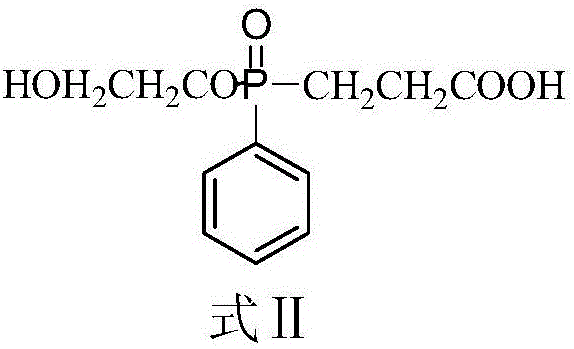
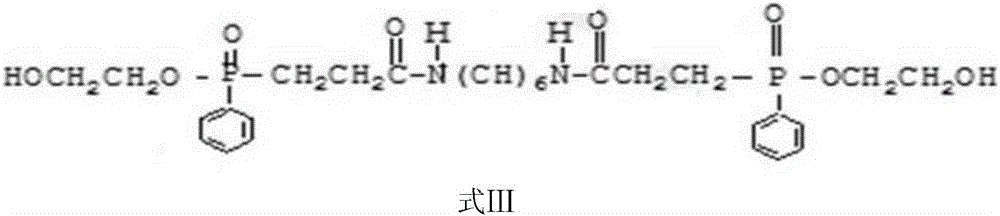
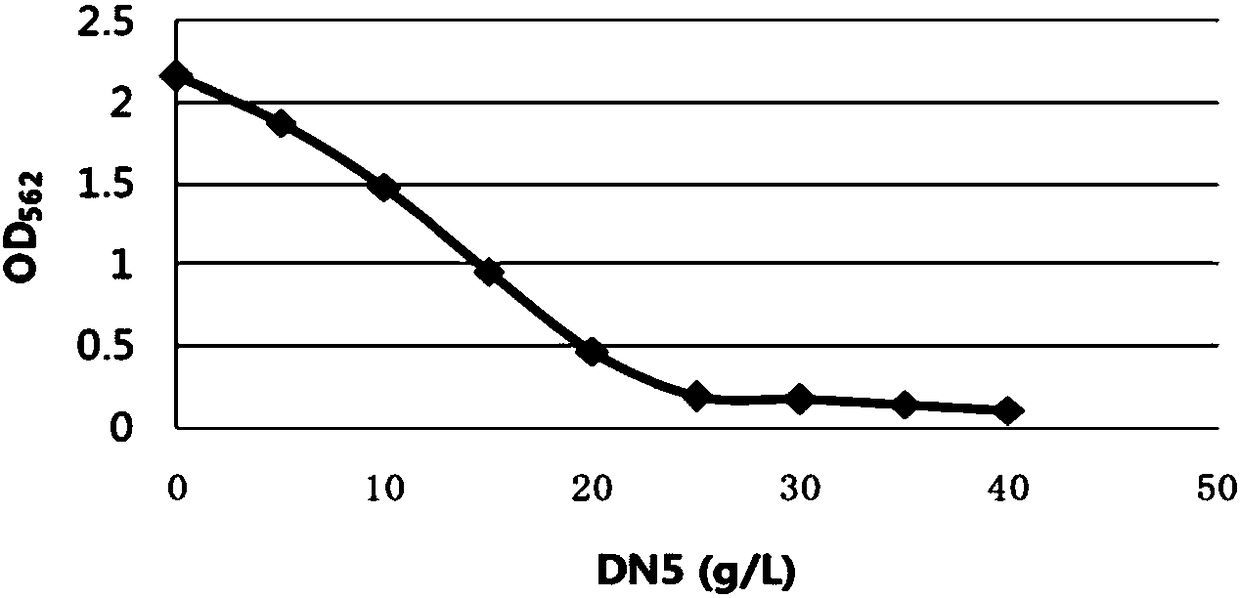
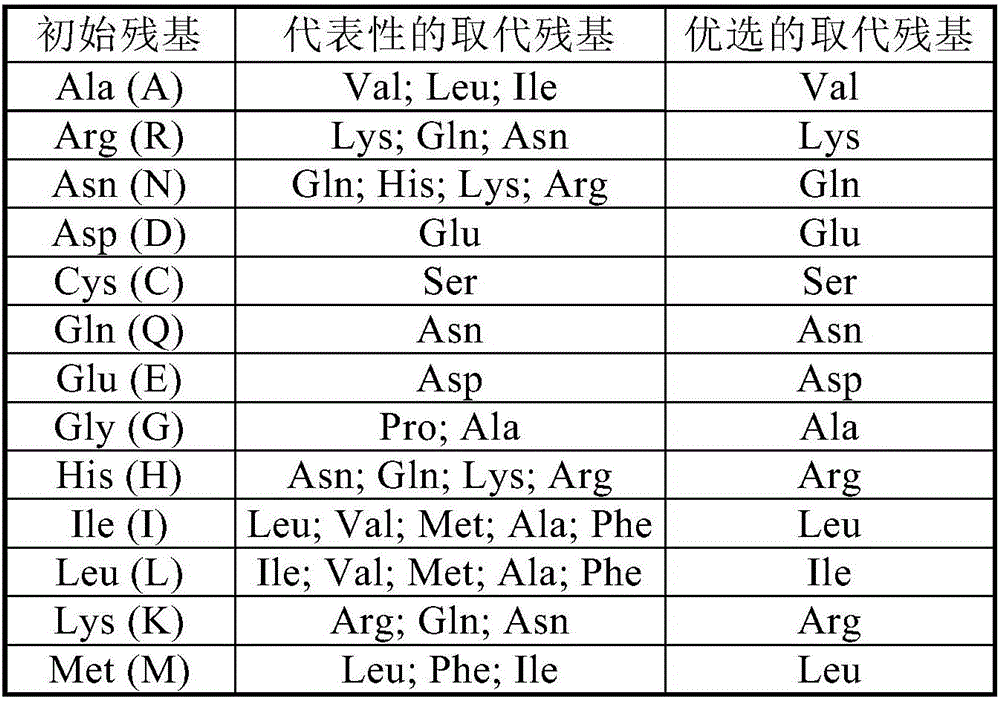
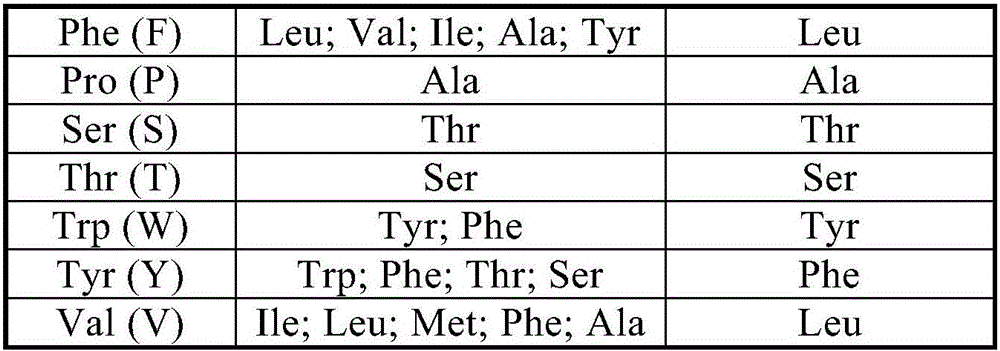
Patents
Literature
105 results about "Lysine decarboxylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lysine decarboxylase is an enzyme that converts lysine to cadaverine.
Method for preparing 1,5-pentanediamine
The invention relates to a method for preparing 1,5-pentanediamine. The method comprises the step of adding lysine decarboxylase into a lysine fermentation broth to synthesize 1,5-pentanediamine. The method utilizes the lysine fermentation broth but not purified lysine as the substrate, so that the process is simpler and more economical.
Owner:CATHAY R&D CENT CO LTD +1
Cadaverine-producing engineering strain
InactiveCN102424811AOversynthesisCurb global warmingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSynthesis methodsFermentation
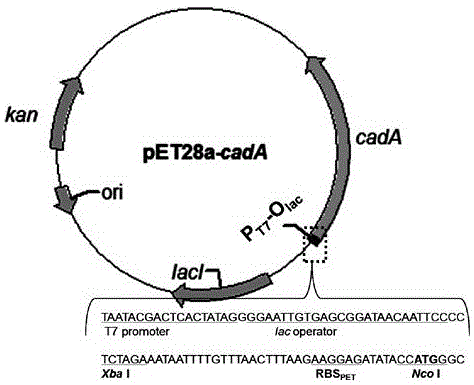
The invention relates to a cadaverine-producing engineering strain, a construction method thereof and a method for producing cadaverine by using the strain. Based on a gene engineering technology, an L-lysine decarboxylase gene (cadA / LDC) and a cadaverine-lysine antiporter gene (cadB) are respectively or simultaneously cloned into Corynebacterium glutamicum and subjected to induced coexpression, the lysine is decarboxylated to generate cadaverine under the catalytic action of the CadA enzyme, and the cadaverine is transported out of cells by the CadB protein, thus constructing a high-yield cadaverine-producing engineering strain and establishing a novel one-step cadaverine synthesis method based on the fermentation of Corynebacterium glutamicum. The one-step cadaverine synthesis method based on microbial fermentation provides a new way for large-scale cadaverine production, thereby having great economic benefits and social benefits and wide market development prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Preparation process of 1,5-pentamethylene diamine
PendingCN109536542AFacilitate the realization of industrial productionReduce toxic effectsMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismLysine fermentation
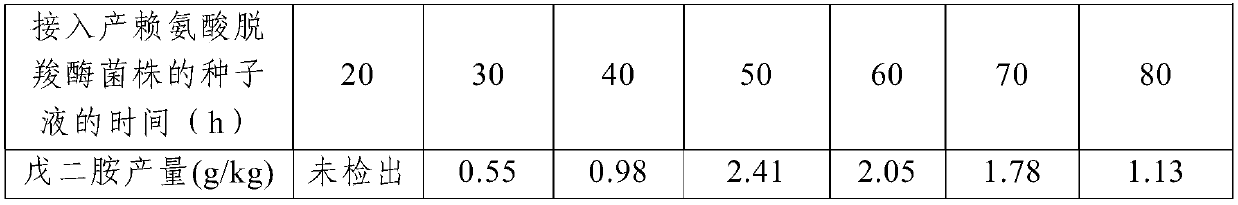
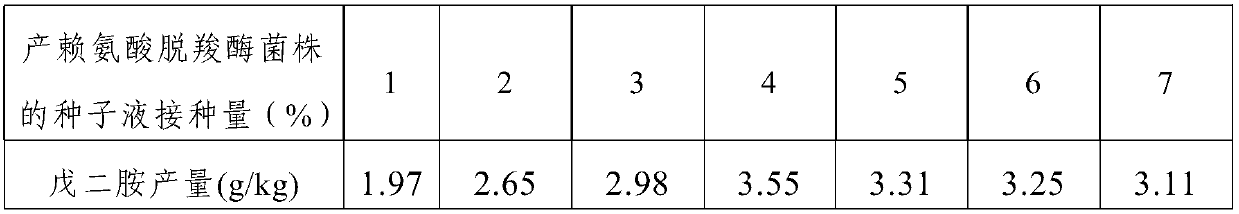
The present invention relates to a preparation process of 1,5-pentamethylene diamine. According to the method, a seed liquid containing lysine decarboxylase strains is introduced during lysine fermentation, and mixed fermentation is carried out. The method is suitable for industrial production of 1,5-pentamethylene diamine, minimizes toxicity of pentamethylene diamine to microorganisms to avoid adverse effects on fermentation, makes the subsequent process more simplified, and has certain commercial value.
