Exosome detection and typing micro-fluidic chip and exosome detection and typing method
A microfluidic chip and exosome technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, measurement devices, analytical materials, etc., can solve the problems of low separation efficiency, limited speed and diversity, and long time consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
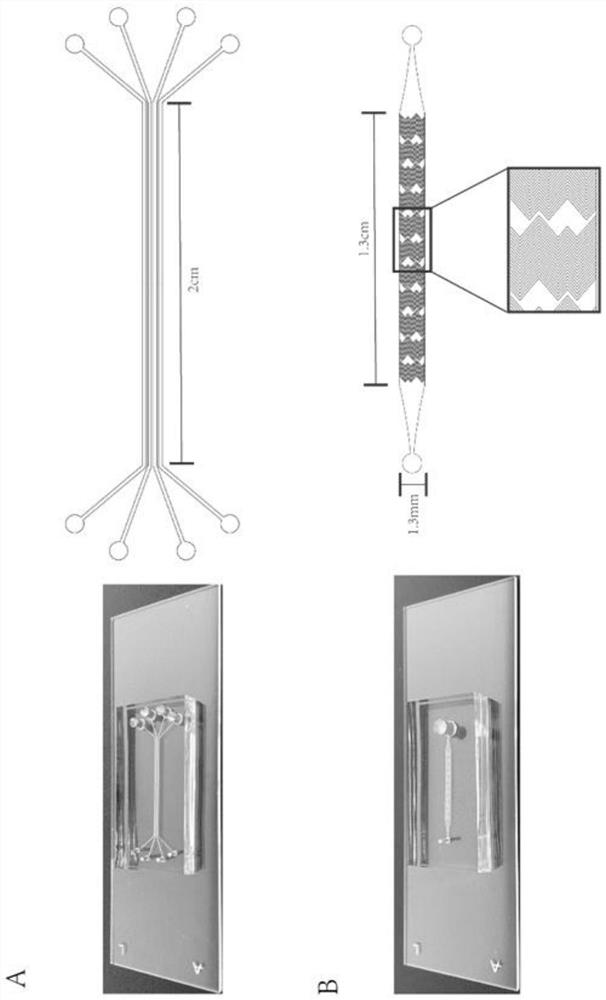
[0037] Embodiment 1 Microfluidic Chip Fabrication Method
[0038] 1. Fabrication of antibody strip chip
[0039] 1. Fabrication of PDMS chips
[0040] (1) Use CAD software to draw the graphics of the chip, use a high-resolution laser phototypesetter to draw a photolithography mask on the photographic film, and then spin-coat the SU-8 photoresist layer on the silicon wafer, and perform high-temperature curing treatment on it After covering with a photolithography mask, expose the cured SU-8 photoresist on a photolithography machine, and finally develop it in a developer to obtain a positive silicon wafer template.
[0041] (2) PDMS prepolymer and PDMS curing agent are mixed at a ratio of 10:1, and poured on the prepared positive mold template after pumping in a vacuum, and peeled off after high temperature curing to obtain a chip with a microstructure, as required Punch holes (antibody perfusion holes, antibody outflow holes).
