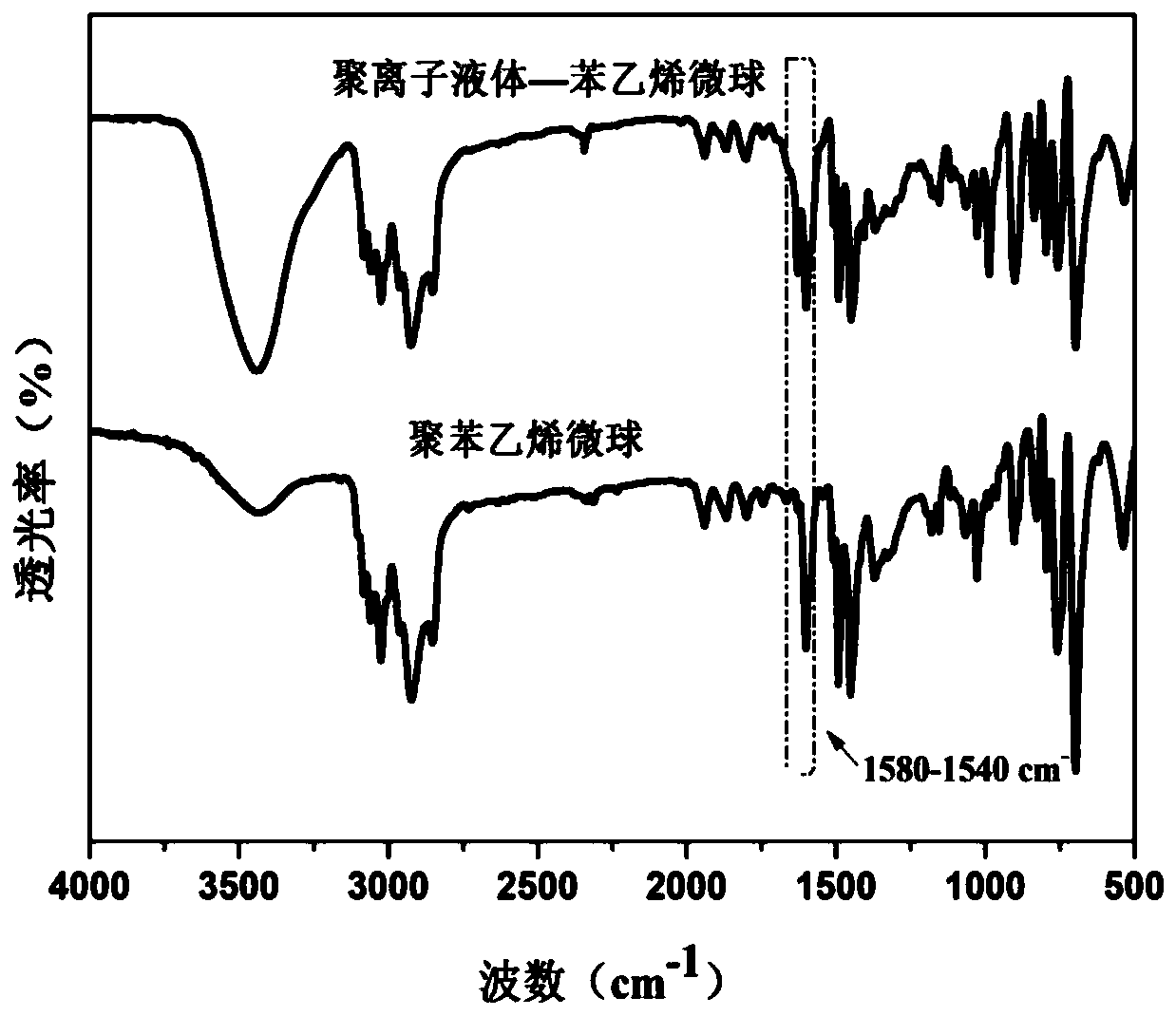
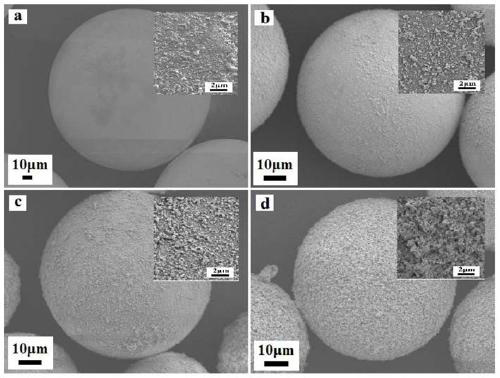
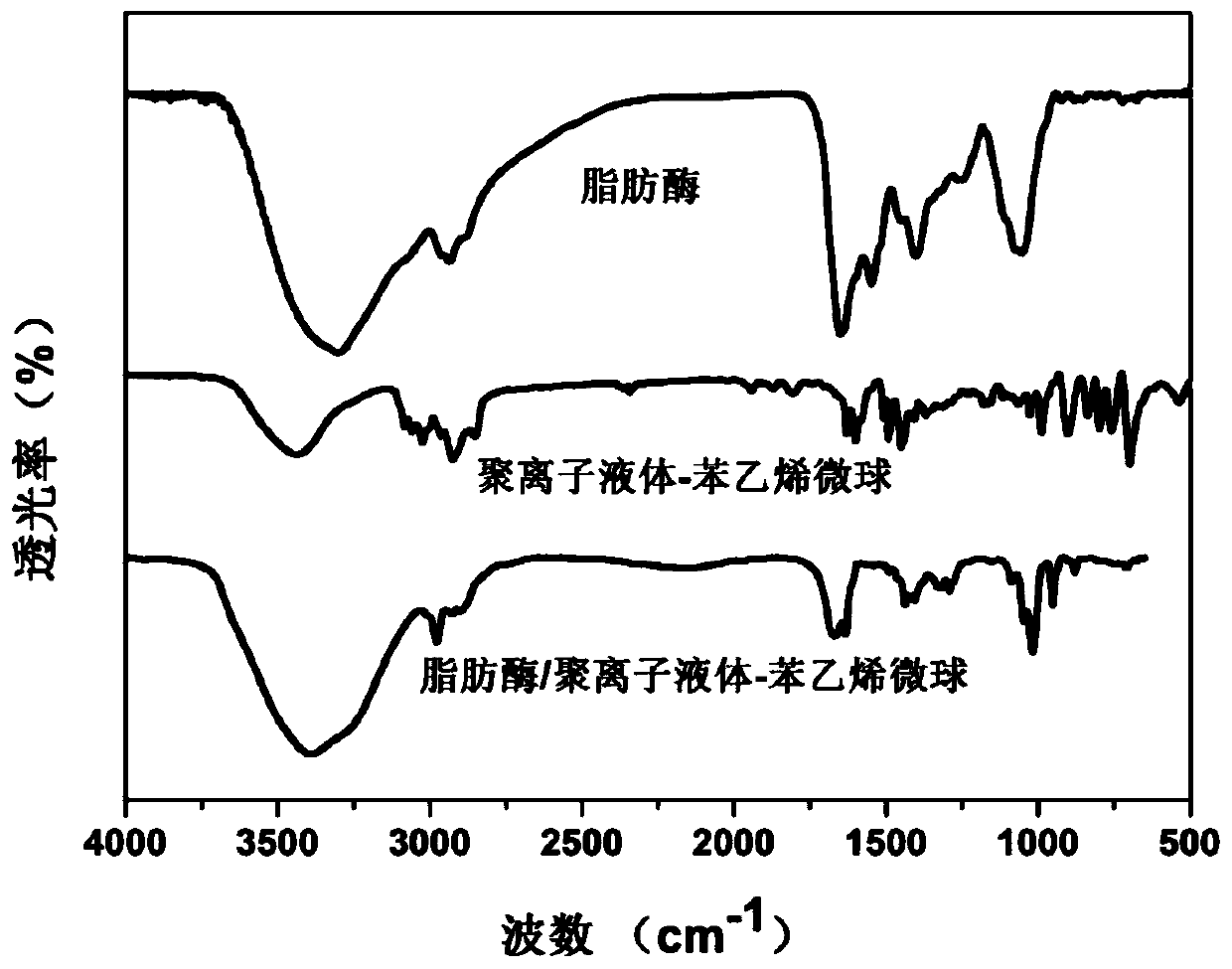
Lipase/polyion liquid-styrene microsphere/hydrogel catalytic material as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of styrene microspheres and polyionic liquids, applied in the direction of microsphere preparation, biochemical equipment and methods, microcapsule preparations, etc., can solve problems such as weak force, destruction of enzyme conformation, difficult substrate contact, etc., to prevent Falling off, not easy to fall off, easy to separate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] (1) Weigh 2.4g of PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) and 2.4g of sodium chloride into 80mL of pure water, and mechanically stir at 95°C until dissolved to obtain the water phase;
[0054] (2) Styrene (5.208g), divinylbenzene (3.256g), toluene (4.608g), and initiator azobisisobutyronitrile (0.2g, 3.0wt%) were mixed and purged with nitrogen for 20min , remove the oxygen in the solution to obtain the mixed solution as the organic phase;
[0055] (3) The organic phase was added to the water phase, and the reactor was vigorously stirred for 1 h to prepare an oil-in-water suspension, and suspension polymerization was carried out at 70° C. for 6 h, and the mechanical stirring rate was kept constant at 650 rpm;