Owner:CATHAY R&D CENT CO LTD +1
Method for coupled production of cadaverine by using microbial fermentation and microbial conversion
ActiveCN105441497AIncrease productionImprove production efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliMicrobial transformation
The invention relates to a method for coupled production of cadaverine by using microbial fermentation and microbial conversion. By use of the gene engineering technology, lysine decarboxylase genes with different sources are cloned in Escherichia coli or corynebacterium glutamicum with high yield of lysine for secretory expression, recombinant stains are fermented, the recombinant strains synthesize lysine at the first stage, lysine decarboxylase genes are induced for secretory expression at the second stage, and the lysine is converted into the cadaverine. The method for coupled production of cadaverine by using microbial fermentation and microbial conversion provides a new way for production of the cadaverine, has enormous economic benefit and social benefit and has broad market development prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing pentamethylene diamine and method for preparing pentamethylene diamine
ActiveCN105368766AAchieve reuseHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesThree stageIntracellular membrane
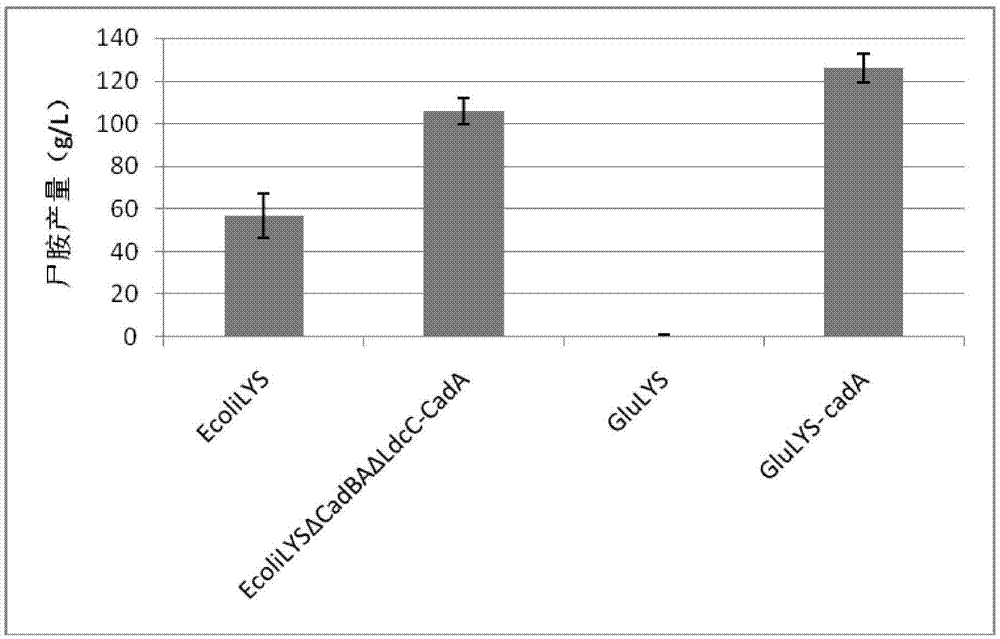
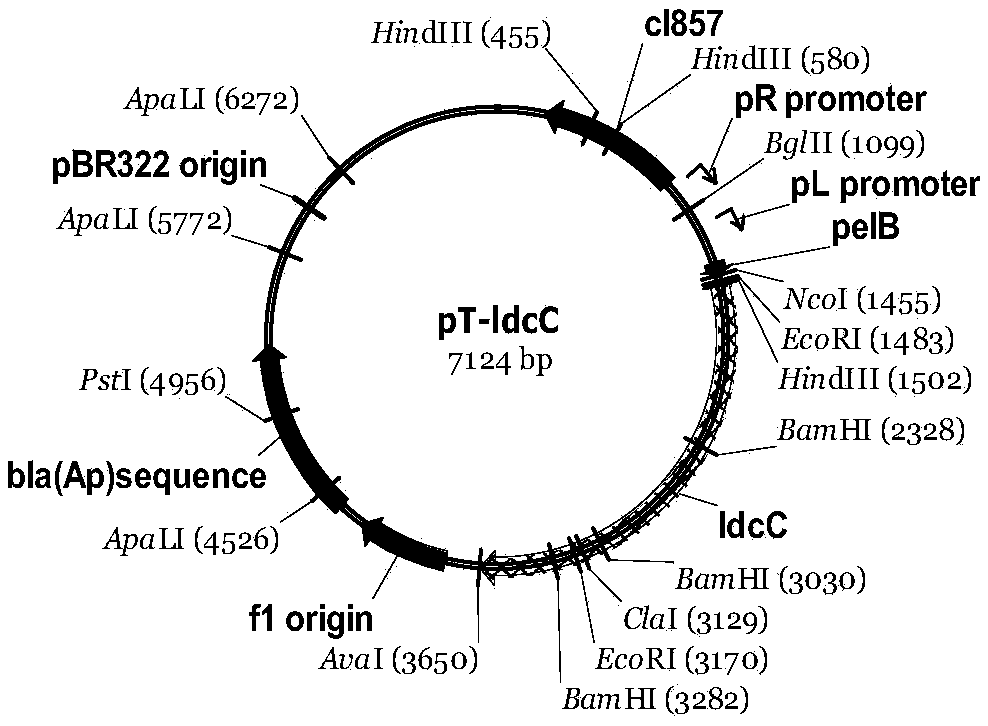
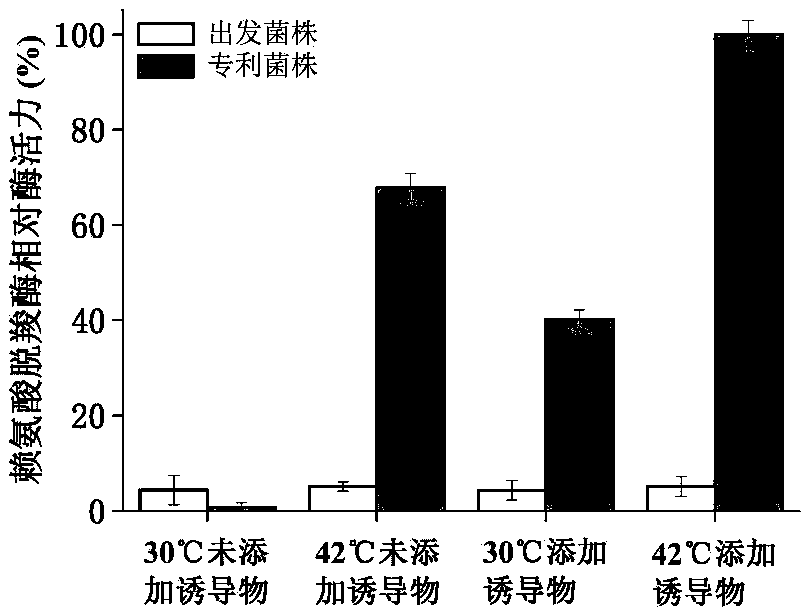
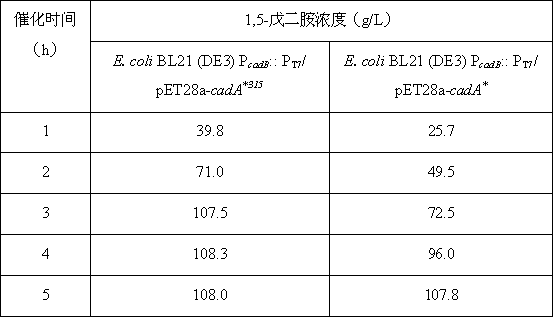
The invention provides a pentamethylene diamine producing strain and a process for efficient production of the pentamethylene diamine. The strain, when a lysine decarboxylase promoter 1dcCp is replaced as an environmental / nutritional factor-control promoter, is capable of simultaneously expressing a signal peptide; the activity of an enzyme of the strain for the catalytic synthesis of the pentamethylene diamine is greatly improved and is adjusted through ambient temperature; and the finally expressed enzyme falls between an intracellular membrane and a cell wall and is not released in a fermentation system, so that the purpose and the effect of the efficient transformation of the pentamethylene diamine are achieved. In three stages, namely strain fermented culture, variable-temperature efficient enzyme production and target product rapid transformation, at 25-50 DEG C, a pentamethylene diamine production level reaches 106-116.8g / L and a lysine transformation rate is 91-97% of a theoretical transformation rate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Polyamide resin
ActiveUS20090099318A1Excellent in lasting thermal stabilityHigh industrial valueNon-fibrous pulp additionPaper/cardboardPolyamideAminocaproic acid
To provide a polyamide resin excellent in lasting thermal stability and having a high biomass ratio.A polyamide resin comprising adipic acid units, pentamethylenediamine units and 6-aminocaproic acid units as constituents, wherein the weight ratio of the sum of the adipic acid units and the pentamethylenediamine units to the 6-aminocaproic acid units is 97:3 to 75:25. The pentamethylenediamine is preferably one produced from lysine using lysine decarboxylase, lysine decarboxylase-producing cells or a treated product of the cells.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Nylon 5X salt and high-purity preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108129329AGuaranteed harmless disposalHigh purityAmino compound purification/separationOrganic compound preparationDesorptionIon exchange
The invention discloses a one-step production process of nylon 5X salt and the prepared high-purity nylon 5X salt. The one-step production process of the nylon 5X salt comprises the steps of carryingout ion exchange adsorption and desorption on a lysine fermentation fluid, obtaining a pure lysine collecting fluid, and after deaminizing, using a nanofiltration membrane for separating part of protein and inorganic salt; utilizing binary acid and lysine for reacting to generate lysine binary acid salt, controlling reaction PH to range from 5 to 6, during a conversion process, directly adding thebinary acid for buffering pH, utilizing a lysine decarboxylase fermentation fluid for one-step converting the lysine binary acid salt into a nylon 5X salt solution, and controlling PH after finishingconversion to be around 7; after filtering and sterilizing through a ceramic membrane, adsorbing impurities, concentrating, crystallizing, extracting and crystallizing a mother liquor through ethyl alcohol after crystallizing, and collecting the nylon 5X salt. The yield and the purity are improved, and the production pollution is reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG SHOUGUANG JUNENG GOLDEN CORN CO LTD +3
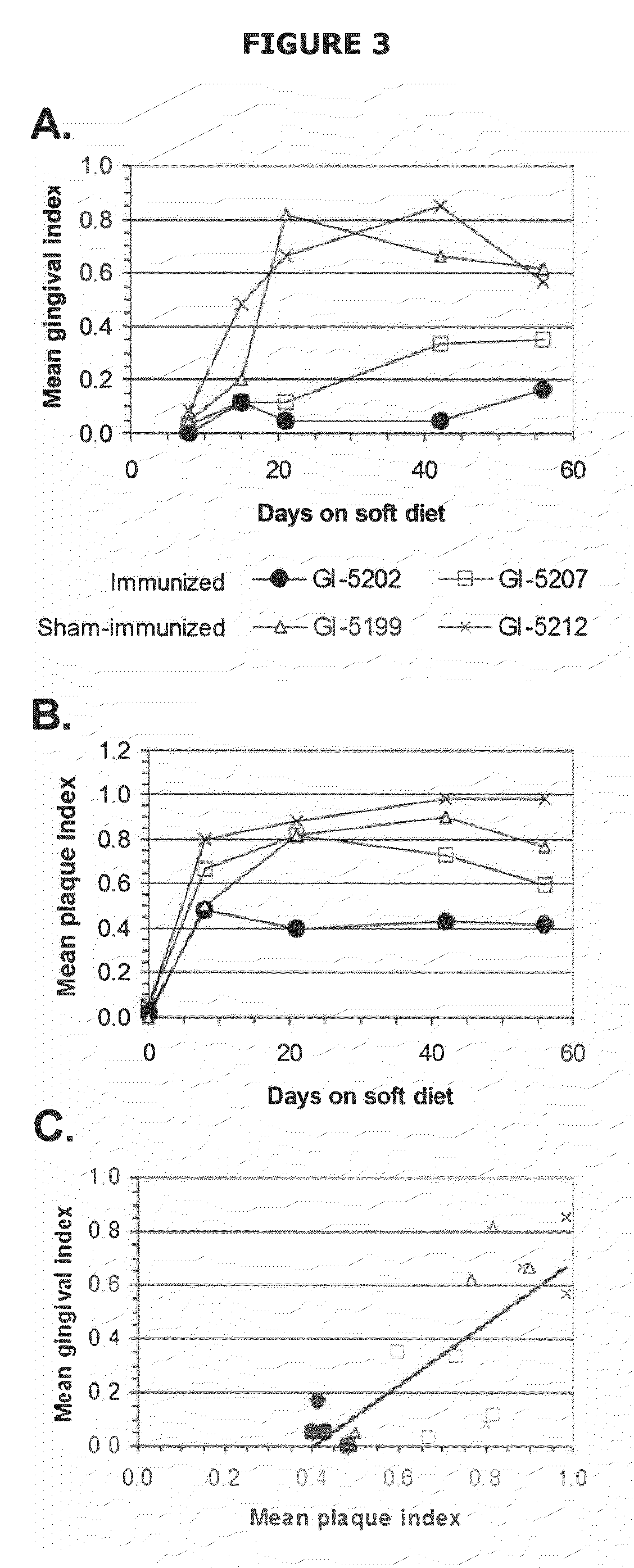
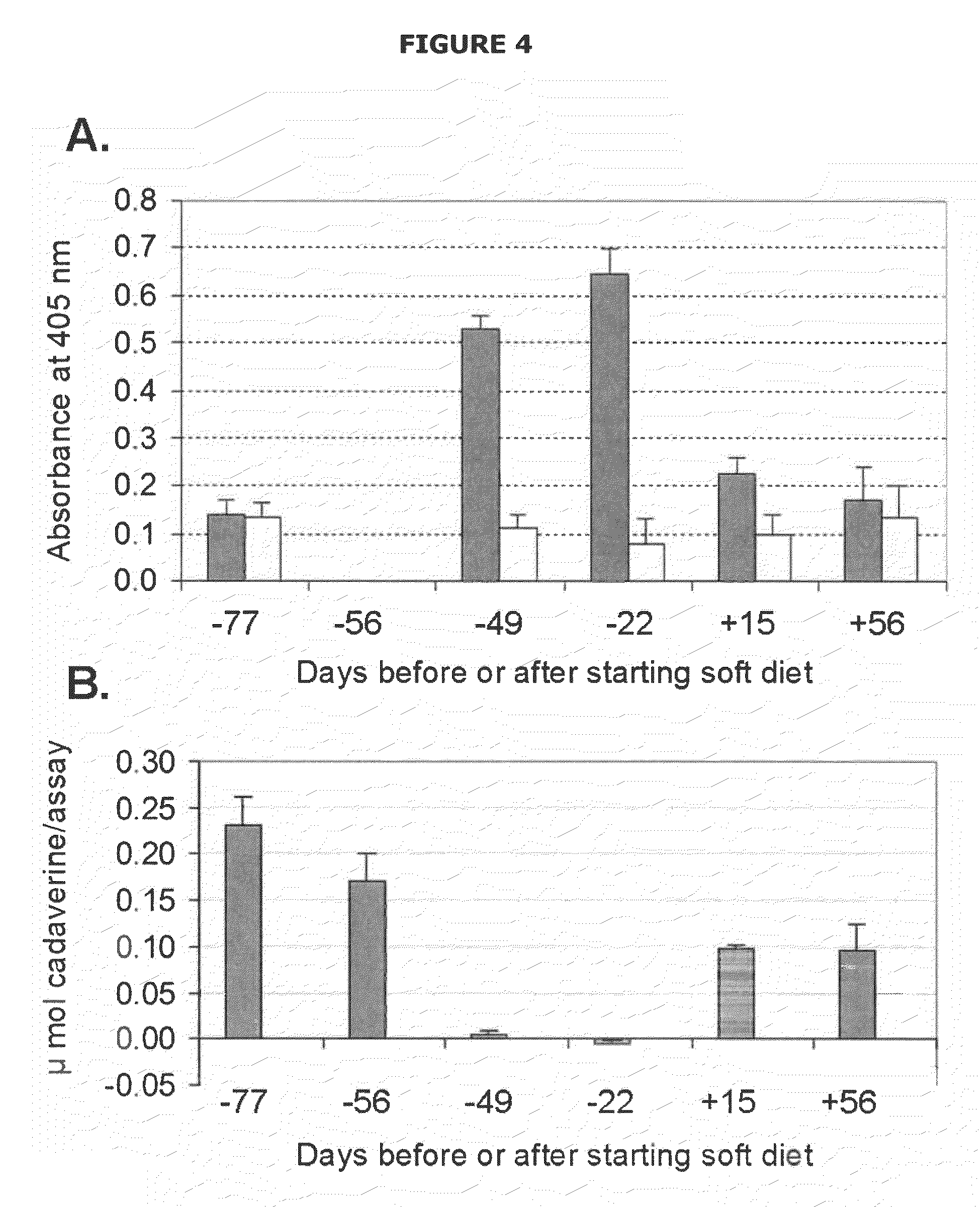
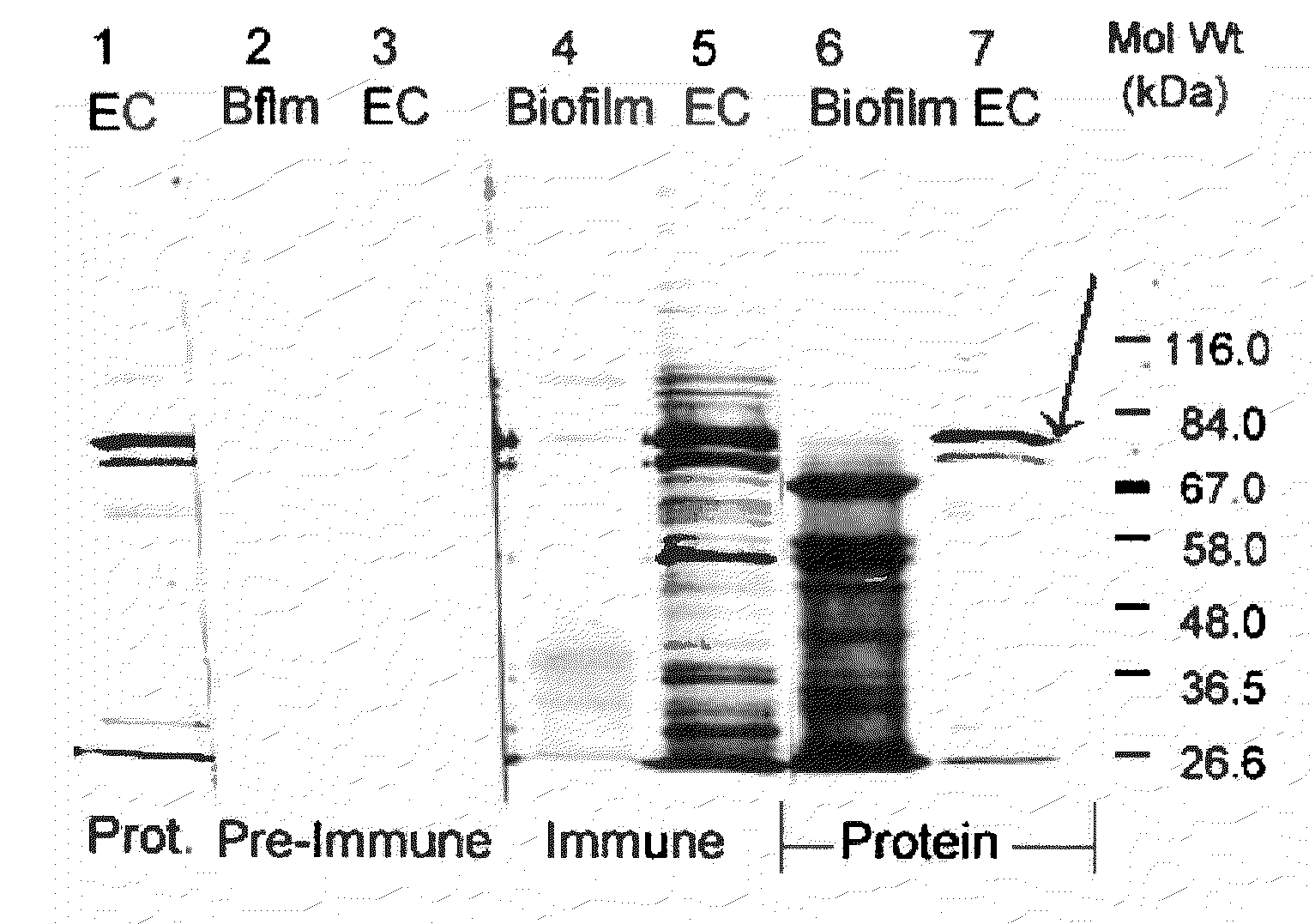
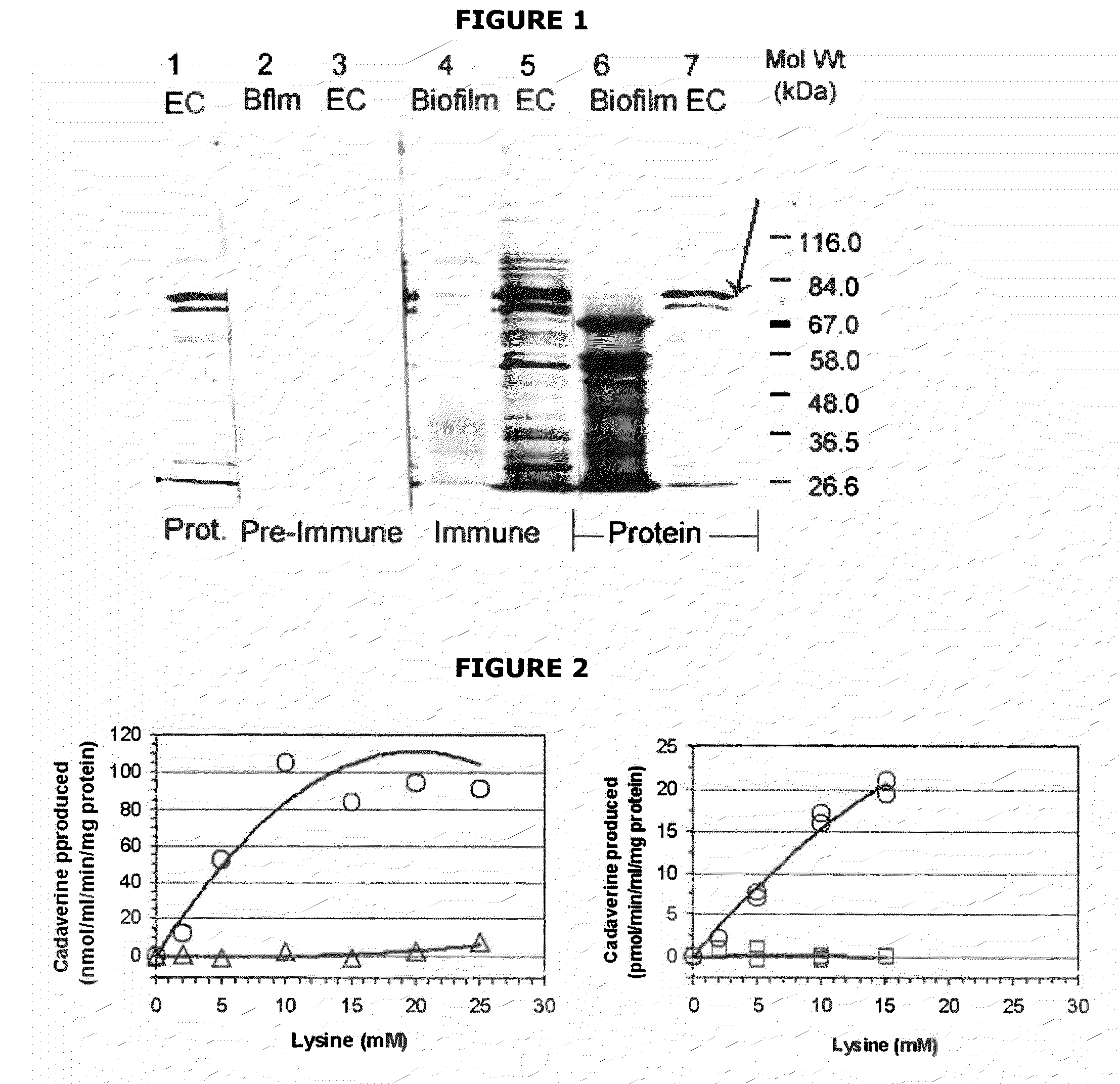
Mutants of lysine decarboxylase, vaccines for periodontitis, and methods of use
