Method for extracting, separating and recycling tungsten carbide and cobalt in waste hard alloy by melt
A technology of separation and recovery of cemented carbide, which is applied in the direction of carbides, tungsten/molybdenum carbides, and reduction of gas emissions. It can solve the problems of low-grade recycled alloys, high iron and oxygen content, and easy to cause fouling, etc., to achieve The scale can be large or small, the cobalt recovery rate is high, and the effect of wide application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
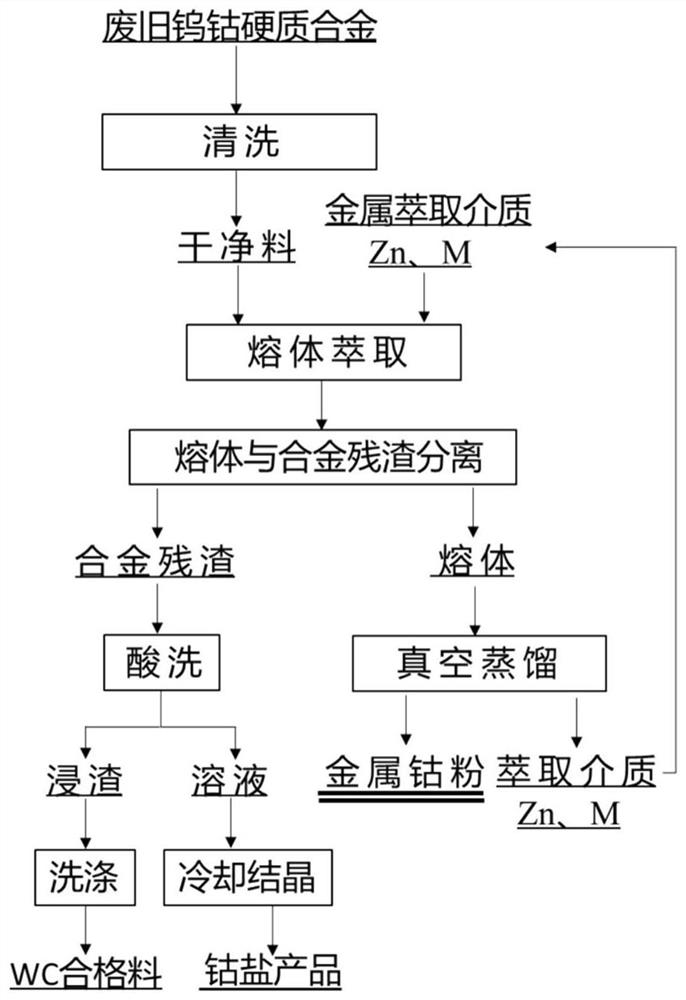
[0043] In this embodiment, the recovery process for extracting cobalt from the waste tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide with a Co content of 5% comprises the following steps:
[0044] (1) Clean the waste tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide material with tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide cleaning agent solution and clear water, dry to obtain clean tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide material, take 900.0g of clean tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide material after cleaning, extract medium Zn -Mg binary alloy 2700.0g, the mole percentages of Zn and Mg in the Mg-Zn binary alloy are 50% and 50% respectively. The clean tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide is placed in a porous and liftable titanium mesh, the extraction medium is placed in a graphite crucible, and then the graphite crucible and the titanium mesh are placed together in a well-type resistance vacuum furnace, and argon gas is introduced into the furnace. The flow rate is 100mL / min, start the heating system, raise the temperature to 900...
Embodiment 2
[0048] In this embodiment, the process of separating and recovering tungsten carbide and metal cobalt from waste tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide with a Co content of 10% comprises the following steps:
[0049] (1) Clean the waste tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide material with tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide cleaning agent solution and clear water, and dry to obtain a clean tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide material. Take 1000.0 g of the cleaned tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide material, extract medium Zn - 5000.0 g of Pb binary alloy, and the molar percentages of Zn and Pb in the Zn-Pb binary alloy are 70% and 30% respectively. The clean tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide is placed in a porous and liftable titanium mesh, the extraction medium is placed in a quartz crucible, and then the quartz crucible and the titanium mesh are placed together in a well-type resistance vacuum furnace, and hexafluoride is introduced into the furnace Sulfur gas, with a flow rate of 150mL / min, sta...
Embodiment 3
[0053] The present embodiment is the recovery process that extracts cobalt from the waste tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide that the content of Co is 15%, comprises the following steps:
[0054] (1) Clean the waste tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide material with tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide cleaning agent solution and clear water, dry to obtain clean tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide material, take 900.0g of clean tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide material after cleaning, extract medium Zn -Sn alloy 7200.0g, the molar percentages of Zn and Sn in the Zn-Sn alloy are 60% and 40% respectively, the clean tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide is placed in a porous and liftable titanium mesh, and the extraction medium is placed in a magnesium oxide crucible Then put the magnesia crucible and titanium mesh together into the well-type resistance vacuum furnace, and argon gas was introduced into the furnace at a flow rate of 150mL / min. The heating system was started and the temperature was r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com