Melittin and flexible polyethylene glycol based antibacterial drug
An antibacterial drug, polyethylene glycol technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of reducing clearance or plasma protein adsorption, weakening the biological activity of modified molecules, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Embodiment 1: antibacterial effect and cytotoxicity test: PEG 12K Preparation of -1*Mel Complex and Improvement of Antibacterial Properties
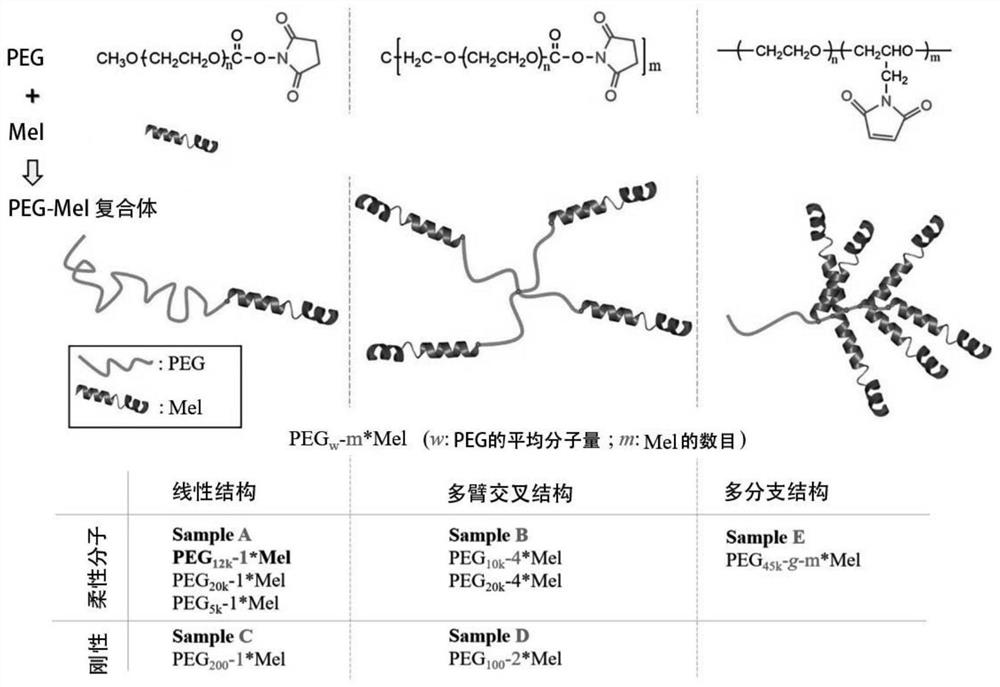
[0054] We pre-designed PEG molecules with different structures and molecular weights, which have active sites that can interact with amino groups of polypeptides (such as unnatural organic group maleimide). The active site of Mel and PEG is chemically coupled to obtain PEGw-m*Mel complexes with different structures (here, w is the molecular weight of PEG, m is the number of polypeptides in each complex, see figure 1 ). in PEG 12K - 1*Mel as an example, wherein each Mel peptide is end-bonded with a single-chain PEG molecule (average molecular weight 12000). Characterizations such as dynamic light scattering (DLS), UV-Vis absorption spectrum, and SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis all confirmed that PEG molecules were successfully modified on Mel ( figure 2 ).
[0055] We first PEG 12k The -1*Mel complex was applied to li...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2: Mechanism study of enhanced antibacterial activity: PEG 12K Kinetic interactions of -1*Mel complexes with membranes
[0060] Antimicrobial peptide-induced physical permeability (such as perforation) of bacterial membranes is considered to be the main molecular mechanism for the antibacterial ability of AMPs by Mel et al. Our SEM images of the bacteria also showed severe disruption of the bacterial membrane due to drug exposure. To monitor the dynamic interaction between the drug and the cell membrane in real time, we performed a GUV leakage kinetic test. Figure 6 The first image in shows a typical GUV consisting of DOPC labeled with 1 mol% red fluorescent Rh-PE encapsulated with green fluorescent calcein. Calcein is a water-soluble, membrane-impermeable fluorophore and is therefore commonly used to test membrane permeability. Under confocal microscopy, this calcein-encapsulated GUVs showed no calcein leakage for more than 4 hours. Addition of native Mel ...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3: The influence of molecular structure on the bactericidal function of the compound
[0066] From a "biophysical" point of view, structure determines the function of biological macromolecules. As mentioned above, a series of PEG-Mel complexes with different structures were constructed by decorating Mel with PEG. Three complex structures were designed ( figure 1 ), including linear structures (i.e., each Mel end is linked to a single-chain PEG), cross-structures (i.e., two or four Mel molecules conjugated to a two-armed or four-armed PEG), and multi-branched structures (in which multiple polypeptides modified on the PEG backbone). PEGs of different molecular weights are also composed of flexible long chains (M W >=5K) or rigid short chains (Mw<=200).
[0067] Table 1. Comparison of biological activities of natural Mel and PEG-Mel complexes with different molecular structures
[0068]
[0069] PEG W -m*Mel complexes were applied to live cells to test the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com