Citrobacter, application of citrobacter in treatment of sulphate-containing waste water, and separation and identification method of citrobacter
A Citrobacter and identification method technology, applied in the field of sulfate-containing wastewater treatment, can solve the problems of long cycle and cumbersome screening process, and achieve the effects of short cycle, simple screening process and easy cultivation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Sediment samples collected from the Hengshi River Basin in Dabaoshan Mining Area, Guangdong Province were used for enrichment culture of sulfate-reducing bacteria under anaerobic conditions using Postgate B-type medium. In order to simulate the acidic environment of acid mine wastewater, the phosphate ratio was adjusted to make the pH of the culture medium 5.6. Dig 0.1-0.5 grams of sediment samples with a spoon and transfer them to a 25mL anaerobic tube in an ultra-clean bench, and add 20mL of postgate B-type medium that has been deaerated and sterilized by autoclaving. Isolated from outside air. The whole operation was carried out in an anaerobic operation box. After the inoculation, the cells were transferred to a constant temperature incubator at 25°C for 7 days of cultivation. During the cultivation process, it was judged whether the enrichment was successful by observing whether its color turned black. After repeated transfer 5 times, a stable sulfate-reducing ba...
Embodiment 2
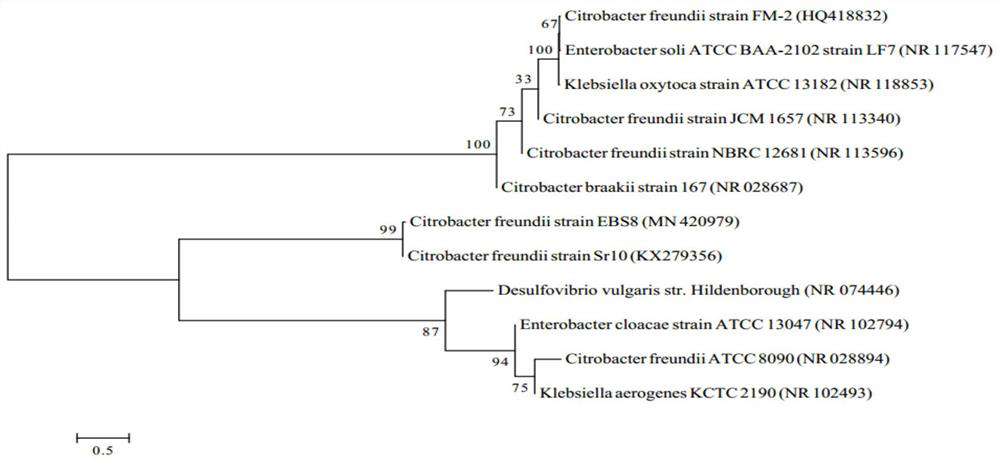
[0046] Dilute the colony collected in the dialysis bag isolation group to 10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 In the anaerobic operation box, take each dilution of the bacterial suspension and spread it on the solid Postgate B-type medium respectively, put part of the plate upside down in the anaerobic tank, and place the other part in the aerobic incubator. The temperature for culturing under aerobic conditions and aerobic conditions was 30°C, and the culturing time for both anaerobic and aerobic conditions was 3 days until colonies grew out. Pick a single colony, inoculate it on a liquid medium, and culture it anaerobically in a shaker at 30°C and 150 rpm for 5-7 days, select an anaerobic tube that turns black, and then continue to streak the bacterial solution in the anaerobic tube with a plate. After 3 times of solid-liquid medium alternate screening, under anaerobic conditions, the 2+ and SO 4 2- On the solid medium, the target strain produced black colonies after one week; under ae...