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Preparation method of nylon 56 salt
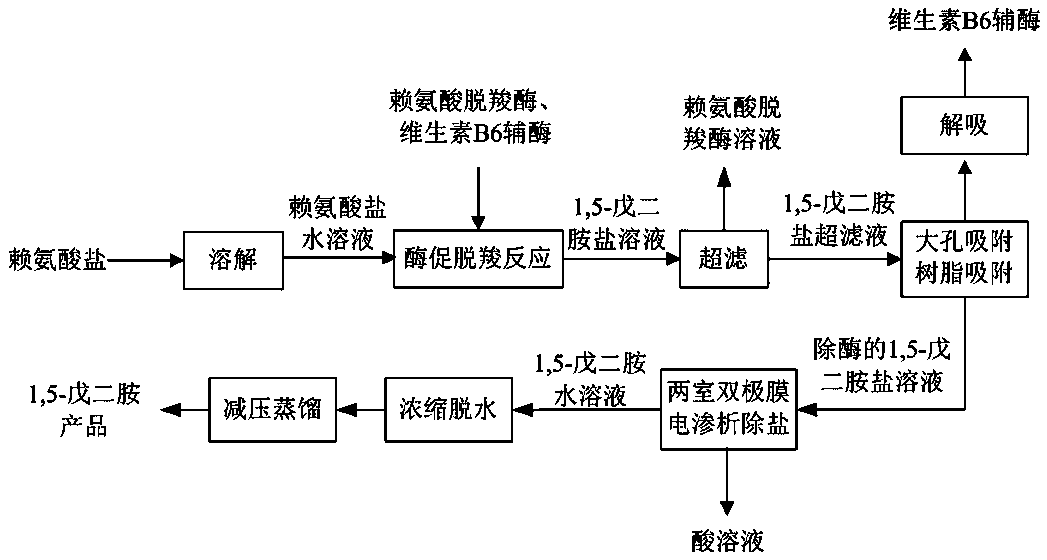
The invention provides a preparation method of nylon 56 salt. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a, performing continuous fermentation and separation of lysine in a lysine continuous fermentation and separation integrated system to obtain a lysine primary filtrate; b, adopting an inorganic ultrafiltration membrane filtration system to remove impurities from the lysine primary filtrate to obtain a lysine secondary filtrate; c, desalting the lysine filtrate by a two-chamber bipolar membrane electrodialysis device; d, then sending a lysine aqueous solution into a continuous enzyme reaction and separation integrated system, adding adipic acid to adjust pH, and simultaneously adding lysine decarboxylase and vitamin B6 coenzyme for decarboxylation reaction; e, adopting macroporous adsorption resin to selectively adsorb the vitamin B6 coenzyme; f, adopting activated carbon for continuous adsorption and decolorization; g, performing concentrating under reduced pressure, crystallizing, separating and drying to obtain a 1,5-pentanediamine adipate product. The preparation method has the advantages of low cost, low environmental protection pressure and high product purity, and is suitable for industrial application.
Owner:河北美邦工程科技股份有限公司
Mutants of lysine decarboxylase, vaccines for periodontitis, and methods of use
InactiveUS20090155296A1Inhibiting and reducing developmentBacterial antigen ingredientsSugar derivativesEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
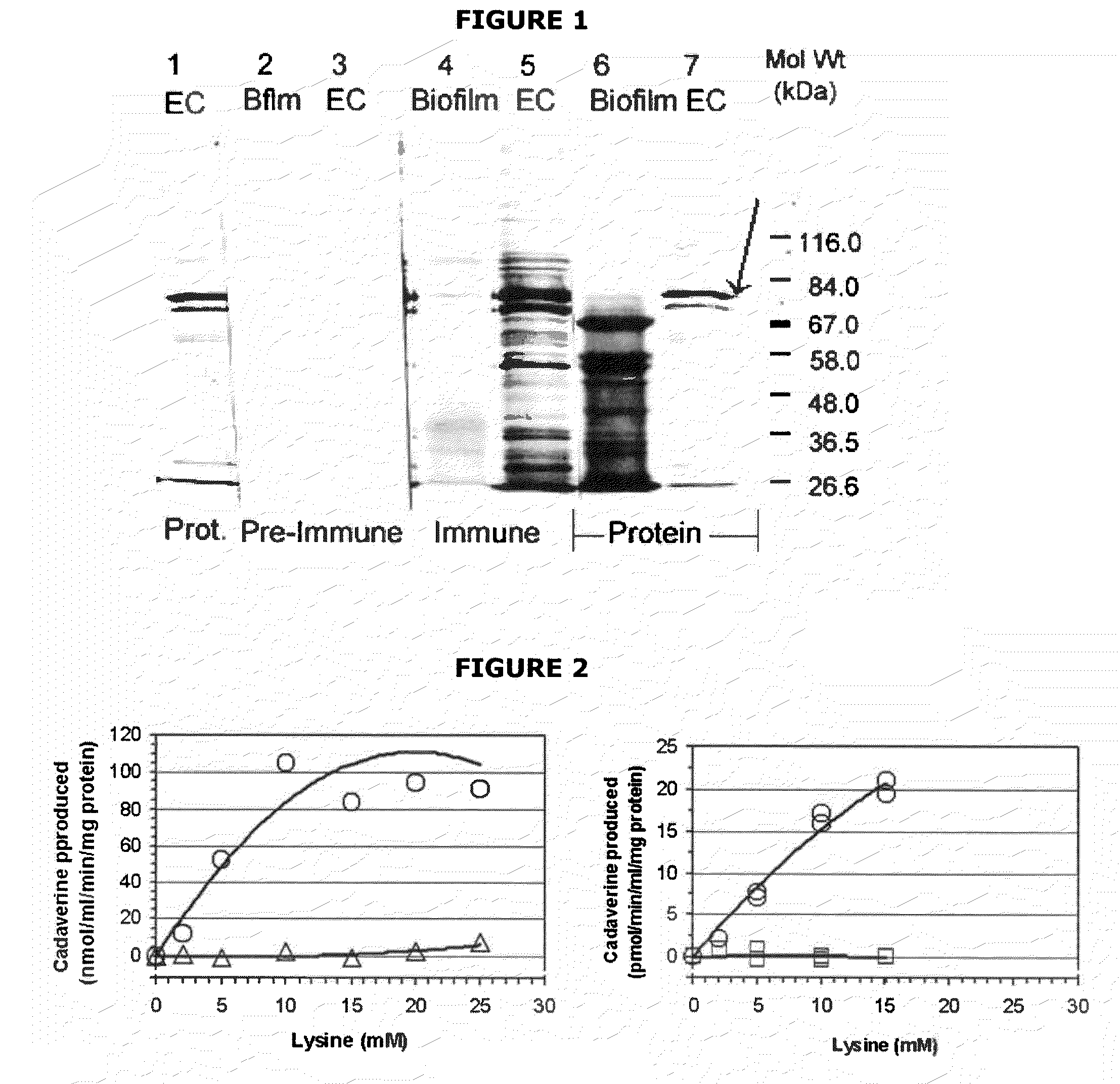
The present invention is directed to mutants of lysine decarboxylase, nucleic acids encoding the mutants, and vaccines comprising the mutants for inhibiting and reducing the development of periodontal diseases, including gingivitis and chronic periodontitis. The vaccine composition comprises a recombinant lysine decarboxylase mutant which is based on a native version of the enzyme from E. corrodens and induces production of antibodies that inhibit the activity of the lysine decarboxylase enzyme in the oral cavity. The recombinant lysine decarboxylase mutant, in one version, comprises a mutation at residue 365 or at other locations within the active site, and in a preferred embodiment is produced from E. coli in large amounts and to form inclusion bodies. The purified inclusion bodies can then be used in the vaccine composition to induce in vivo production of antibodies that inhibit the activity of native E. corrodens lysine decarboxylase.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
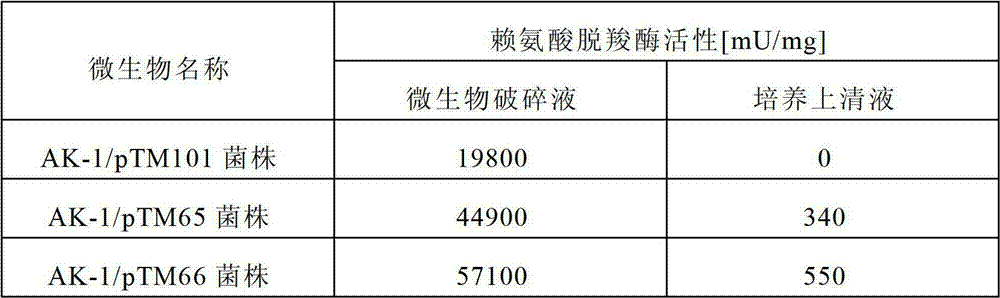
Method for producing 1,5-pentanediamine
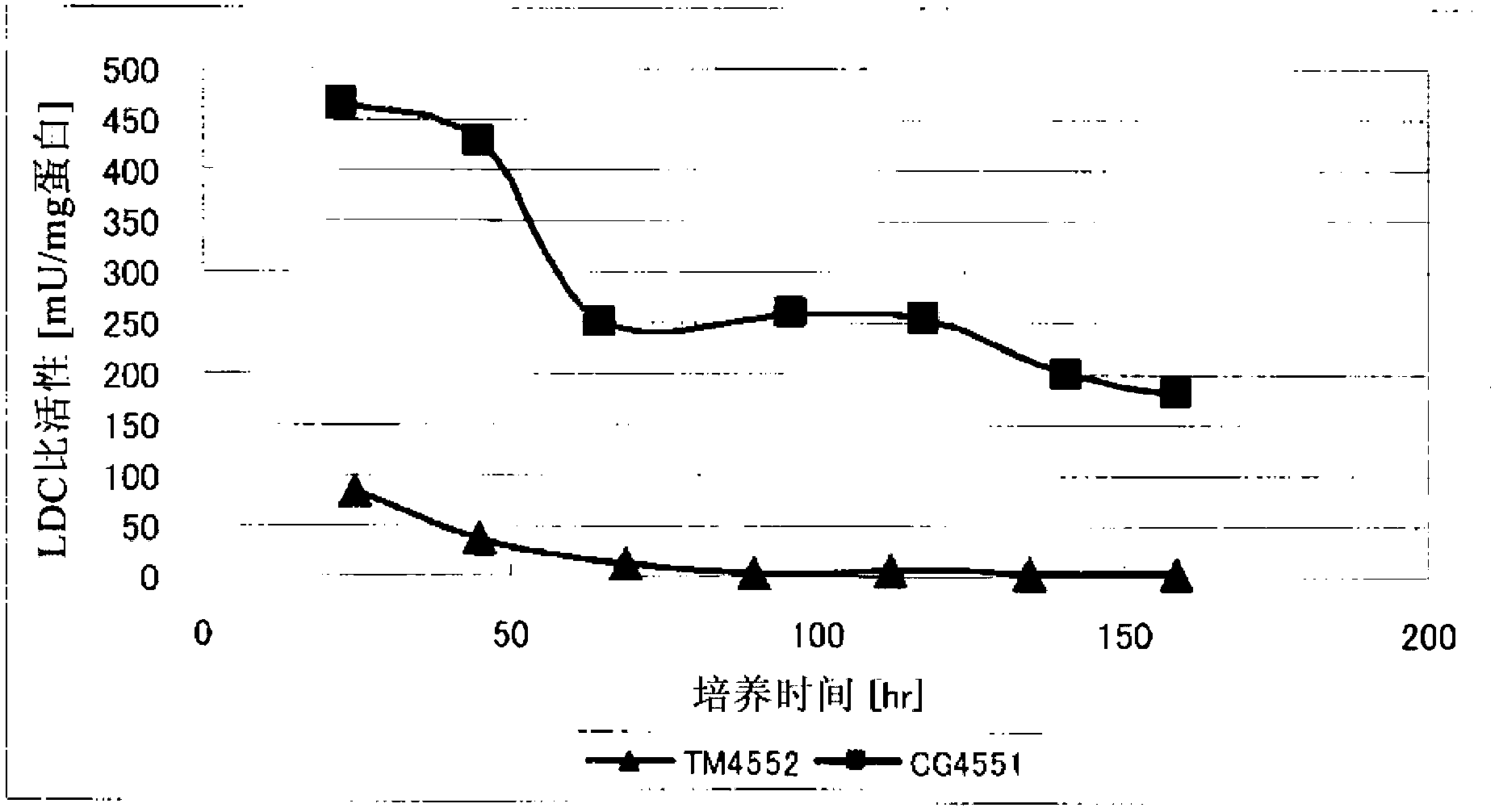
Disclosed is a method for producing 1,5-pentanediamine through fermentation using a microorganism, said microorganism having LDC gene in the chromosome and showing regulated secondary production of L-lysine. In the method for producing 1,5-pentanediamine whereby 1,5-pentanediamine is produced by a coryneform bacterium having a gene encoding lysine decarboxylase in the chromosome, said coryneform bacterium continuously maintains a lysine decarboxylase activity of 50 mU / mg protein or greater during the culture.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Method for producing pentamethylene diamine by using carbon dioxide desorption process through fermentation
ActiveCN105861586AReduce the amount of strong alkaliReduce the amount of salt residueMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesCulture cellDesorption
Owner:HEILONGJIANG EPPEN NEW MATERIALS LTD
Method for preparing 1,5-pentanediamine
ActiveCN108997141ALow costReduce usageAmino compound purification/separationFermentationVitamin b6Aqueous solution
The invention provides a method for preparing 1,5-pentanediamine. The method comprises the steps of: a, dissolving lysine salt to obtain an aqueous solution of lysine salt; b, adding lysine decarboxylase and vitamin B6 coenzyme to the aqueous solution of lysine salt for a decarboxylation reaction of lysine; c. filtering a 1,5-pentanediamine salt solution obtained in step b by using an ultrafiltration membrane having a interception molecular weight being 3000-6000; d. selectively adsorbing vitamin B6 coenzyme in a 1,5-pentanediamine salt ultrafiltrate obtained in step c by using macroporous adsorption resin; e, sending the enzyme-removed 1,5-pentanediamine salt solution obtained in step d to a two-chamber bipolar membrane electrodialysis device for desalting; and f. performing concentrationand dehydration on the 1,5-pentanediamine aqueous solution obtained in the step e, then performing vacuum distillation, and performing condensation on a light phase to obtain a 1,5-pentanediamine product. The preparation method of the invention has the advantages of low cost, small environmental protection pressure, and high product purity, and is suitable for industrial application.
