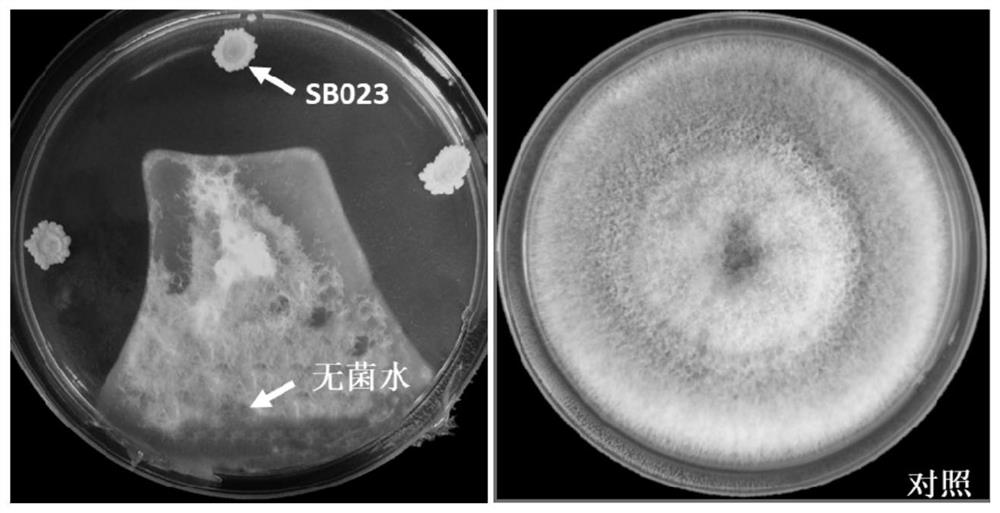
Gentiana rhodantha endophytic bacillus velezensis strain and application thereof
A technology of bacillus and safflower gentian, which can be applied in application, bacteria, biocide and other directions, can solve problems such as threats to human health, environmental pollution, and difficulty in prevention and control.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1, Isolation and identification of Gentiana safflower endophytic Bacillus Velez SB023 strain
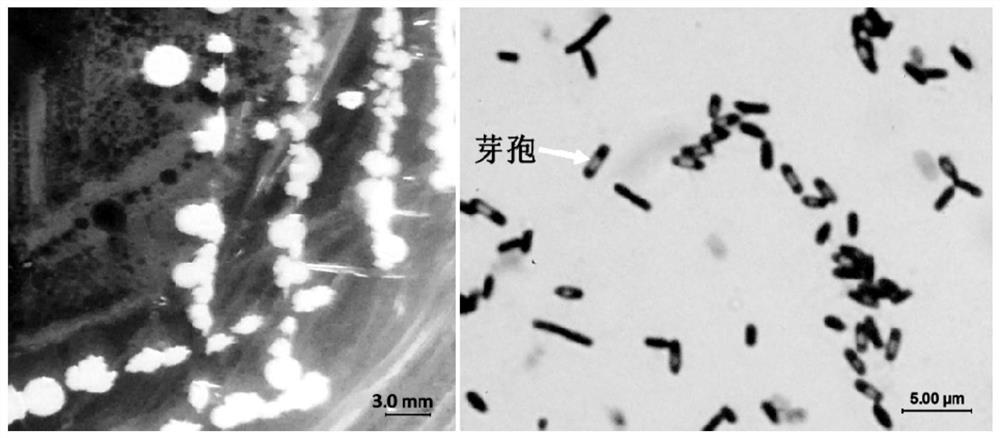
[0031] Bacillus Velez SB023 was obtained by separating from healthy stalks of G. rhodantha by tissue block separation method and purified by plate streaking method; the morphological characteristics of Bacillus Velez SB023 are as follows: Bacillus Velez Bacillus SB023 can grow on NB medium and PDA medium, and the colony morphology of cultured at 32°C for 48 hours is as follows: figure 1 shown. The colony on NB medium is small, 0.5-2mm, transparent to white, with moist surface, wrinkled, and irregular edges; it grows rapidly on PDA plate, 3-12mm, fried egg-like, surface wrinkled and raised, and edges are irregular tidy. Observed by staining, the strain is long rod-shaped, with a size of 0.46-0.63×1.4-3.3μm ( n=30), Gram-positive, endo-spore, peri-flagellate.
