Heterologous expression method and application of L-lysine decarboxylase from thermophilic bacteria
A technology of lysine decarboxylase and thermophilic bacteria, which is applied in the field of heterologous expression of lysine decarboxylase, and can solve problems such as leaky expression, bacterial toxicity, and influence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Cloning of embodiment 1 lysine decarboxylase gene cadA
[0052] Using primers cadA-SacI-F (SEQ ID No:22) and cadA-XbaI-R (SEQ ID No:23) to encode lysine decarboxylase (SEQ ID No:3) gene cadA (SEQ ID No:4) It was amplified from the genome of Escherichia coli MG1655 K12 (E.coliMG1655 K12, purchased from Beijing Tianenze Biotechnology Co., Ltd.). Bioengineering (Dalian) Co., Ltd.). Using CaCl 2 The competent method was prepared, and the ligated product was transformed into Escherichia coli E.coli BL21 (purchased from Treasure Bioengineering (Dalian) Co., Ltd.) cells by heat shock method, and the ampicillin antibiotic was added to the LB medium for screening, cloning PCR and sequencing After the verification is correct, the plasmid is extracted to obtain the pCIB60 plasmid.
[0053]Using plasmid pCIB60 as a template, primers cadA-F2 (SEQ ID No: 24) and cadA-R2 (SEQ ID No: 25) were further used to optimize the sequence upstream of the initiation codon ATG of the cadA gene...
Embodiment 2
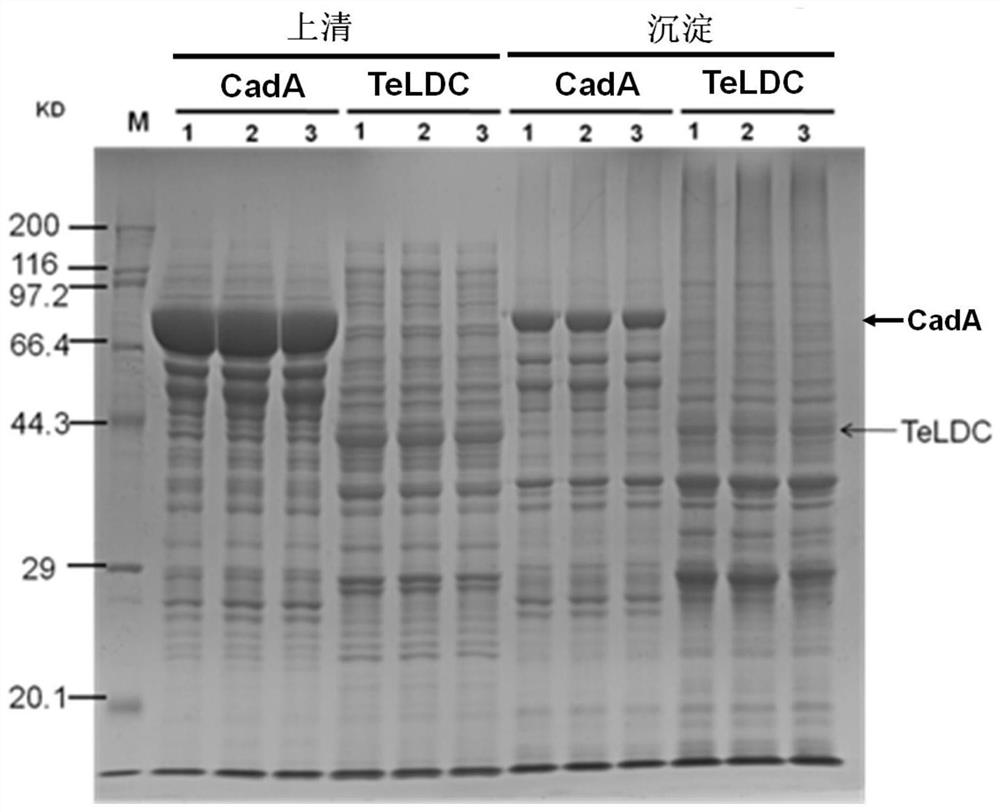
[0054] Example 2 Cloning and expression verification of the lysine decarboxylase Teldc of the thermosynechoccus elongatus
[0055] The lysine decarboxylase TeLDC (SEQ IDNO: 1, GenBank ID BAC09418.1) from the thermosynechoccus elongatus was synthesized by splicing primers after optimizing the full-length codon of the gene (SEQ ID NO:2), codon optimization and gene synthesis methods refer to Hoover DM&LubkowskiJ, Nucleic Acids Research30:10,2002, using TeLDC-SacI-F (SEQ ID No:26) and TeLDC-XbaI-R (SEQ ID No: 27) The spliced Teldc was amplified, digested with SacI and XbaI, and then ligated into the same double-digested pCIB71 plasmid. Using CaCl 2 Prepare competent cells by using the heat shock method, and transform the ligation product into E. coli E.coli BL21 (purchased from Bao Biological Engineering (Dalian) Co., Ltd.) competent cells, use LB medium to add ampicillin antibiotics for screening, clone PCR After being verified correctly by sequencing, the plasmid was extrac...