Owner:河北美邦工程科技股份有限公司
Lysine decarboxylase strain and application thereof in production of pentamethylenediamine
InactiveCN109652356AIncrease productivityBacteriaMutant preparationEscherichia coliLysine decarboxylase activity
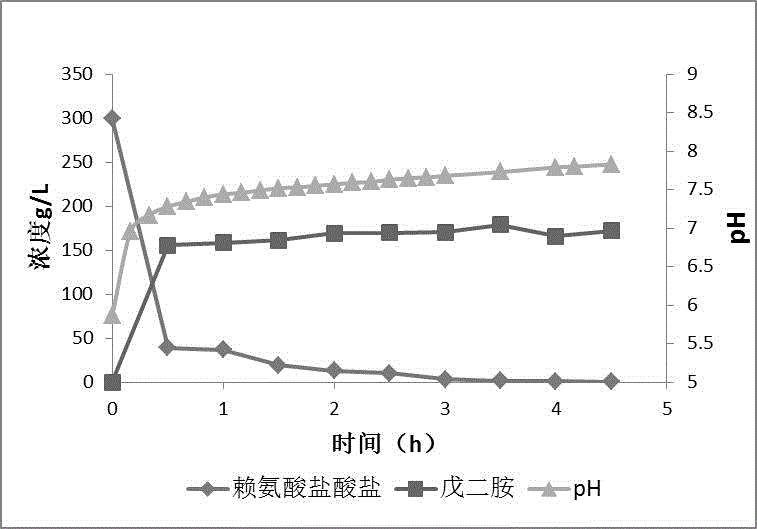
The invention discloses a lysine decarboxylase strain and an application method thereof in the production of pentamethylenediamine. The lysine decarboxylase strain adopts recombinant bioengineering bacteria obtained by introducing a lysine decarboxylase gene into escherichia coli by a genetic engineering method as a starting strain, a high enzyme activity lysine decarboxylase strain is obtained bymutagenesis screening, the preservation number is CGMCC No. 16762, and compared with original engineering bacteria, the lysine decarboxylase activity is increased by 3.93 times. The invention furtherdiscloses the application of the lysine decarboxylase strain in the production of the pentamethylenediamine, the lysine decarboxylase strain is subjected to fermentation culture to obtain a fermentation broth containing the lysine decarboxylase, the fermentation broth is added in an amount of 5% in the lysine hydrochloride and a coenzyme solution, the conversion is carried out for 3 h at 40 DEG C, the highest content of the pentanediamine is 326.3 g / L, and the molar conversion of the lysine hydrochloride reaches 99.98%.
Owner:SHANDONG SHOUGUANG JUNENG GOLDEN CORN CO LTD +3
Process for production of cadaverine
ActiveCN102770550AIncreased sugar yieldReduce loadPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifRecombinant DNA-technologyMicroorganismPolyamide
Disclosed is a process for producing cadaverine, characterized by culturing a microorganism capable of secreting lysine decarboxylase outside cells thereof. According to the process, the by-production of lysine can be prevented, the yield of cadaverine on glucose consumption is improved compared with those in conventional processes, and the load in a purification step for purifying cadaverine as a polyamide raw material can be reduced.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
E. coli engineering bacteria producing 1,5-pentanediamine through whole cell catalysis and application thereof
ActiveUS20170226544A1High efficient protein expressionImprove catalytic performanceMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliTranslocator protein
The present invention discloses an E. coli engineering bacteria producing 1,5-pentanediamine through a whole cell catalysis and its application. The engineering bacteria according to the present invention, is Escherichia coli (E. coli) strain B or its derivative strains with the overexpression of a lysine decarboxylase gene and a proper expression of a lysine-cadaverine antiporter gene cadB. The engineering bacteria according to the present invention is the engineering bacteria producing 1,5-pentanediamine through the whole cell catalysis constructed from Escherichia coli B derivative strains, which has an overexpression of a lysine decarboxylase gene cadA and a proper expression of the lysine-cadaverine antiporter gene cadB. The present invention further discloses a method of producing a 1,5-pentanediamine catalyzed by the engineering bacteria, the yield and production intensity of 1,5-pentanediamine in bio-based production could be significantly improved through the method, hence it could be applied to mass production and convenient for extending applications.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG EPPEN NEW MATERIALS LTD
Flame-resistant modified nylon 56 polymer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106084213AImprove flame retardant performanceHigh limiting oxygen indexAdipic acidFire retardant
The invention discloses a flame-resistant modified nylon 56 polymer and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps that 1, bio-based pentane diamine reacts with adipic acid in water under protection of nitrogen to obtain a nylon 56 saline solution, wherein bio-based pentane diamine is obtained by removing two carboxyl-terminated groups from lysine or lysinate under the action of lysine decarboxylase; 2, the nylon 56 saline solution, a molecular weight regulator and a flame retardant are added into a reaction vessel, pressure maintaining is conducted at the temperature of 210 DEG C to 240 DEG C under the pressure of 1.7 MPa to 1.85 MPa, the pressure in the reaction vessel is released, the temperature is increased to 265 DEG C to 275 DEG C, vacuumizing and stirring are conducted, and then the flame-resistant modified nylon 56 polymer is obtained. Compared with products such as common nylon 66 and nylon 6, the flame-resistant modified bio-based nylon 56 prepared through the method has the greatest advantages of achieving the flame retarding and melting drop resisting characteristics and being suitable for being used at high-temperature, high-humidity and high-voltage places, safe and environmentally friendly; in addition, due to the fact that the physical property is not obviously reduced in the modification process, so that subsequent further modifying, processing and manufacturing are conveniently conducted.
Owner:优纤科技(丹东)有限公司 +2
Lysine decarboxylase mutant and application thereof