[0056] (4) After the polymerization reaction is finished, first use ethanol, then thoroughly wash with hot water, remove unreacted monomers, and obtain polystyrene microspheres;
[0057] (5) Weigh 0.5g polystyrene microspheres in 5mL lipase fermentation broth, then put them on a...
Embodiment 2
[0060] (1) Weigh 2.4g of PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) and 2.4g of sodium chloride into 80mL of pure water, and mechanically stir at 95°C until dissolved to obtain the water phase;
[0061] (2) styrene (5.208g), divinylbenzene (3.256g), toluene (4.608g), 1-vinyl-3-butylimidazolium bromide (1.450g) and initiator azobisisobutyl Nitrile (0.436g, 3.0wt%) mixed, and purged with nitrogen for 20min, removed the oxygen in the solution, and obtained the mixed solution as the organic phase;
[0062] (3) The organic phase was added to the water phase, and the reactor was vigorously stirred for 1 h to prepare an oil-in-water suspension, and suspension polymerization was carried out at 70° C. for 6 h, and the mechanical stirring rate was kept constant at 650 rpm;
[0063] (4) After the polymerization reaction finishes, first use ethanol, then thoroughly wash with hot water, to remove unreacted monomers, obtain polyionic liquid-styrene microspheres;
[0064] (5) Weigh 0.5g polyionic liquid-styre...
Embodiment 3
[0067] (1) Weigh 2.4g of PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) and 2.4g of sodium chloride into 80mL of pure water, and mechanically stir at 95°C until dissolved to obtain the water phase;
[0068] (2) styrene (5.208g), divinylbenzene (3.256g), toluene (4.608g), 1-vinyl-3-butyl imidazolium bromide (2.890g) and initiator azobisisobutyl Nitrile (0.479g, 3.0wt%) was mixed, and purged with nitrogen for 20min, removed the oxygen in the solution, and obtained the mixed solution as the organic phase;
[0069] (3) The organic phase was added to the water phase, and the reactor was vigorously stirred for 1 h to prepare an oil-in-water suspension, and suspension polymerization was carried out at 70° C. for 6 h, and the mechanical stirring rate was kept constant at 650 rpm;
[0070] (4) After the polymerization reaction finishes, first use ethanol, then thoroughly wash with hot water, to remove unreacted monomers, obtain polyionic liquid-styrene microspheres;
[0071] (5) Weigh 0.5g polyionic liquid-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com