Novel F-doped g-carbon nitride photocatalytic material prepared by microwave method and application of material
A technology of photocatalytic materials and microwave method, which is applied in the field of analytical chemistry to achieve the effect of improving photocatalytic performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0096] 1) Novel microwave etching of F-doped g-C 3 N 4 Preparation of photocatalytic materials
[0097] Weigh 10-15 g of precursor urea powder and pour it into an alumina crucible with a cover, and place it in a muffle furnace after the overall sealing is completed, then set the heating rate at 10 °C / min to heat to 550 °C, and Keep at this temperature for 3 h. After the firing is complete, take out the reactant, put it into a mortar and grind it into powder after fully cooling, without obvious particles, and obtain the bulk g-C 3 N 4 sample.
[0098] 2) Using 0.1 mol / L hydrofluoric acid solution, the prepared bulk g-C 3 N 4 Perform microwave etching:
[0099] ① In the preparation process, start the microwave digestion instrument, check the smoothness of the pipeline and open the fume hood;
[0100] ②Sample loading: Use an analytical balance to accurately weigh 1 g of carbon nitride powder, then use a pipette gun to measure 15 ml of hydrofluoric acid with a concentratio...
Embodiment 2
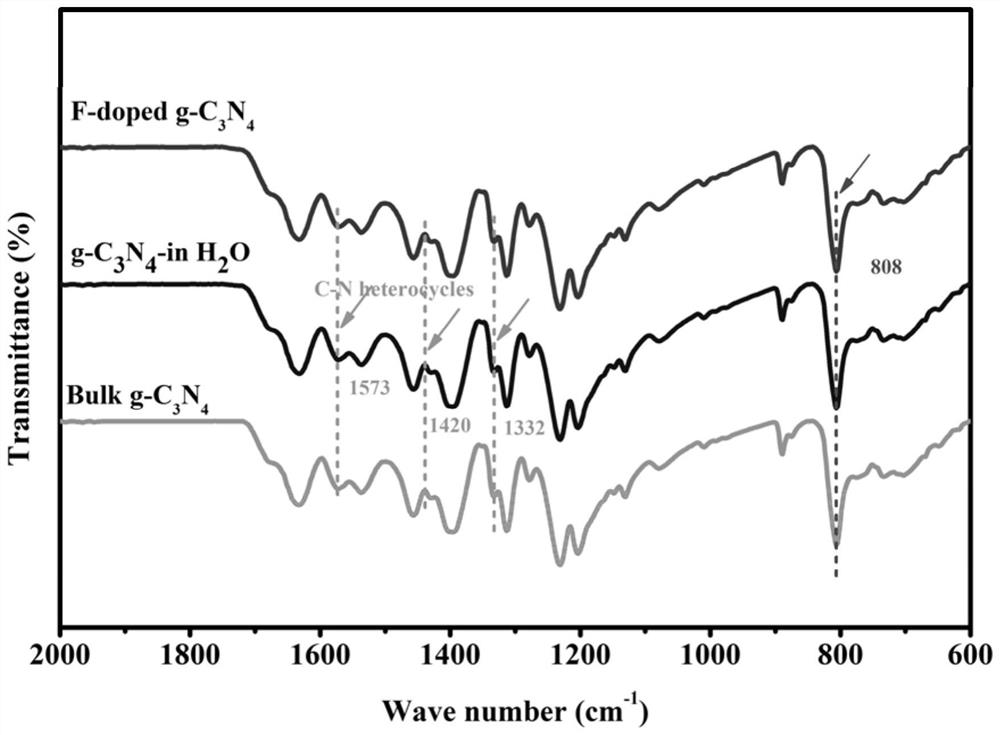
[0109] to combine figure 2 Fourier transform infrared spectrum shows that, 2800 to 3400 cm -1 The broad absorption peak of is due to the N–H stretching mode and the surface-adsorbed H 2 Due to O. at 1200 to 1700 cm -1 A series of peaks in the range correspond to the typical C–N stretching mode of C–N heterocycles. at 808 cm -1 The sharp peak at is attributed to the ring-shaped breathing vibration mode characteristic of the conjugated heptazine heterocycle. No obvious changes were observed in the FTIR of the three samples, only a slight decrease in the intensity of the FT-IR bands, proving that after the introduction of F atoms, the overall g-C 3 N 4 The structural integrity remains unchanged. Furthermore, F-doped g-C 3 N 4 (-4.063 mV) and bulk g-C 3 N 4 (-3.29mV) exhibited a negative zeta potential, indicating that g-C 3 N 4 There is a net positive surface charge on the structure. The small change in zeta potential proves that corrosion and exfoliation occurred ...