The invention relates to a lysine decarboxylase mutant and application thereof, in particular to lysine decarboxylase modification aiming to allow lysine decarboxylase to be suitable for L-lysine production using microbial fermentation and coupling catalyzing L-lysine decarboxylic reaction to generate 1,5-pentamethylene diamine so as to use glucose to produce the 1,5-pentamethylene diamine in onestep. The lysine decarboxylase mutant has the advantages that the activity-lowered lysine decarboxylase mutant is acquired by using random mutation and high-throughput screening; when recombinant L-lysine production strains containing the lysine decarboxylase mutants are used to produce the 1,5-pentamethylene diamine in one step, the toxic effect of the 1,5-pentamethylene diamine in the system inthe early fermentation stage on thallus when the thallus uses glucose fermentation can be reduced, the balance between L-lysine and the 1,5-pentamethylene diamine can be maintained, the yield of the 1,5-pentamethylene diamine produced by the L-lysine production strains can be increased, and the quantity of the residual L-lysine is less than 2.2g / L.
Owner:CATHAY R&D CENT CO LTD +2
Method for producing 1,5-pentanediamine through immobilized lysine decarboxylase
InactiveCN109880859AImmobilizationImprove adsorption capacityOn/in organic carrierFermentationProtein CChitin binding
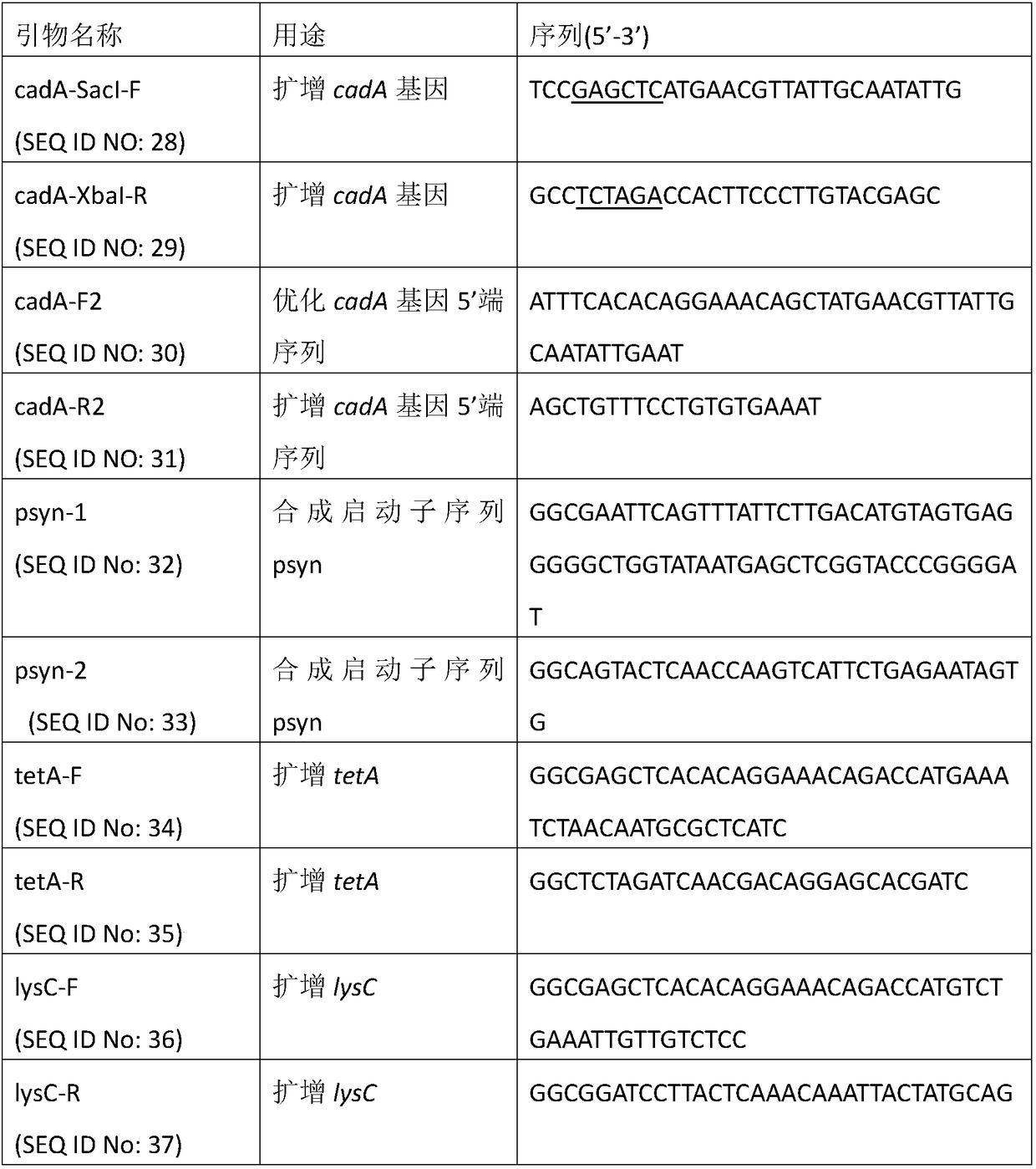
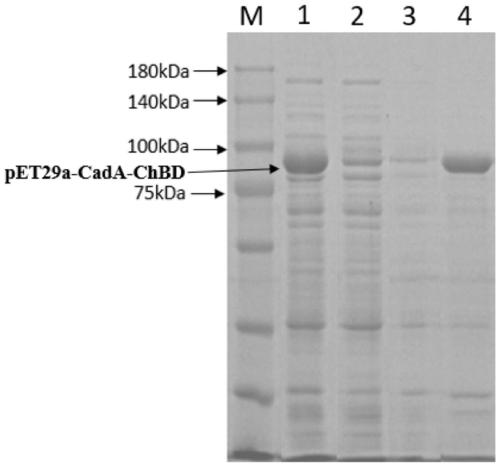
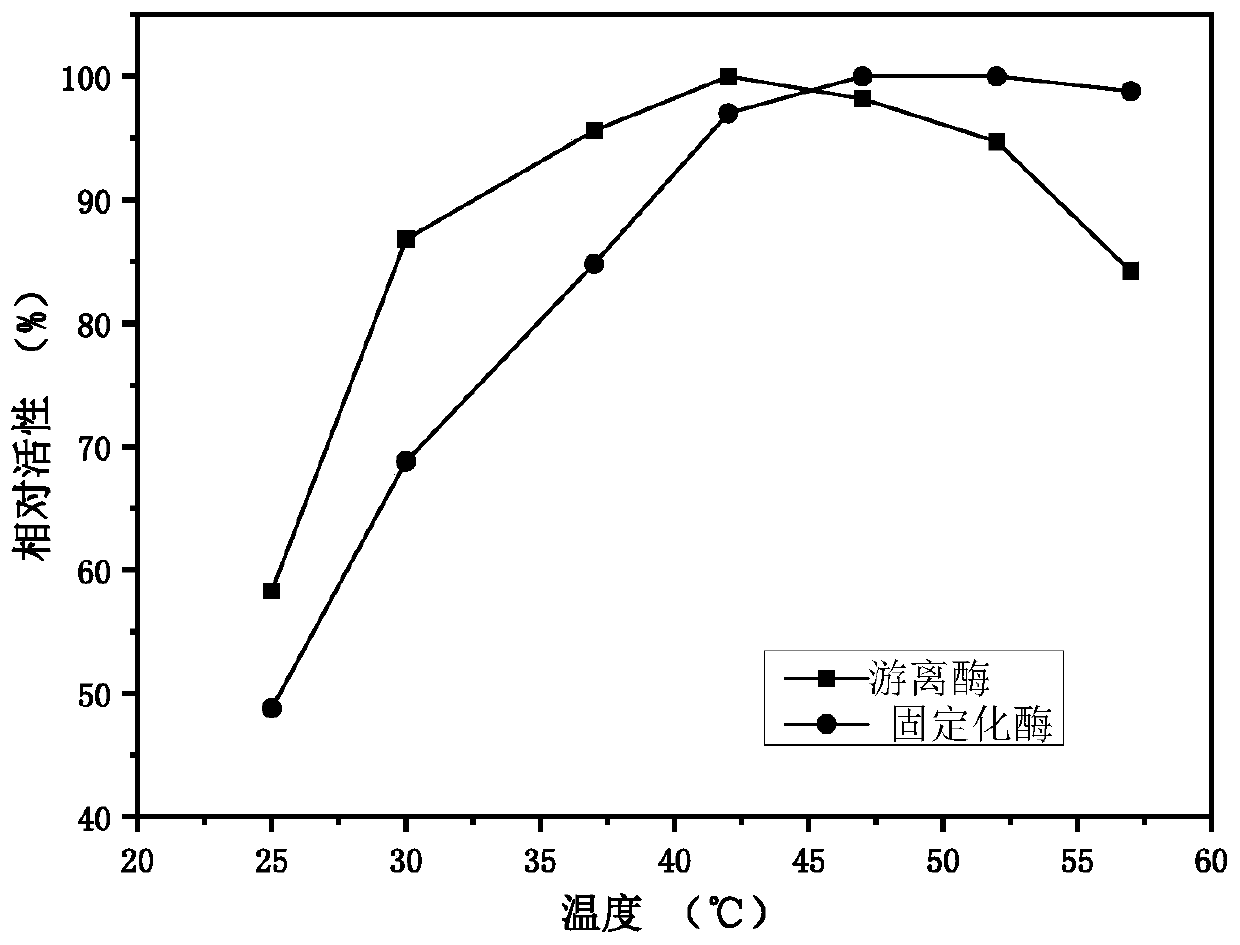
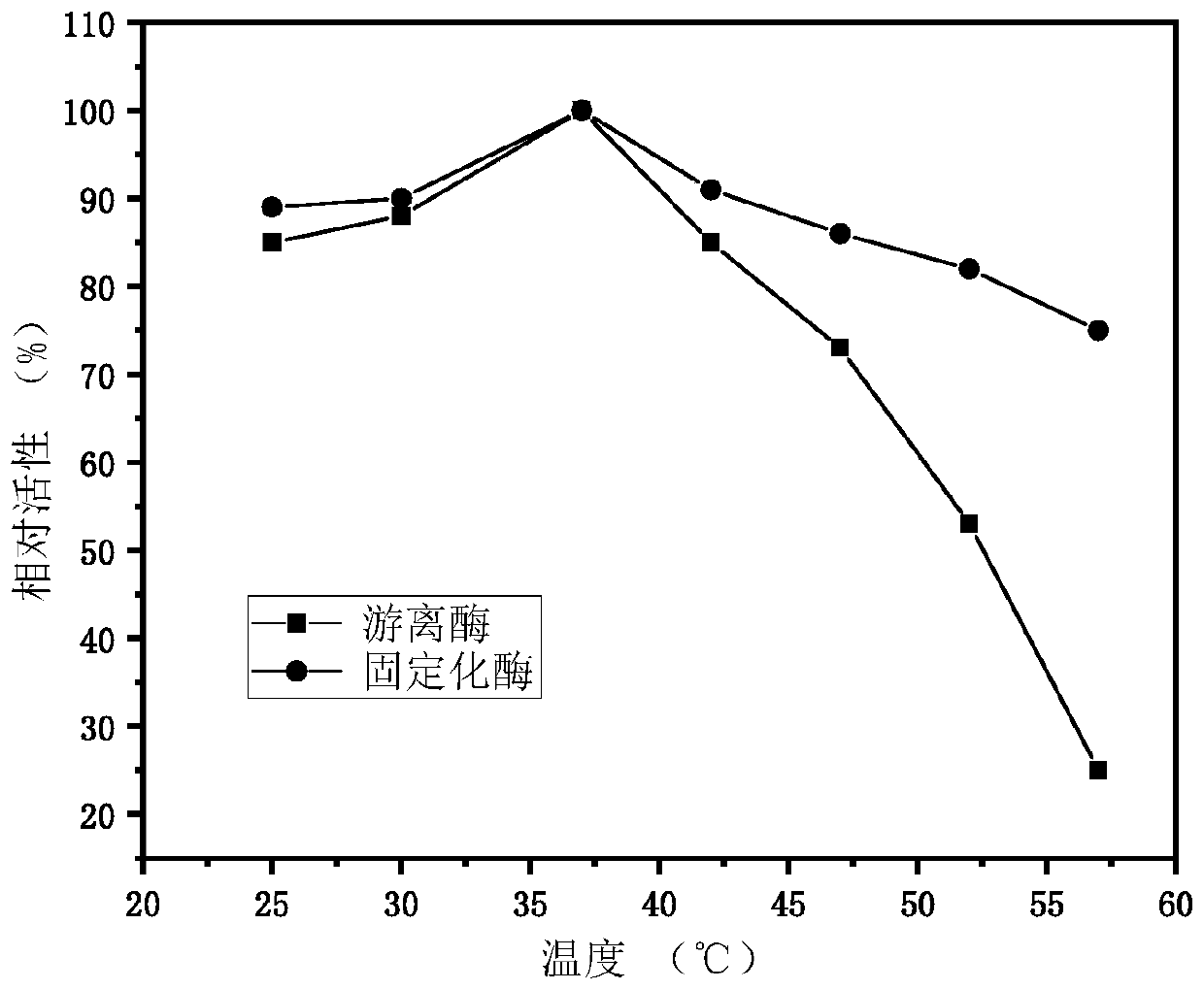
The invention discloses a method for producing 1,5-pentanediamine through immobilized lysine decarboxylase. The method comprises the following steps of connecting a chitin binding domain (ChBD) gene to the N end of a lysine decarboxylase gene (CadA) to construct a fusion protein; fermenting the fusion protein to obtain a crude lysine decarboxylase enzyme solution; adding chitin into the crude enzyme solution to obtain immobilized lysine decarboxylase; finally, enabling the obtained immobilized lysine decarboxylase to participate in a decarboxylation reaction of L-lysine to prepare 1,5-1,5-pentanediamine. According to the method, the specific affinity effect of the substrate chitin and the fusion protein is skillfully utilized to adsorb the lysine decarboxylase, the cost of the immobilizedcarrier chitin is low, the immobilization efficiency is high, the activity stability of enzymes is high, and meanwhile, the procedure of protein purification can be omitted through specific affinity adsorption. The provided method achieves repeated production of 1,5-1,5-pentanediamine and can reduce the production cost, simplify the separation procedure of downstream products and enzymes and achieve remarkable economic benefits.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing pentanediamine through fermentation and method for extracting pentanediamine
ActiveCN109402189AHigh purityQuality improvementAmino compound purification/separationFermentationAmino acid fermentationSulfate
The invention belongs to the field of biological fermentation engineering, and provides a method for producing 1,5-pentanediamine through fermentation with lysine sulfate and a method for extracting the 1,5-pentanediamine without solid waste. The method for preparing the 1,5-pentanediamine through fermentation comprises the steps that the pH value of a conversion liquid is adjusted by using cell catalyzing lysine sulfate expressing lysine decarboxylase, extraction is performed to obtain an oil phase and an aqueous phase, the oil phase is rectified, and the 1,5-pentanediamine capable of being used for generating polyamide is obtained. Waste is comprehensively utilized, and therefore no solid waste is generated, and the aqueous phase is concentrated to obtain sulfate capable of being used for preparing an amino acid fermentation culture medium. Additionally, the invention also provides the improved lysine decarboxylase.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG EPPEN NEW MATERIALS LTD
Novel lysine decarboxylase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN107164352AImprove performanceRealize industrial productionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionMutantLysine decarboxylase
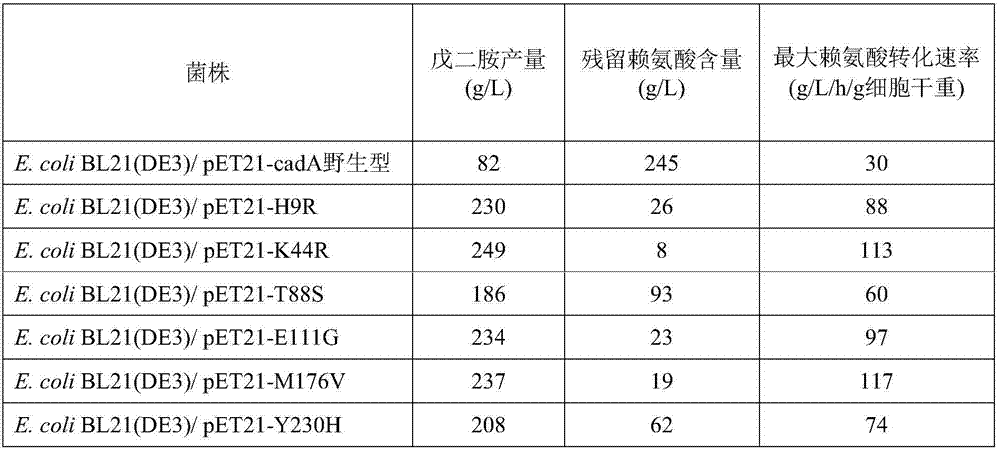
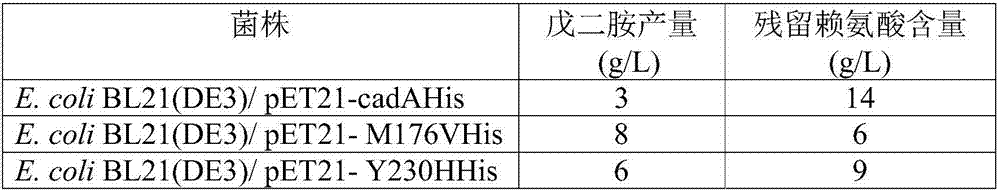
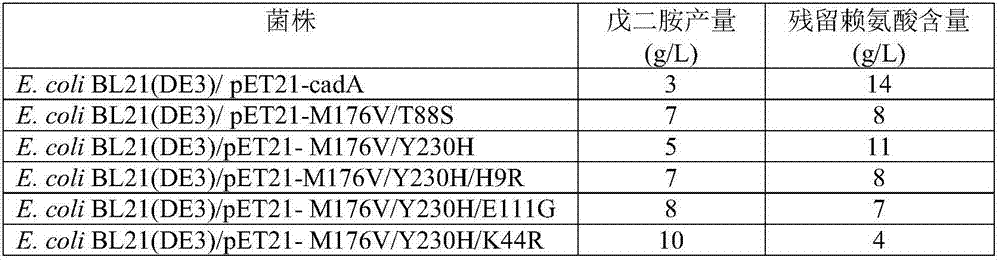
The invention discloses a novel lysine decarboxylase, the amino acid sequence of which is from the mutation of a sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:1, and one or more amino acid residue sites chosen from the following group are mutated: site 9, site 44, site 88, site 111, site 176 and site 230. The activity of 1,5-pentanediamine produced from lysine catalyzed by lysine decarboxylase disclosed by the invention is remarkably increased, consequently, the dosage of a catalyst can be reduced, and ultimately the production cost is reduced. The invention further provides an expression vector containing a coded sequence of the lysine decarboxylase, a host cell capable of expressing the lysine decarboxylase, application of the expression vector and the host cell in the production of the 1,5-diaminopentane and production methods.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