Embodiment 3
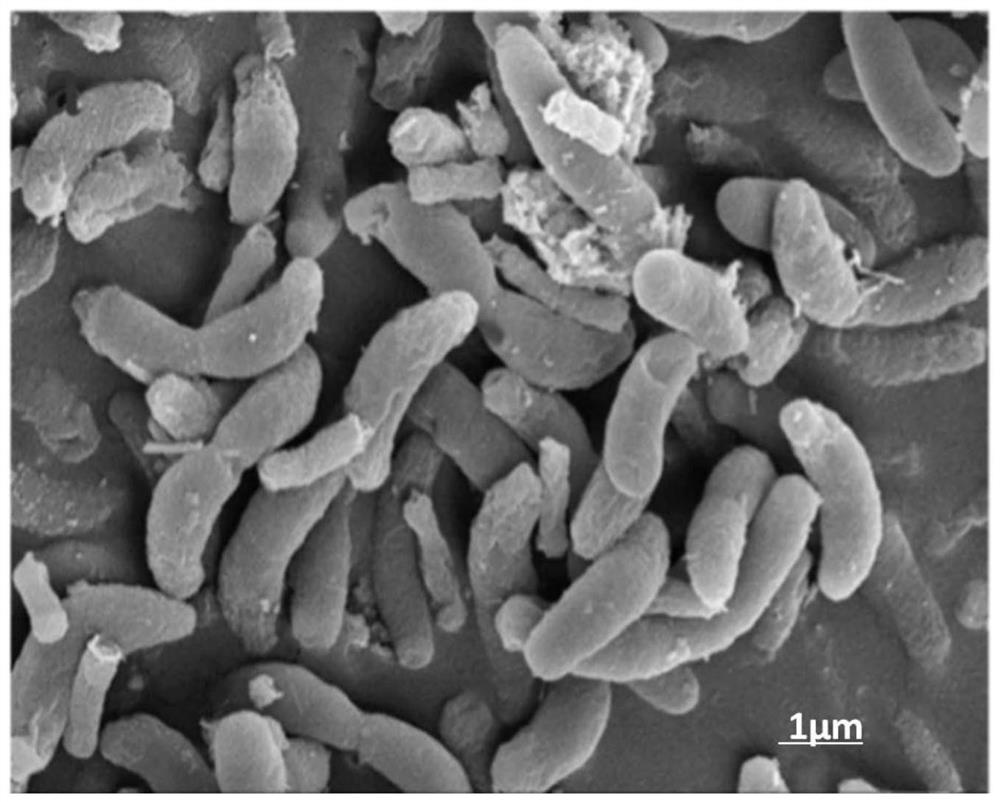
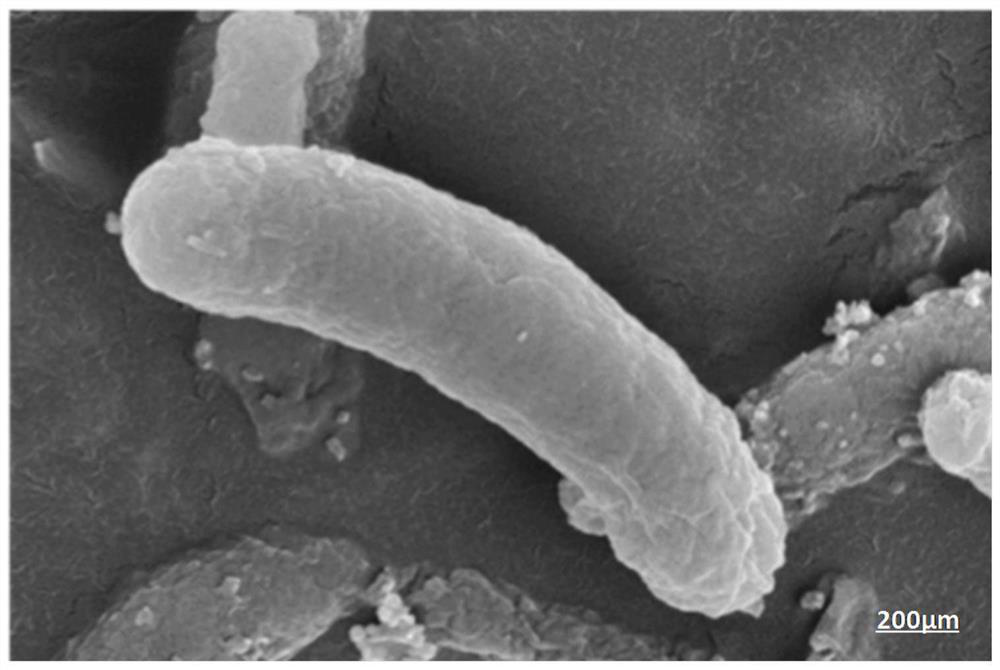
[0050] Take the bacterial solution grown to the logarithmic phase (OD 600 is about 0.3), centrifuged at 4°C and 8000×g for 5 min, and discarded the supernatant. After adding 5mL of 2.5wt% pentanediol solution and fully shaking, place it in a refrigerator at 4°C for 2-4h. After washing with 10mmol / L phosphate buffer for 3 times, use ethanol gradient dehydration, followed by 30%, 50%, 70%, 85%, and 95% ethanol once each (gradient concentration of ethanol is prepared with phosphate buffer ), dehydrated twice with 100% ethanol, and finally washed twice with isoamyl acetate. Each step needs to be fully shaken and maintained for more than 20 minutes, and finally centrifuged at 8000×g for 5 minutes, discard the supernatant, and proceed to the next step. After the treated bacteria were freeze-dried, a small amount of bacteria was placed on a sample plate covered with conductive glue, sprayed with gold for 120 seconds, and observed with a field emission scanning electron microscope. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com