Embodiment 3
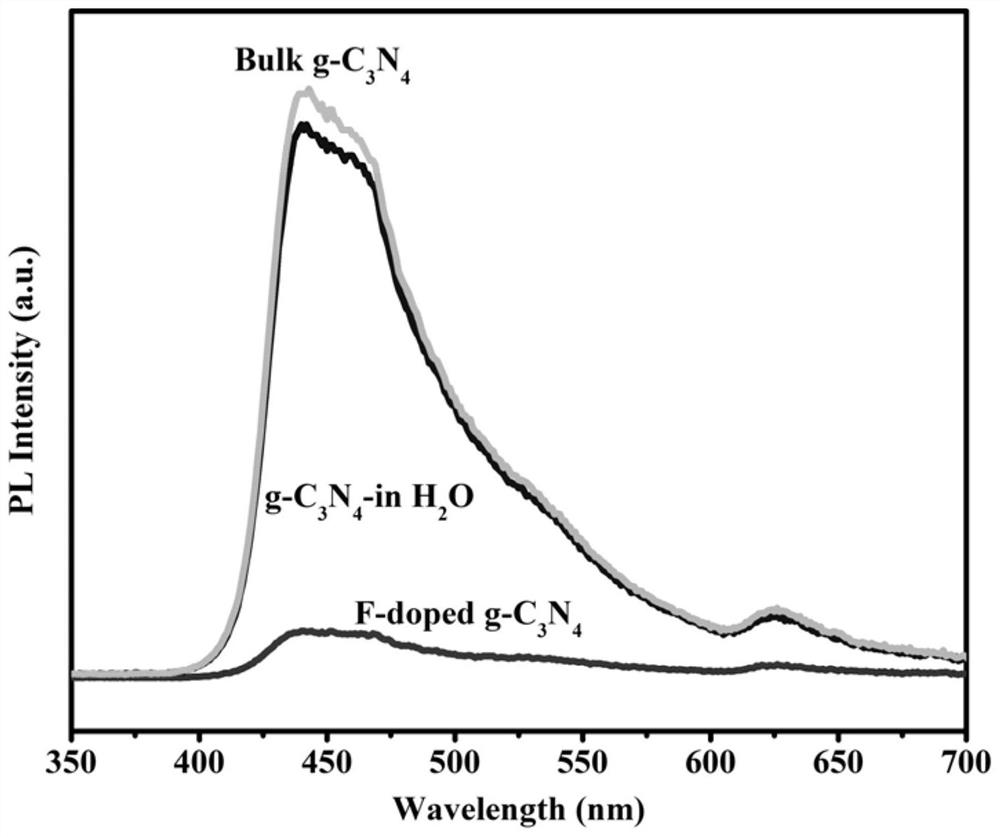
[0111] Preparation of F doped g-C by hydrofluoric acid 3 N 4 , Ontology g-C 3 N 4 and water digestion g-C 3 N 4 The fluorescence spectrum, such as image 3 As shown, the samples all exhibited a broad emission peak centered at about 450 nm with a tail extending to 700 nm. with body g-C 3 N 4 and water digestion g-C 3 N 4Compared to the F-doped g-C 3 N 4 Has a weaker emission peak, exhibits significant fluorescence quenching behavior, and highly inhibits the recombination of carriers due to the enhanced migration of electron-hole pairs, indicating the photocatalytic activity of the material after hydrofluoric acid microwave etching Significant improvement.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com