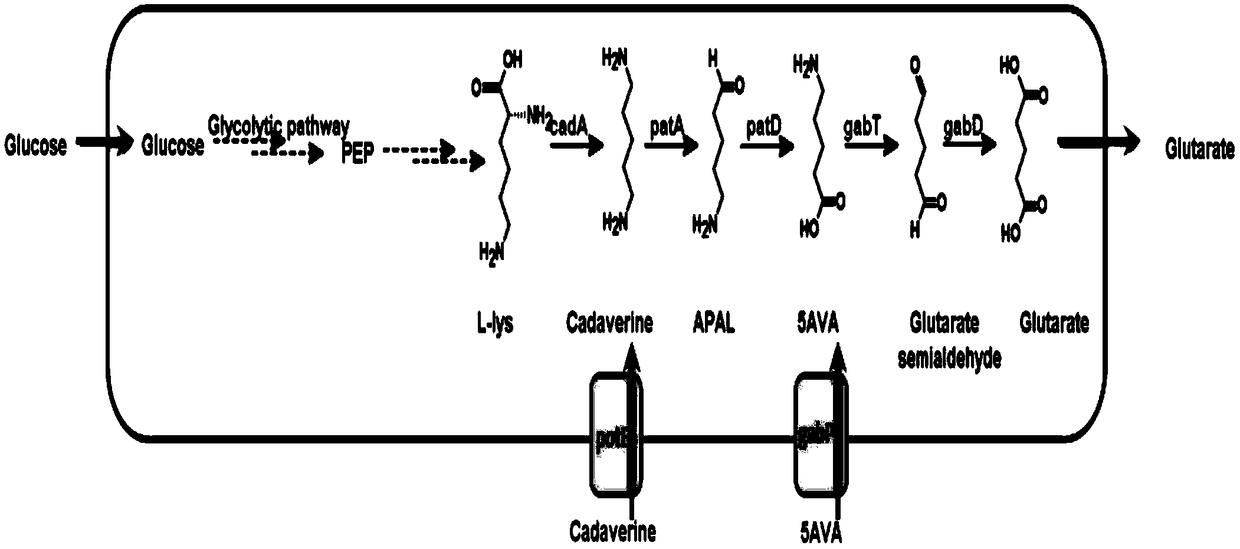
Recombinant escherichia coli for efficiently producing glutaric acid and construction method of recombinant escherichia coli
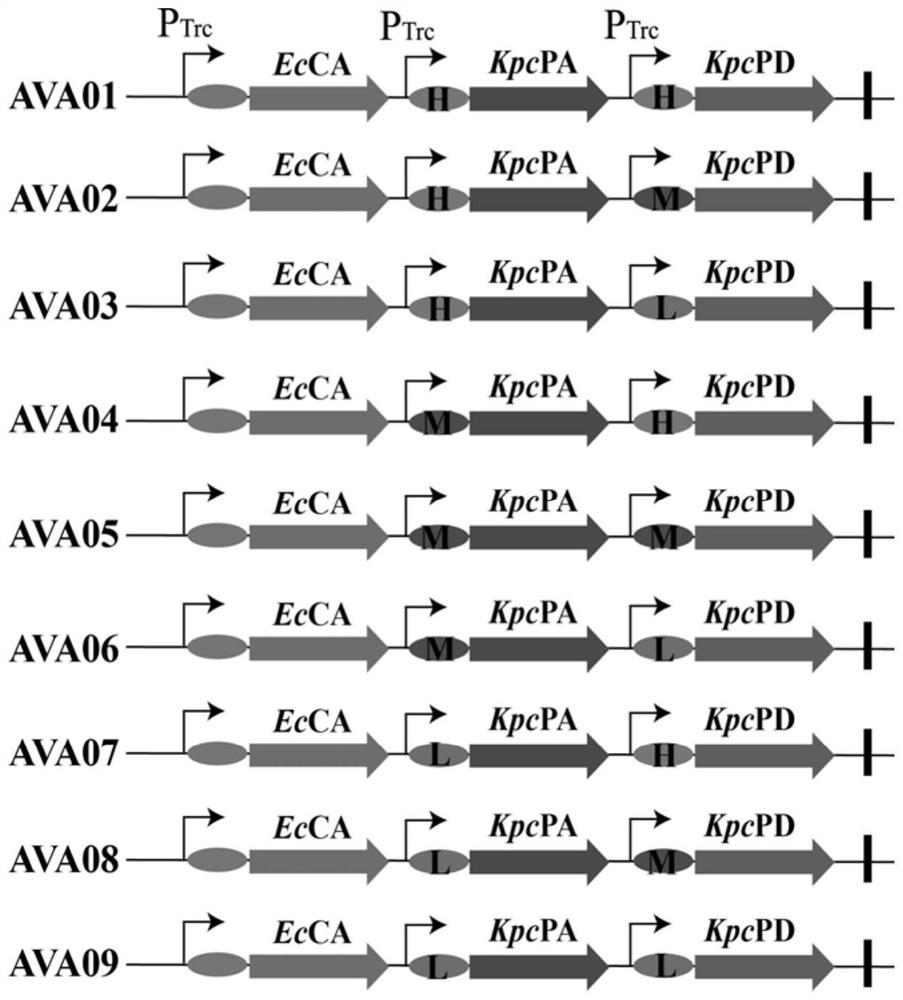
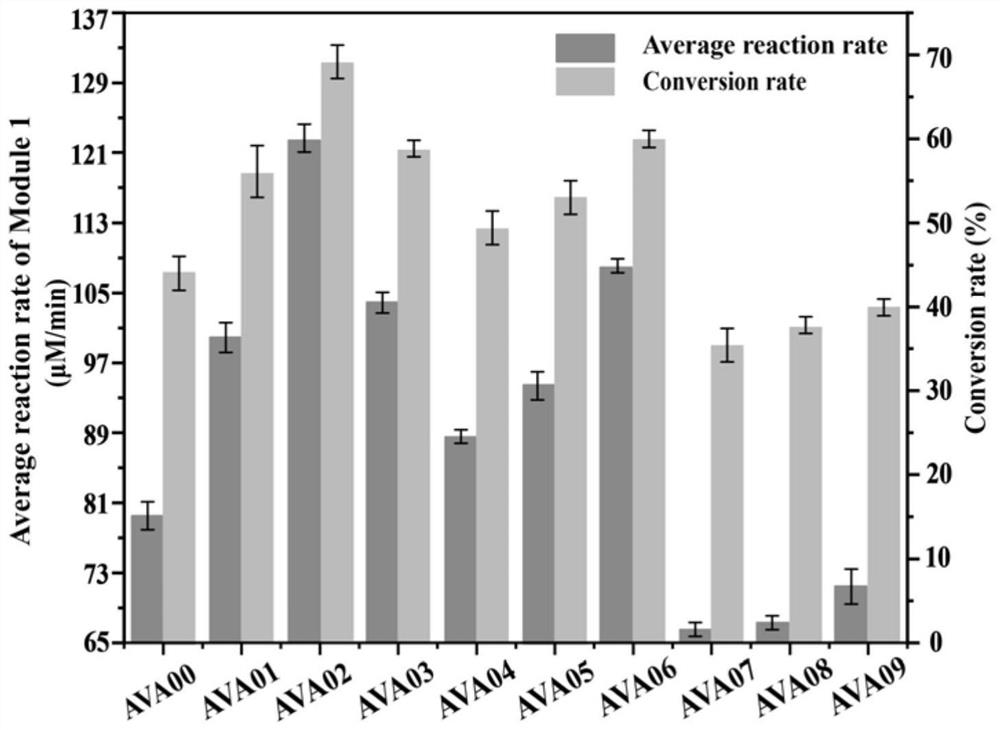
ActiveCN112226398AIncrease productionAchieve metabolic flux balanceBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliAmpicillin
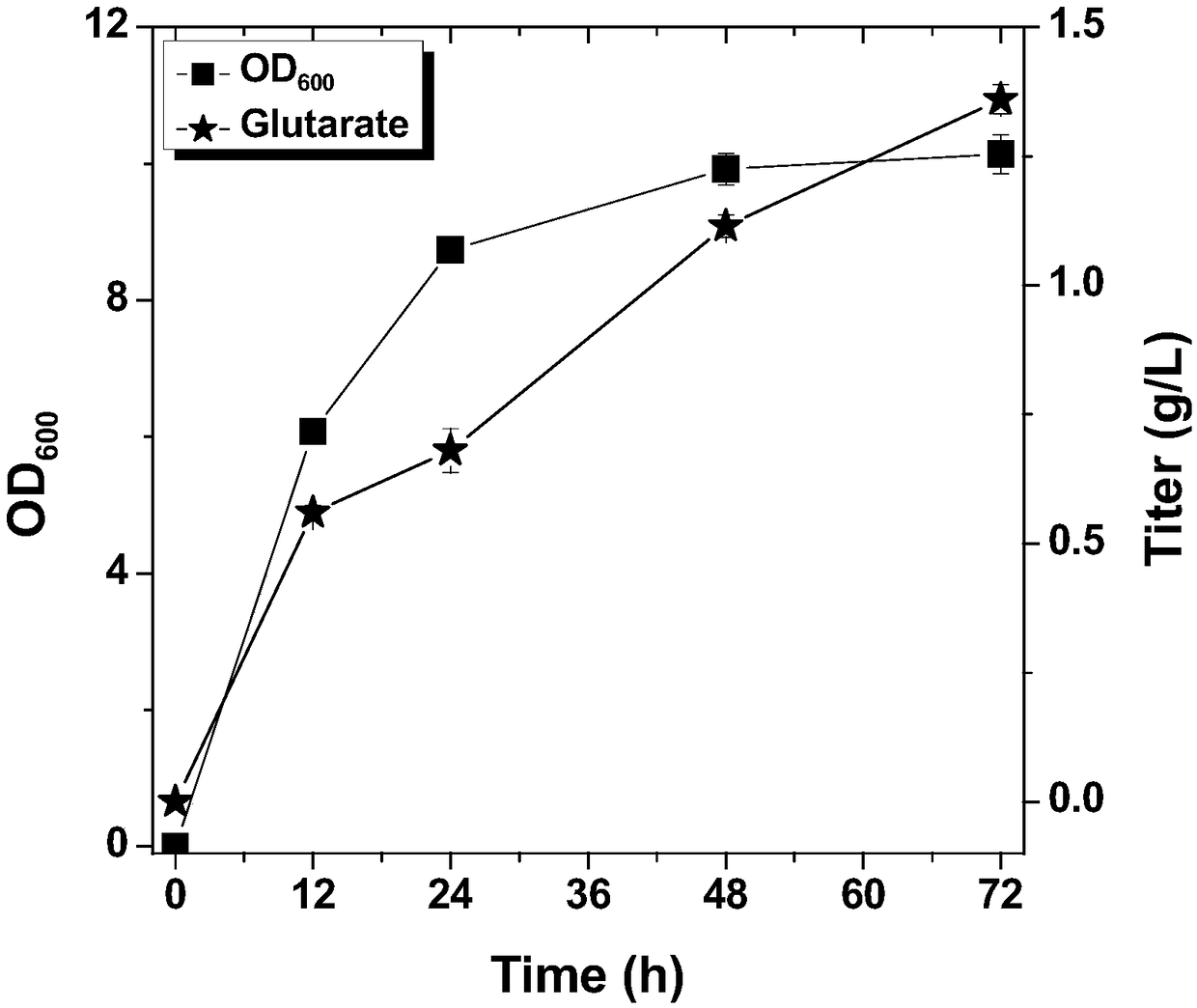
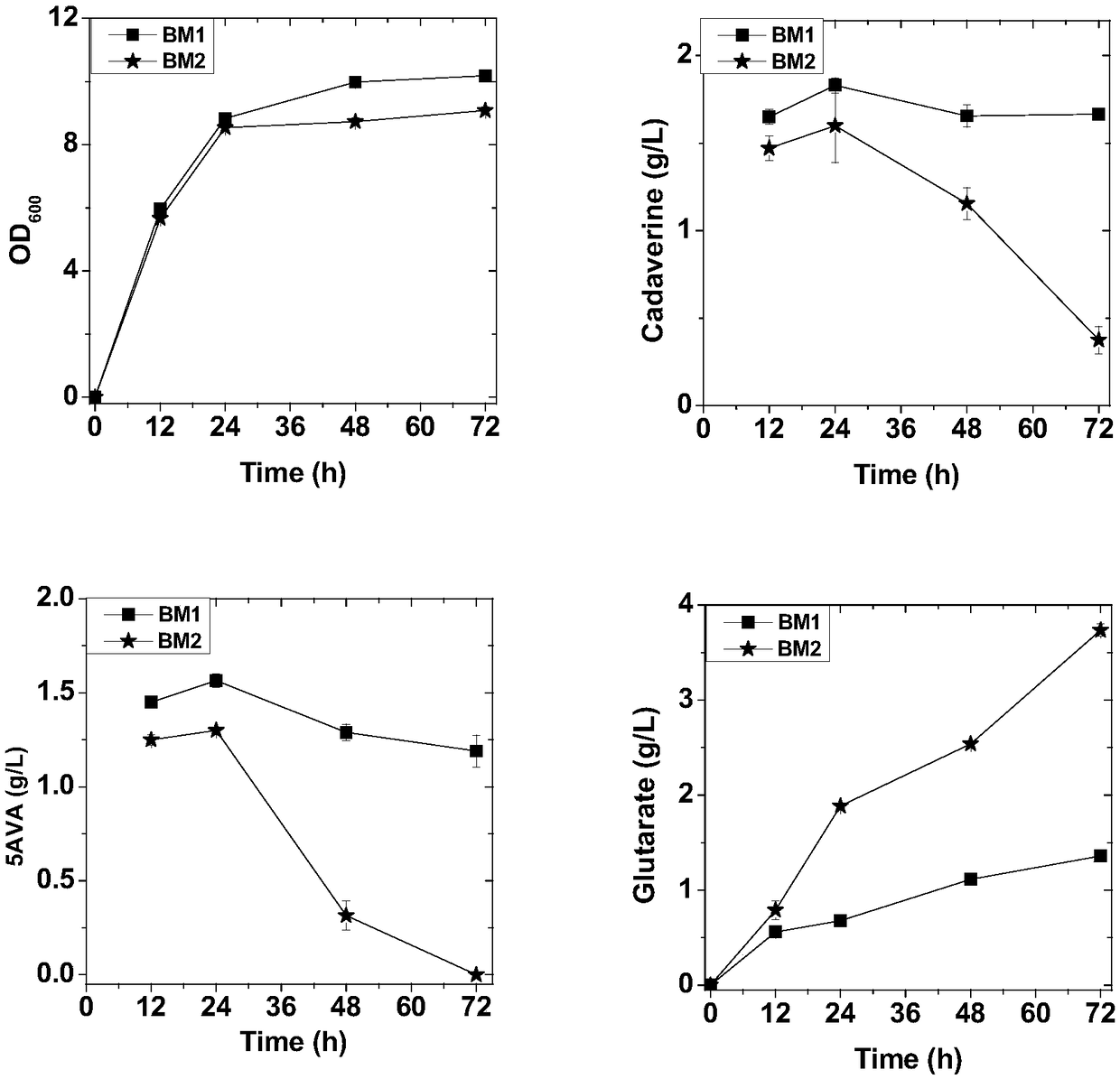
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli for efficiently producing glutaric acid and a construction method of the recombinant escherichia coli, and belongs to the technical field of metabolic engineering. According to the invention, a lysine decarboxylase gene cadA, a butanediamine transaminase gene patA and a gamma-aminobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase gene patD are obtained by cloning from an Escherichia coli MG1655 genome through a molecular biological means, and a 4-aminobutyric acid transaminase gene gabT and a succinic acid hemialdehyde dehydrogenase gene gabD are obtained by cloning from a Pseudomonas fluorescens genome. After a constructed recombinant expression vector pETM6R1-cadA-RBS01-patA-RBS02-patD-gabT-gabD is introduced into E.coli W3110, a recombinant strain Glu-02 for efficiently producing the glutaric acid is obtained through ampicillin resistance plate screening. The recombinant strain is fermented for 60 hours in a 5L fermentation tank by adopting a fed-batchfermentation strategy, the glutaric acid yield reaches 56.2 g / L, and the conversion rate is 62.2%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Engineered Escherichia coli strain capable of realizing high-yield production of pentamethylene diamine and method for high-yield production of pentamethylene diamine via same
ActiveCN111117940ALow costReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliInducer
The invention relates to an engineered Escherichia coli strain capable of realizing high-yield production of pentamethylene diamine and method for high-yield production of pentamethylene diamine via the same. The engineered Escherichia coli strain is Escherichia coli with an accession number of CGMCC No. 17454. The method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing engineered Escherichia colistrain TJU-cadA-1 for exogenous expression of L-lysine decarboxylase, wherein the enzyme activity of the L-lysine decarboxylase is about 100 times the enzyme activity of a no-load strain; (2) carryingout permeability treatment on L-lysine decarboxylase-rich whole cells, wherein the enzyme activity of the L-lysine-rich decarboxylase in permeabilized cells is 3-4.5 times the enzyme activity of thewhole cells; and (3) catalyzing L-lysine hydrochloride to produce pentamethylene diamine by using the permeabilized cells, wherein the yield of pentamethylene diamine is 90%-100%, and the concentration of pentamethylene diamine can reach 220 g / L or above. According to the method, the L-lysine hydrochloride is used for efficiently producing the pentamethylene diamine; and compared with the prior art, an expensive IPTG inducer is not needed in the invention, so the method has the advantages that mass transfer efficiency is high, yield is high, production cost is low, and higher economic feasibility and practicability are obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Novel lysine decarboxylase and application thereof
PendingCN107177641AImprove stabilityImprove temperature stabilityBacteriaFermentationMicrobiologyThermal stability
The invention discloses novel lysine decarboxylase. The amino acid sequence of the novel lysine decarboxylase is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID NO: 2. The lysine decarboxylase can be expressed efficiently in a host cell, has superior thermal stability, and has the characteristics of high activity under a neutral to weakly-alkaline condition, so that the novel lysine decarboxylase is superior to conventional lysine decarboxylase. The invention further provides an expression vector including an encoding sequence of the lysine decarboxylase, a host cell capable of expressing proteins, application of the expression vector and the host cell to production of 1,5-pentamethylene diamine, and a production method.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
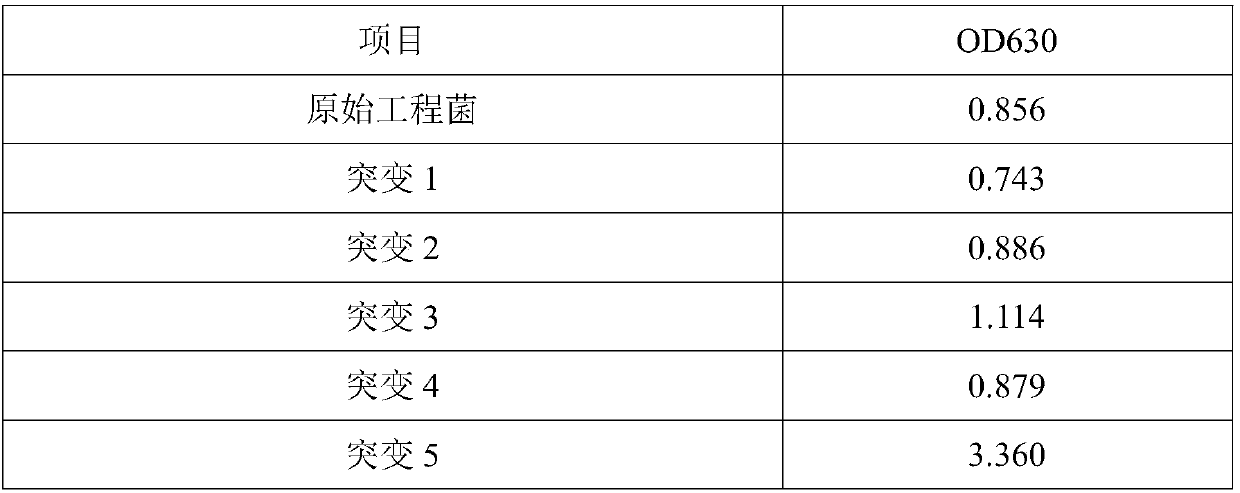
Lysine decarboxylase mutant library construction method and high-throughput screening method of high-activity or low-activity mutant strains
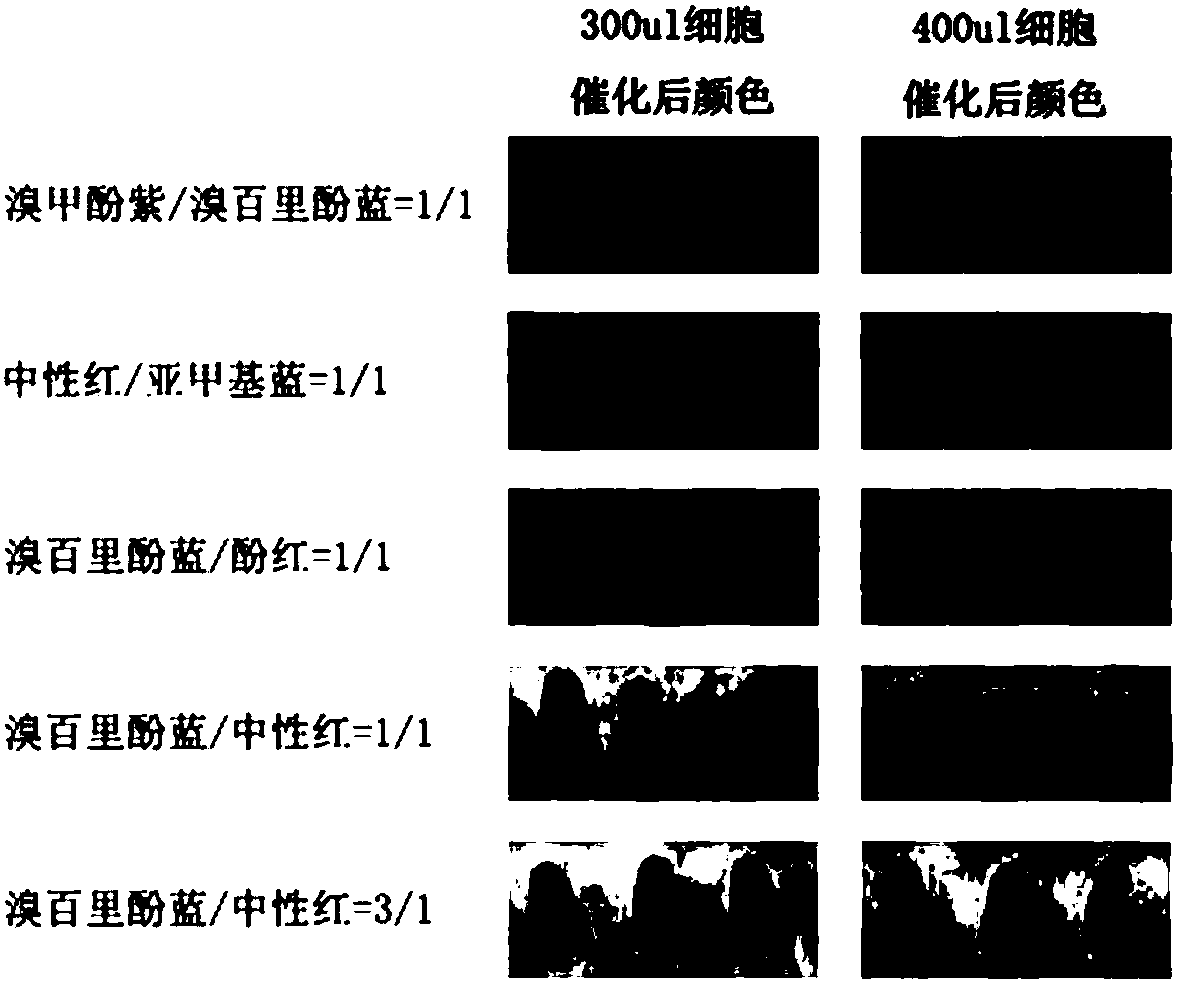
PendingCN108796619AOvercoming the shortcomings of low efficiency and difficult success in error-prone PCROvercome the shortcomings of low efficiency and difficult successMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEnzymatic digestionLow activity