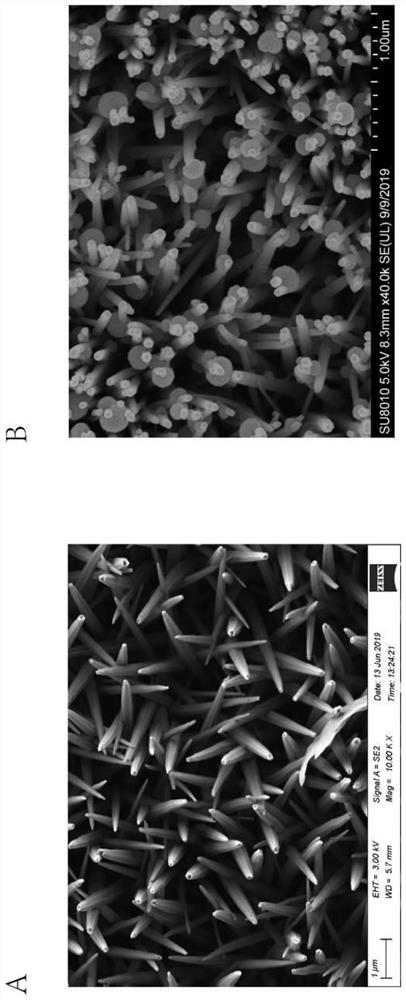
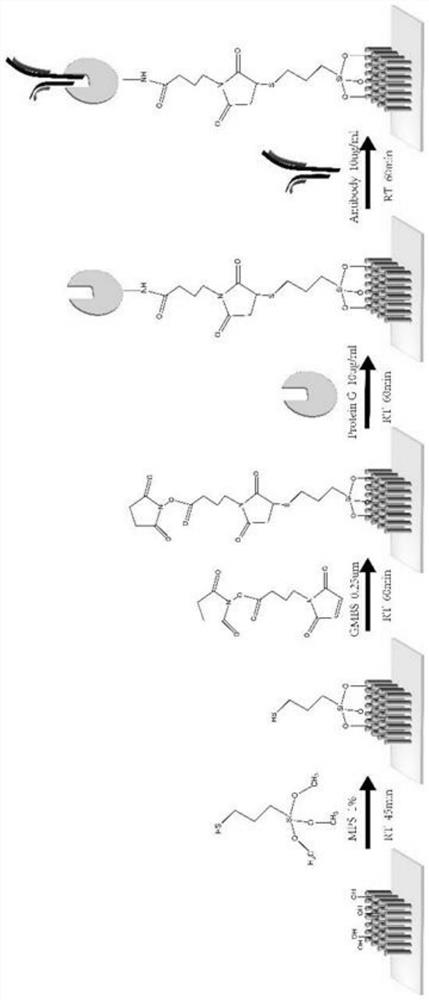
[0042] 2. Preparation of ZnO seed layer on gla...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Example 2 Application of microfluidic chip for detection and typing of exosomes
[0081] 1. Sample injection
[0082] Take 50 μl of HOS cell-derived exosome suspension, add it into the injection hole, the syringe pump draws the sample at a speed of 2 μL / min, and collect the outflowing waste liquid at the sample outlet.
[0083] 2. Rinse the channel with PBS.
[0084] 3. Fluorescent dye perfusion:
[0085] DiO dye is a lipophilic membrane dye. The membrane of exosomes is the same as the cell membrane, which is a phospholipid bilayer, so DiO dye can quickly bind to the membrane surface of exosomes, making the exosomes emit green fluorescence, so that Observe under a fluorescence microscope.
[0086] DiO preparation: Weigh 0.001 g of DiO powder with an analytical balance, dissolve it in 226 μl of DMSO, and prepare a 5 mM DiO stock solution, and store the stock solution in a -20 degree refrigerator. Take 1 μl of DiO dye stock solution in an EP tube, add 99 μl of PBS to ...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Example 3 Optimization of Microfluidic Chip Structure and Detection Conditions
[0092] Some parameters of the structure and detection conditions of the microfluidic chip were changed, and the remaining parameters were the same as in Examples 1 and 2, so as to compare the exosome capture efficiency under different structures and detection conditions.
[0093] 1. Chip injection flow rate screening
[0094] 1. Zinc oxide chip preparation.
[0095] 2. Zinc oxide surface modified CD63+CD81 antibody.
[0096] 3. Put 6 zinc oxide chips prepared and modified above CD63+CD81 on the table, add 50 μl of HOS cell line exosome suspension respectively, turn on the syringe pump and inject 0, 1, 2, 4 , 8, 10μl / min speed to draw samples.
[0097] 4. After the above process, wash the channel with PBS 3 times.
[0098] 5. Add 50 μM DiO solution and incubate at room temperature for 50 min.
[0099] 6. Rinse with PBS 3 times.
[0100] 7. Observe under a fluorescence microscope and co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com