solution, add paclitaxel and stir Uniformly, the alginate sodium alginate solution containing 10mg / mL paclitaxel is obtained, and an equal volume of 20mg / mL carboxyethyl chitosan phosphate buffer solution is injected into the body cavity simultaneously with two syringes to obtain paclitaxel. Injection implanted in situ hydrogel.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com