The invention relates to a lysine decarboxylase mutant library construction method and a high-throughput screening method of high-activity or low-activity mutant strains, in particular to an error-prone PCR orthogenesis mutant library construction method applicable to genes with the length being higher than 2000bp such as the lysine decarboxylase and the high-throughput screening method of the high-activity or low-activity mutant strains. The lysine decarboxylase mutant library construction method and the high-throughput screening method have the advantages that the method using error-prone PCR subsection mutation, PCR integration and DpnI enzymatic digestion and using series of pH indicators to indicate pH change is adopted, the difficulties that a conventional error-prone PCR method cannot effectively build a long-fragment-gene mutant library and is low in connecting efficiency, and the pH change of the method exceeds the indicating range of indicators are solved, and the fast and simple method is provided to screen enzyme-activity-increased or enzyme-activity-lowered mutant strains from a lysine decarboxylase mutant library.
Owner:CATHAY R&D CENT CO LTD +1
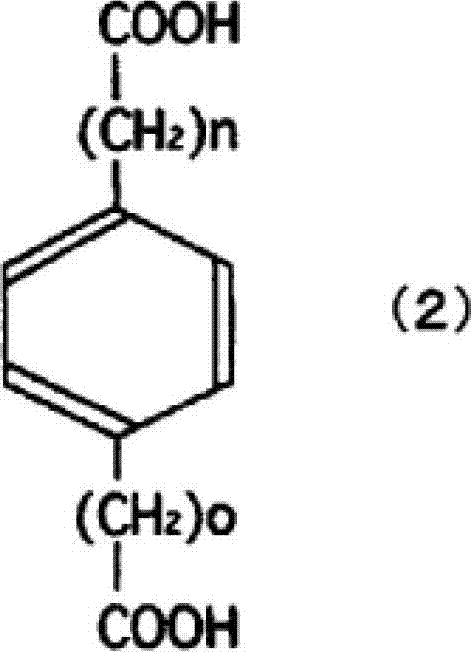
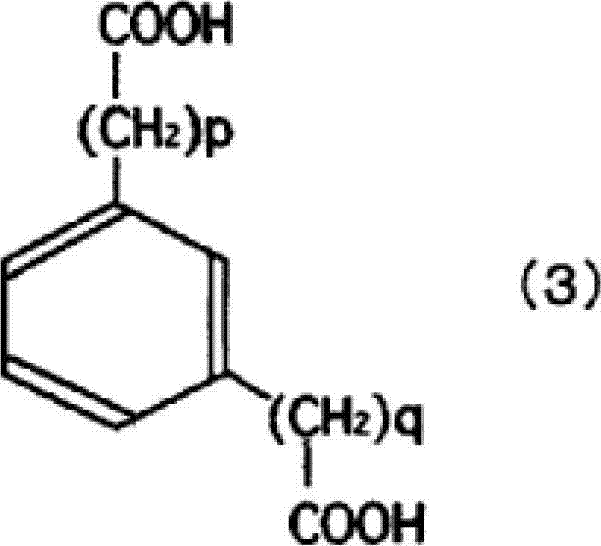
Method for biologically synthesizing glutaric acid
ActiveCN109136295ASolve the accumulationGood effectTransferasesOxidoreductasesDe novo synthesisLysine
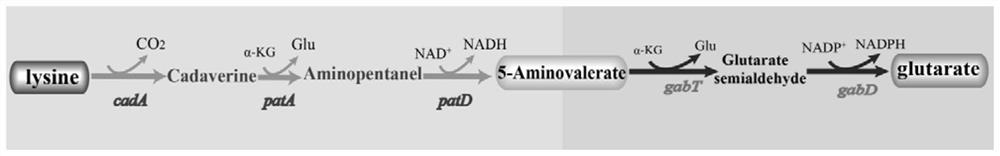
The invention discloses a method for biologically synthesizing glutaric acid. A synthetic route comprises five enzymes which include lysine decarboxylase (cadA), pentadiamine transaminase (patA), 5-aminovalerate hemialdehyde dehydrogenase (patD), 5-aminovalerate transaminase (gabT) and glutarate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (gabD). Genes encoded by the enzymes are expressed in a host, and a production host for producing glutaric acid by lysine can be acquired. The genes are led into a high-yield strain of the lysine, so that denovo synthesis of the glutaric acid is achieved. The invention further discloses a method for reinforcing production of the glutaric acid. Pentane diamine transport protein and 5-aminovaleric acid transport protein co-expressed in engineering strains, intermediates outside cells are transported into the cells, so that the glutaric acid is efficiently produced. The method has application prospects in industrial production of the glutaric acid.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Recombinant escherichia coli for producing pentamethylene diamine and application of recombinant escherichia coli
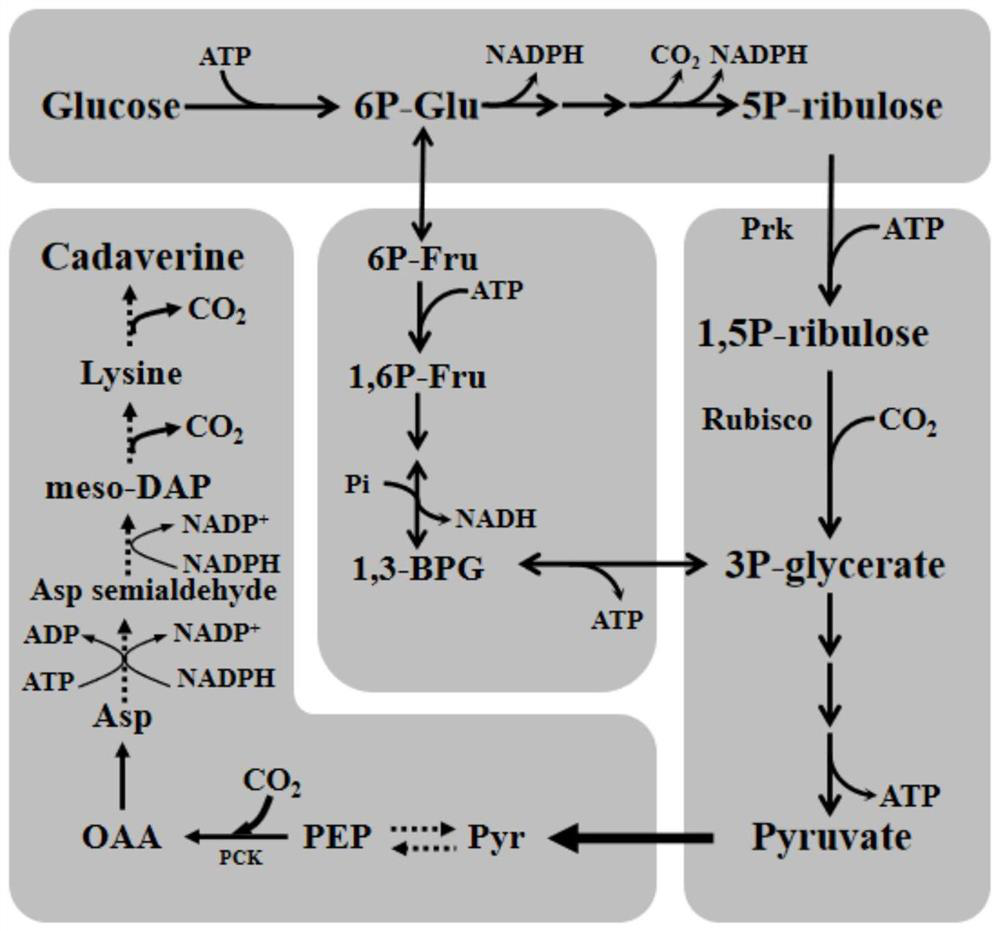
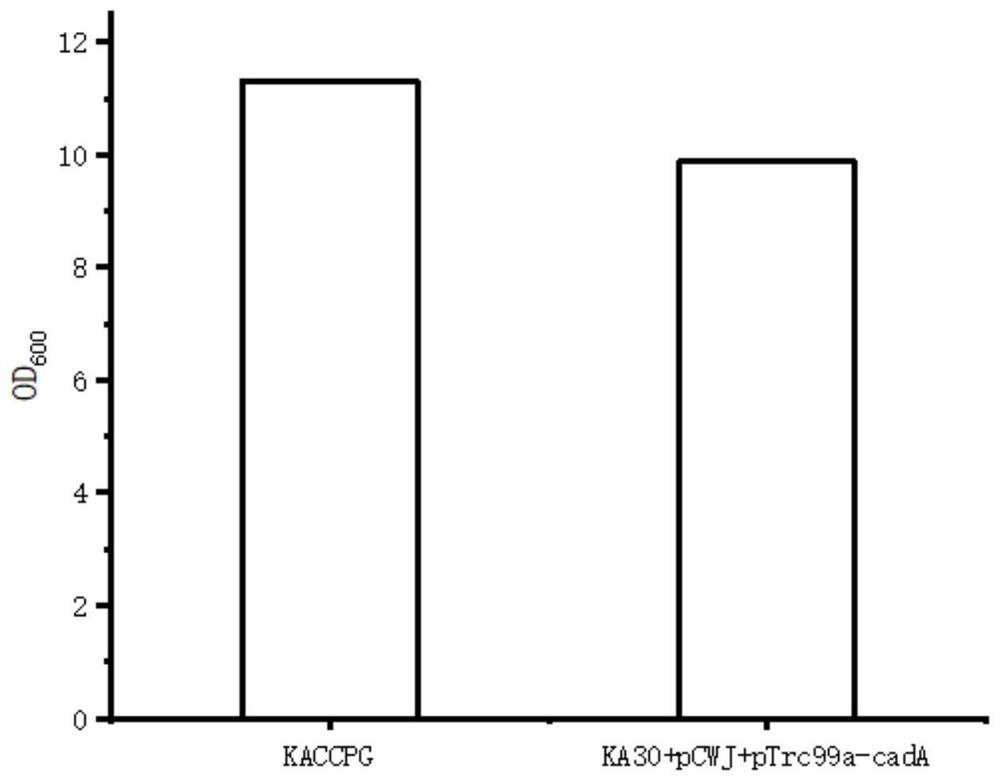
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli for producing pentamethylene diamine and application of the recombinant escherichia coli. A ribulose diphosphate carboxylase gene in rhodospirillum, a ribose phosphate kinase gene and a lysine decarboxylase gene in spinach are synthesized from the beginning, PCR copy an escherichia coli molecular chaperone gene to construct a plasmid pTrc99a-cadA-cbbM and a plasmid pCWJ-prkA-GroEL / GroES, the double-plasmid recombinant bacteria grow well in a specific culture medium, and glucose is efficiently utilized. According to the recombinant escherichia coli, inducers arabinose and IPTG are respectively added in different time periods, the heterologous gene expression is stable, the reaction system is simple, the condition is mild, the period is short, few byproducts are produced, the method is clean and pollution-free, the method is a simple, rapid and efficient production way, and the fermentation result shows that the yield of the recombinant escherichia coli KACCPG is obviously improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Molecular modification method for improving activity and stability of lysine decarboxylase
InactiveCN110004131AAvoid uncertaintyImprove stabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEnzyme stabilisationRandom mutationOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a molecular modification method for improving the activity and stability of lysine decarboxylase. One end of a lysine decarboxylase (LDC) molecule is connected with a polypeptide segment (EK). The method includes the steps of firstly, obtaining a gene segment of the lysine decarboxylase molecule; secondly, connecting a gene segment for encoding an EK polypeptide to one endof a lysine decarboxylase gene; thirdly, connecting the lysine decarboxylase gene connected with an EK polypeptide gene to an expression carrier, transferring the gene into a host, and expressing themodified lysine decarboxylase (LDC-EK). By rationally modifying the enzyme molecule, the random mutation uncertainty and the complicated screening process are avoided; the modified lysine decarboxylase has high stability and catalytic activity. The catalytic activity of the LDC-EK is tripled, the high activity can be kept within the wide temperature range, and various organic solvents can be tolerated. The method is easier to operate, and protein is easier to prepare after modification.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Modifications to lysine decarboxylase enzymes
Provided are CadA polypeptides with mutations that increase activity in alkaline pH compared to the wild-type lysine decarboxylase. Methods of generating such mutant polypeptides, microorganisms genetically modified to over-express the mutant polypeptides, and methods of generating such microorganisms are also provided.