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2, the physiological and biochemical characteristics of Bacillus Velez SB023
[0033] According to the method provided by "Bergey's Bacteria Identification Manual", different culture media were prepared for physiological and biochemical identification of the SB023 strain. The identification results are shown in Table 1. According to conventional physiological and biochemical indicators, it is a close species of Bacillus subtilis. The bacterial strain was positive for lecithin hydrolysis, and the "Common Bacterial System Identification Manual" (Dong Xiuzhu, Cai Miaoying. Common Bacterial System Identification Manual [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001) reported the reconciliation of Bacillus subtilis (B.subtilis) B. amyloliquefaciens cannot hydrolyze lecithin, so the strain SB023 was initially identified as B. velezensis.
[0034] Table 1. Physiological and biochemical characteristics of B. velezensis SB023 strain
[0035]
[0036]
[0037] Note: + means...
Embodiment 3
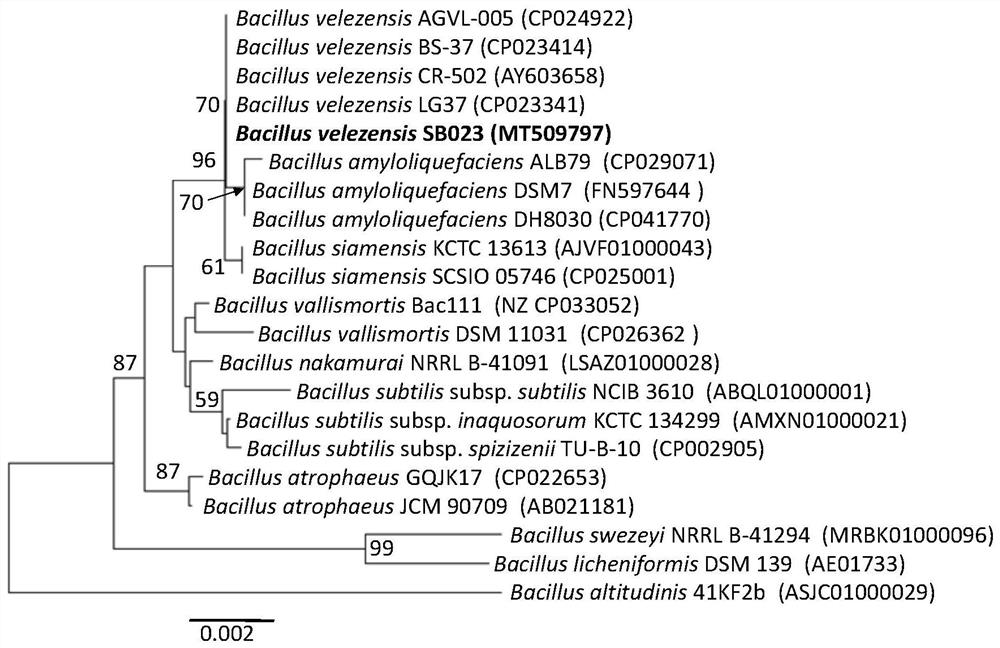
[0038] Embodiment 3, Bacillus Velez SB023 molecular biology identification
[0039] Using the DNA of Bacillus Velez SB023 as a template, PCR amplification was carried out using bacterial 16S universal primers, and the amplification primers were:
[0040] 27F: 5'-caggcctaacacatgcaagtc-3 (SEQ ID NO.1);
[0041] 1492R: 5'-gggcggwgtgtacaaggc-3 (SEQ ID NO. 2);
[0042] The PCR reaction system is 20 μL, 2×PCR Mix 10 μL, upstream and downstream primers 0.5 μL, template DNA 1 μL, ddH 2 O8μL; PCR reaction conditions: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5min; denaturation at 95°C for 30s, annealing at 55°C for 30s, extension at 72°C for 90s, 30 cycles; extension at 72°C for 7min. The PCR products were detected by agarose gel electrophoresis and sent to Beijing Qingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for purification and sequencing. The resulting DNA sequence has been submitted to GenBank, accession number: MT509797.
[0043]The sequence was input into BLAST in GenBank for homology comparison. After...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com