Embodiment 3
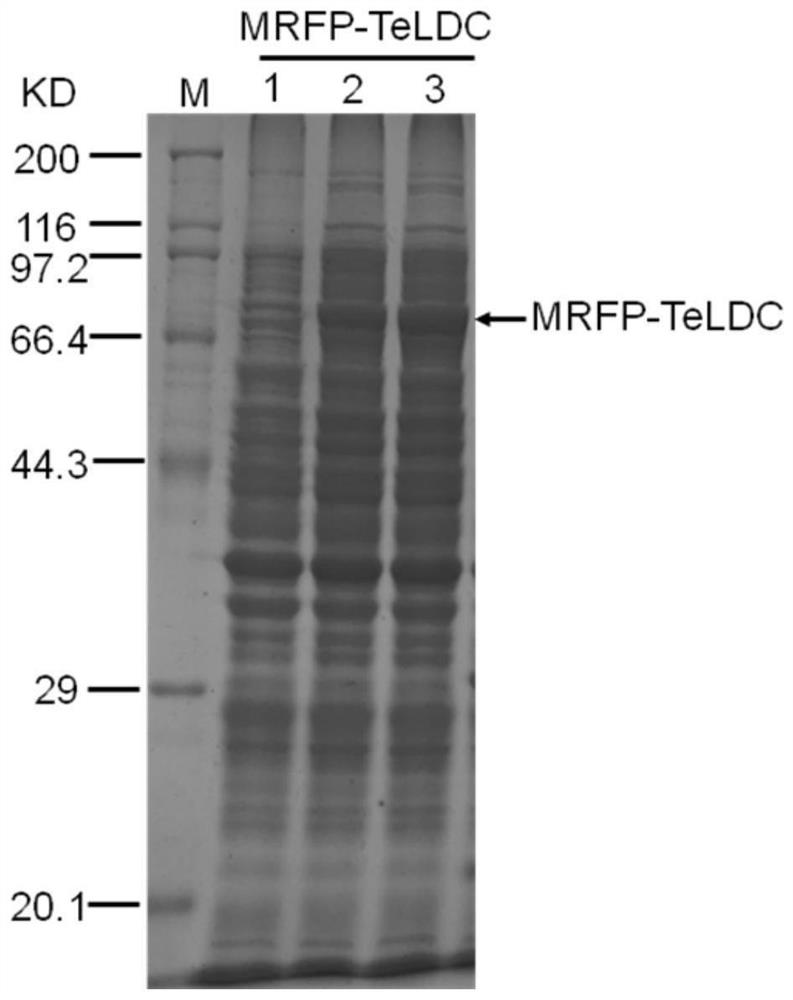
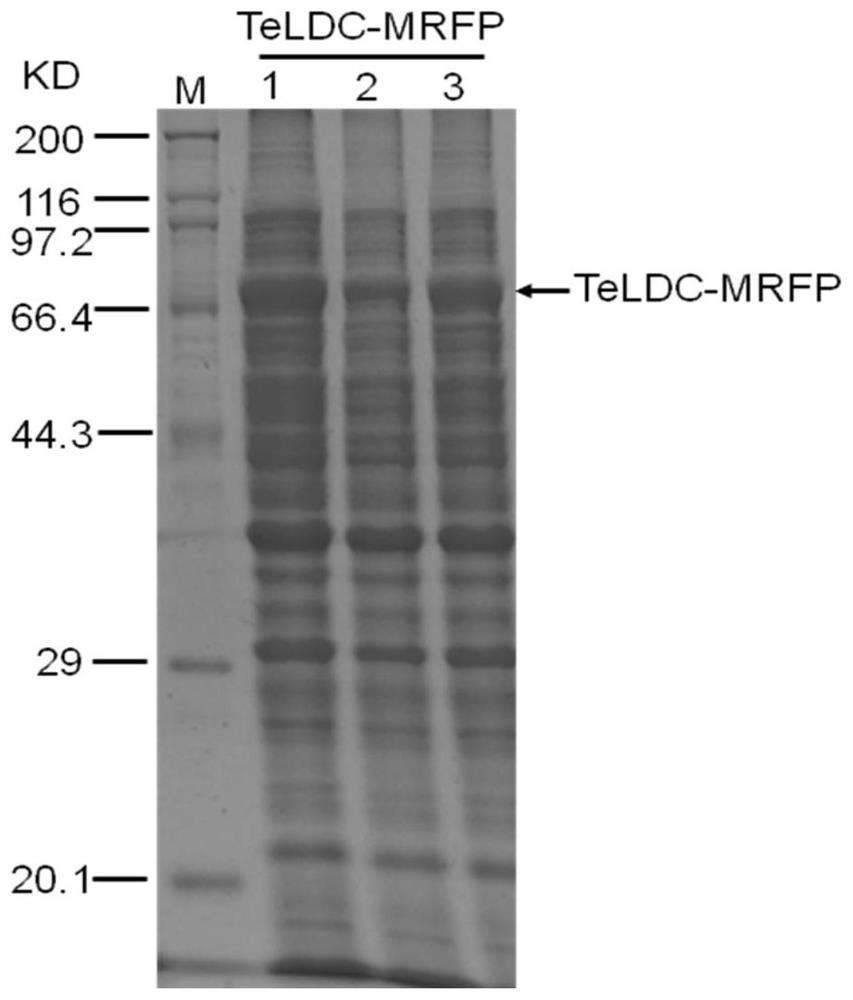
[0058] Example 3 Construction of TeLDC and Red Fluorescent Protein Fusion Expression Plasmid
[0059] The red fluorescent protein MRFP (ie mCherry, SEQ ID No: 6) from corals was synthesized by primer splicing after codon optimization of the full length of the gene (mCherry, SEQ ID No: 5) , codon optimization and gene synthesis methods refer to Hoover DM&Lubkowski J, Nucleic Acids Research30:10, 2002, using spliced MRFP as a template, using primers SacI-MRFP-TeLDC-F (SEQ ID No: 30) and linker-MRFP- R (SEQ ID No:31) was amplified, using plasmid pCIB91 as a template, using primers linker-TeLDC-F (SEQ ID No:32) and TeLDC-XbaI-R (SEQ ID No:27) to amplify, respectively After gel cutting and recovery of the target fragment, use primers SacI-MRFP-TeLDC-F (SEQ ID No: 30) and TeLDC-XbaI-R (SEQ ID No: 27) for fusion PCR, after the target fragment is purified, use SacI and XbaI Double enzyme digestion, ligation into the same double enzyme digestion plasmid pCIB91, to obtain MRFP-TeLDC ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com