Owner:CATHAY R&D CENT CO LTD +1
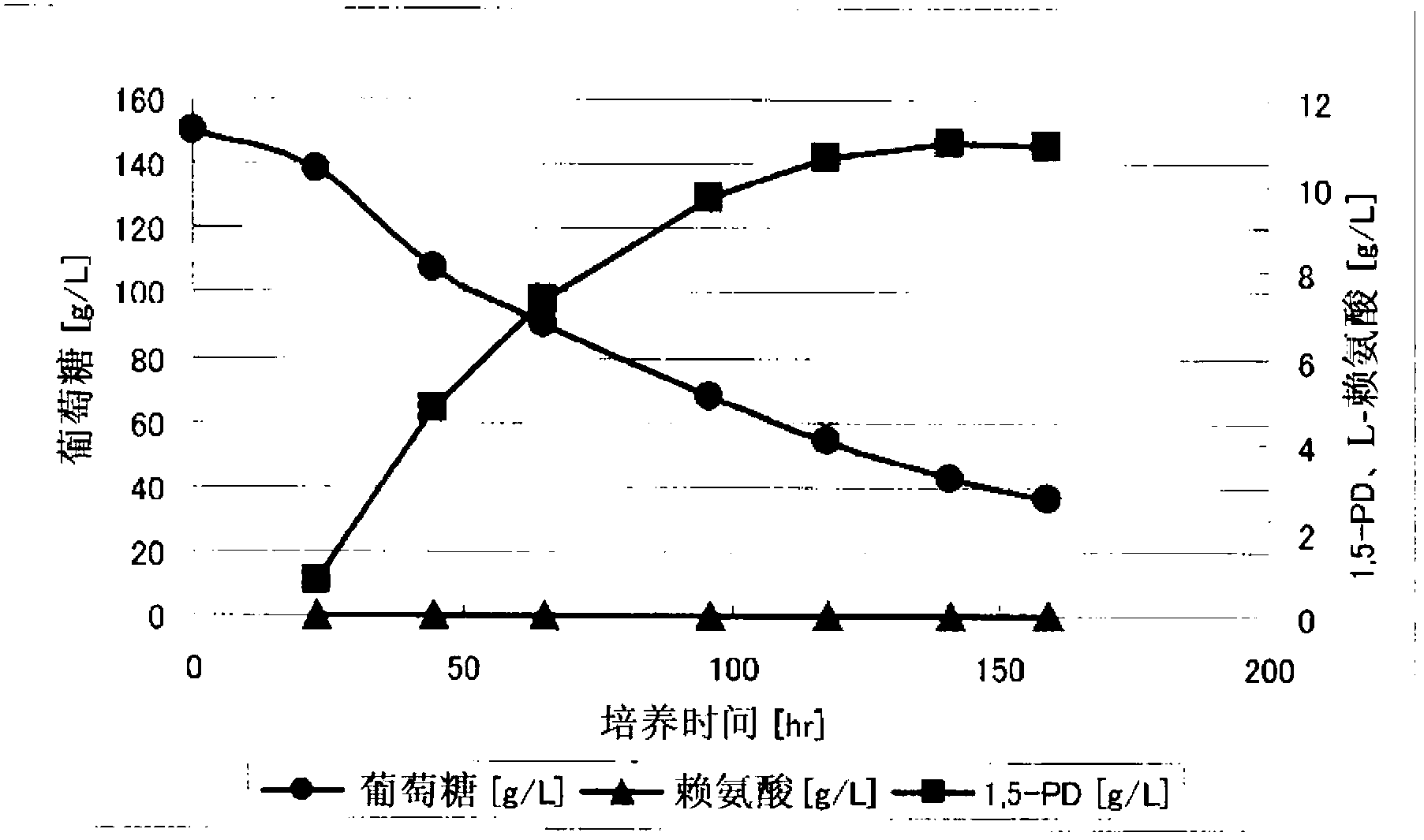
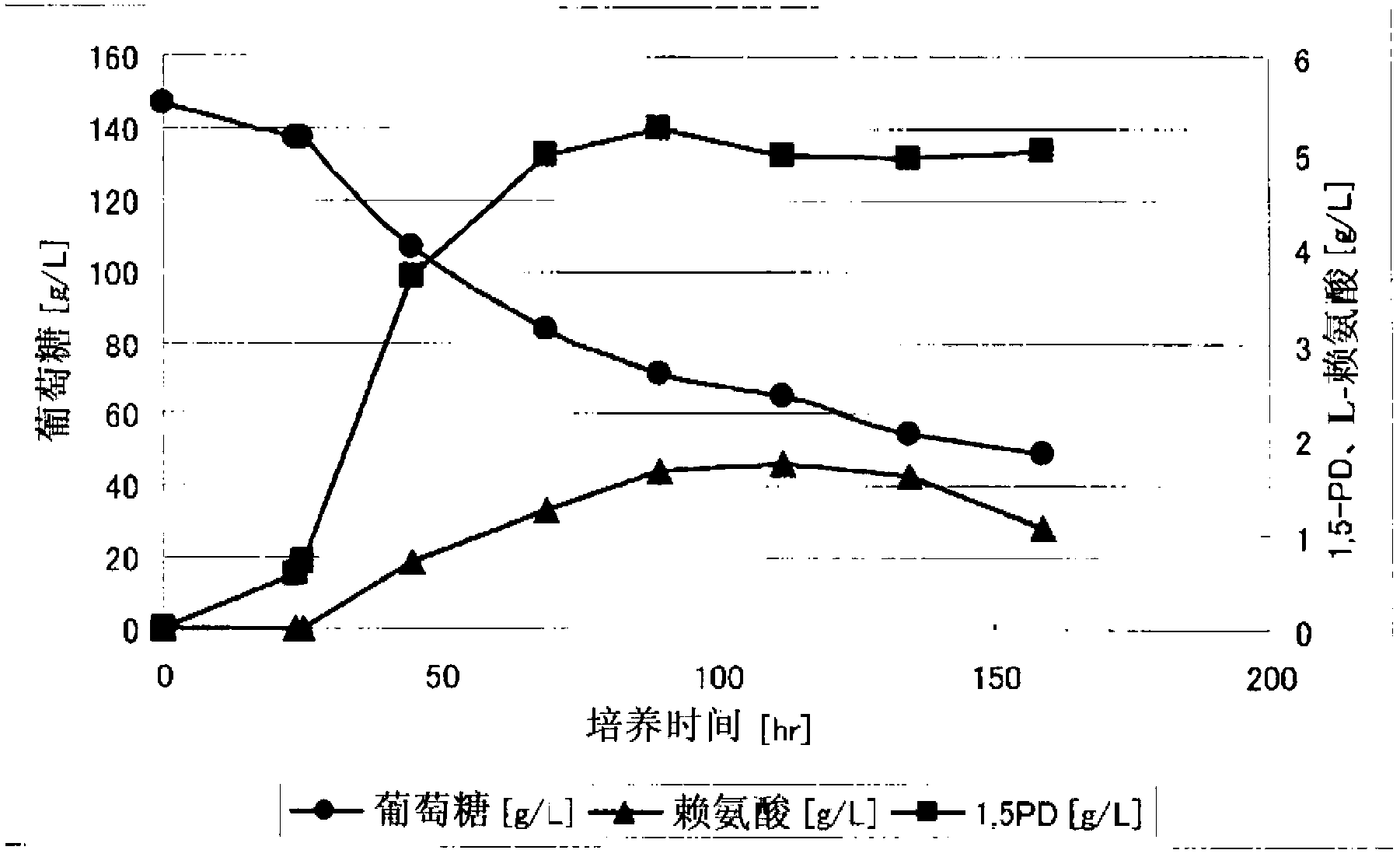
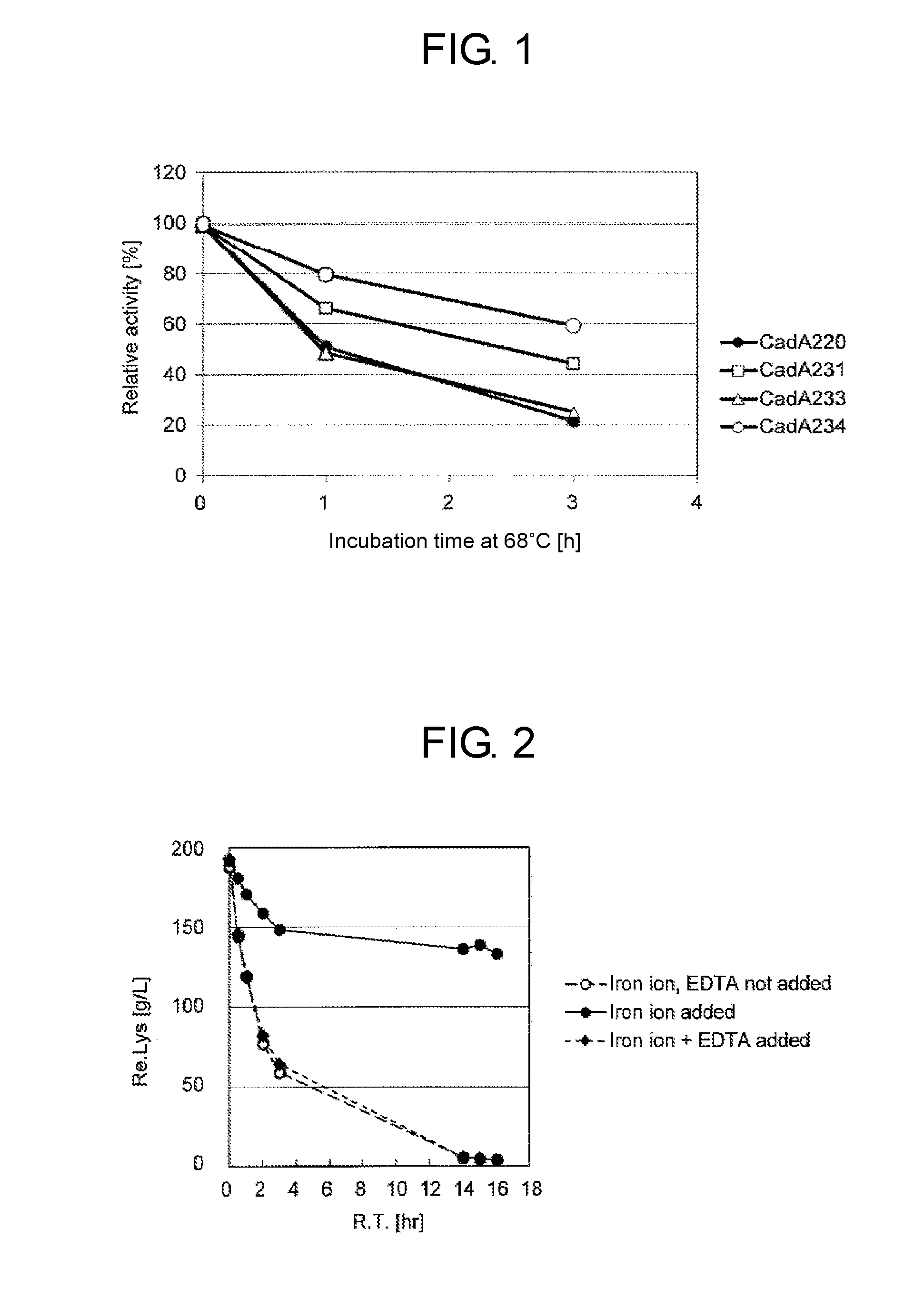
Method of Producing 1,5-Pentadiamine Using Lysine Decarboxylase Mutant Having Improved Thermal Stability
ActiveUS20160376580A1Efficient productionSuitable for productionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMutantThermal stability
The present invention provides methods for producing 1,5-pentamethylenediamine (“1,5-PD”) efficiently in a manner suitable for an actual production. Specifically, the present invention provides a method of producing 1,5-pentamethylenediamine including allowing a lysine decarboxylase mutant to act on L-lysine and / or a salt thereof, wherein said lysine decarboxylase mutant has an amino acid sequence selected from the group consisting of:(a) the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1,(b) an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, but having one or several amino acid residue substitutions, deletions, insertions or additions, and(c) an amino acid sequence having 90% or more identity to the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1, and having a lysine decarboxylation activity,and wherein said lysine decarboxylase has improved thermal stability.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com