A strain of Rhodotorula biobversus producing carotenoids and its application
A carotenoid and red yeast technology, applied in the field of marine microorganisms, can solve the problems of low content, high cost, complex carotenoid extraction process, etc., and achieve the effects of low nutritional requirements, high safety, and easy control of fermentation conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Example 1: Screening of marine rhodotorula producing carotenoids
[0015] 1. Preparation of culture medium
[0016] 1) The selection medium for Rhodotorula marinae is WL nutrient agar medium: 5g / L yeast powder, 5g / L peptone, 50g / L glucose, 0.55g / L potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.425g / L potassium chloride, 0.125g / L calcium chloride, 0.125g / L magnesium sulfate, 0.0025g / L ferric chloride, 0.0025g / L manganese sulfate, 0.022g / L bromocresol green, 20g / L agar powder, 0.1g / L chloramphenicol , pH6.5. The above-mentioned culture medium was prepared with old sea water, and after autoclaving at 115°C for 20 minutes, it was poured into a plate for later use, and bromocresol green and chloramphenicol were added separately when the sterilization medium was cooled to 65°C.
[0017] 2) Carotenoid-producing screening medium: 20g / L glucose, 2g / L ammonium sulfate, 1g / L potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.5g / L magnesium sulfate, 1g / L calcium chloride, 5g / L yeast powder, Prepared with ol...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Embodiment 2: the genus identification of marine rhodotorula ZQ38
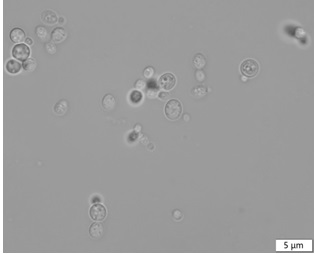
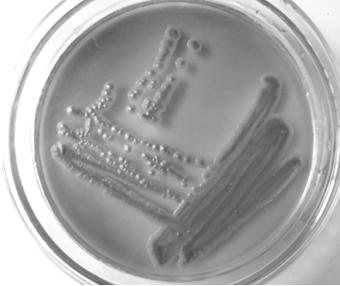
[0025] Morphological features: such as figure 1 As shown, the colonies of Rhodotorula marina ZQ38 grown on WL nutrient agar medium are medium-sized, round or oval, with smooth and moist surface, raised in the middle, neat edges of colonies, and uniform color, showing brick red; figure 2 As shown, the morphology of the bacterial cells observed under a microscope is round or oval, and it is polygonal budding.
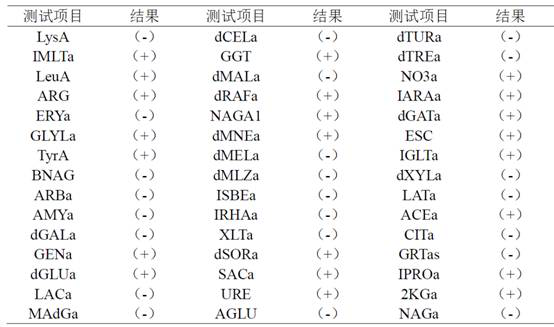
[0026] Physiological and biochemical identification was carried out by an automatic microbial analyzer. The results of the test and identification are shown in Table 2. It was in line with the physiological and biochemical characteristics of Rhodotorula, and it was preliminarily determined to be Rhodotorula double obovata.
[0027] Table 2 Physiological and biochemical identification results of Rhodotorula marinum ZQ38
[0028]
[0029] Sequence analysis of the 26S rDNA D1 / D2 region of Rhodo...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3: Production of carotenoids by fermentation of Rhodotorula biobversus ZQ38
[0033] 1) Activation of strains: Pick one ring of Rhodotorula biobovata ZQ38 strains preserved on the slope, inoculate into a 50mL / 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, and activate and cultivate at 28°C and 200r / min for 48h. Activation medium used: 20g / L glucose, 20g / L peptone, 10g / L yeast powder, prepared with aged sea water, natural pH, sterilized at 115°C for 20min.
[0034] 2) Fermentation to produce carotenoids
[0035] Using optimal fermentation medium 1: 15g / L sucrose, 2g / L ammonium sulfate, 1g / L potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.5g / L magnesium sulfate, 1g / L calcium chloride, 5g / L yeast powder, and aged seawater. The pH is natural, the filling volume is 100mL / 500mL, and it is sterilized at 121°C for 20min. Inoculate the activated strain with 6% (v / v) inoculum, ferment and cultivate for 3 days in a constant temperature shaker with a culture temperature of 28°C and a rotation speed of 200r / m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com