Direct vitrification arsenic fixation method for arsenite-containing arsenic-containing material
An arsenite and vitrification technology, used in chemical instruments and methods, solid waste removal, transportation and packaging, etc. Long process and other problems, to achieve the effect of wide application, harmless treatment and simple treatment method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
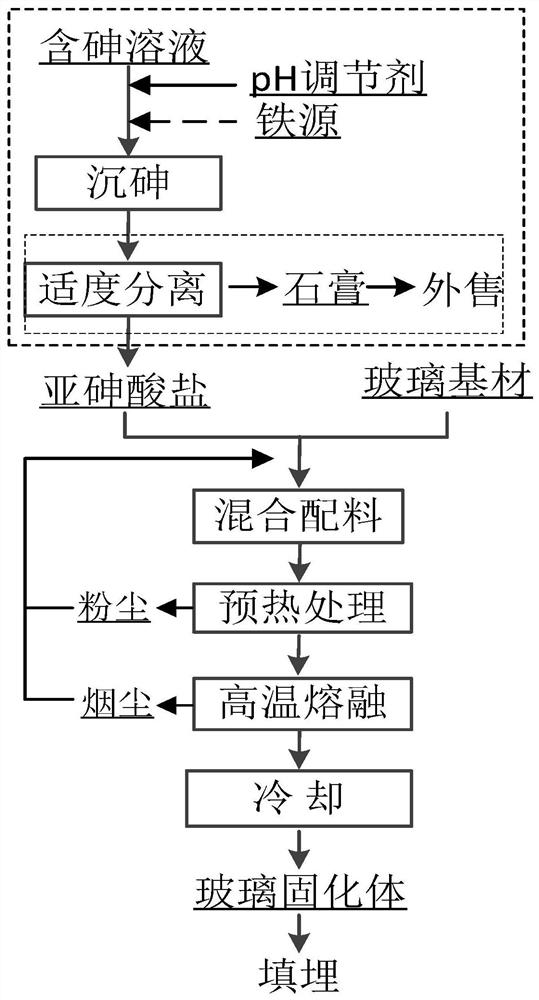
[0039] This embodiment provides a method for direct vitrification of arsenic-containing materials mainly composed of ferric arsenite to fix arsenic. like figure 1 As shown, the specific steps of the method in this embodiment are as follows:
[0040] Wherein said arsenic-containing material is the ferrous arsenite slag (arsenic and iron contents are respectively As 32.08%, Fe 27.12%).
[0041]The glass substrate contains copper smelting slag (the main component is: Fe 2 o 3 63.6%, SiO 2 23.75%, As 2 o 3 0.264%, Al 2 o 3 2.86%, CaO 1.76%, MgO 1.08%), quartz sand and sodium carbonate.
[0042] Mix the arsenic-containing material, copper smelting slag, quartz sand, and sodium carbonate according to the mass ratio of 27:20:36:14.2, grind them to a powder with a particle size of 0.8mm, and preheat at 250°C for 2.0h (preheat treatment The advantage is to slowly heat the mixture in advance to remove moisture and reduce the impact on the high-temperature melting process), ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] This embodiment provides a method for direct vitrification of arsenic-containing materials mainly composed of ferric arsenite to fix arsenic.
[0045] The arsenic-containing material is the ferrous arsenite slag obtained by adding ferric sulfate to deposit arsenic after the arsenic-containing polluted acid (As 8.86g / L) is neutralized by lime to reduce the acidity (the arsenic and iron contents are respectively As 32.08%, Fe 27.12% %), the glass substrate contains quartz sand and sodium carbonate.
[0046] The specific steps of the present embodiment method are as follows:
[0047] Mix the arsenic-containing material, quartz sand, and sodium carbonate according to the mass ratio of 58.65:26.6:14.75, grind to a powder with a particle size of 0.6mm, and preheat at 100°C for 0.5h. Then heat up to 1400°C for high temperature melting and heat preservation for 2 hours. After the reaction is completed, it is naturally cooled with the furnace to obtain arsenic-containing glass...
Embodiment 3
[0049] This embodiment provides a method for vitrifying arsenic fixation using calcium arsenite as the main arsenic-containing material.
[0050] The arsenic-containing material is calcium arsenite slag obtained from arsenic-containing polluted acid (As 10.8g / L) through lime neutralization and precipitation (As and calcium contents are respectively As 31.39%, Ca 28.9%), and the glass substrate contains quartz sand and sodium carbonate.
[0051] The specific steps of the present embodiment method are as follows:
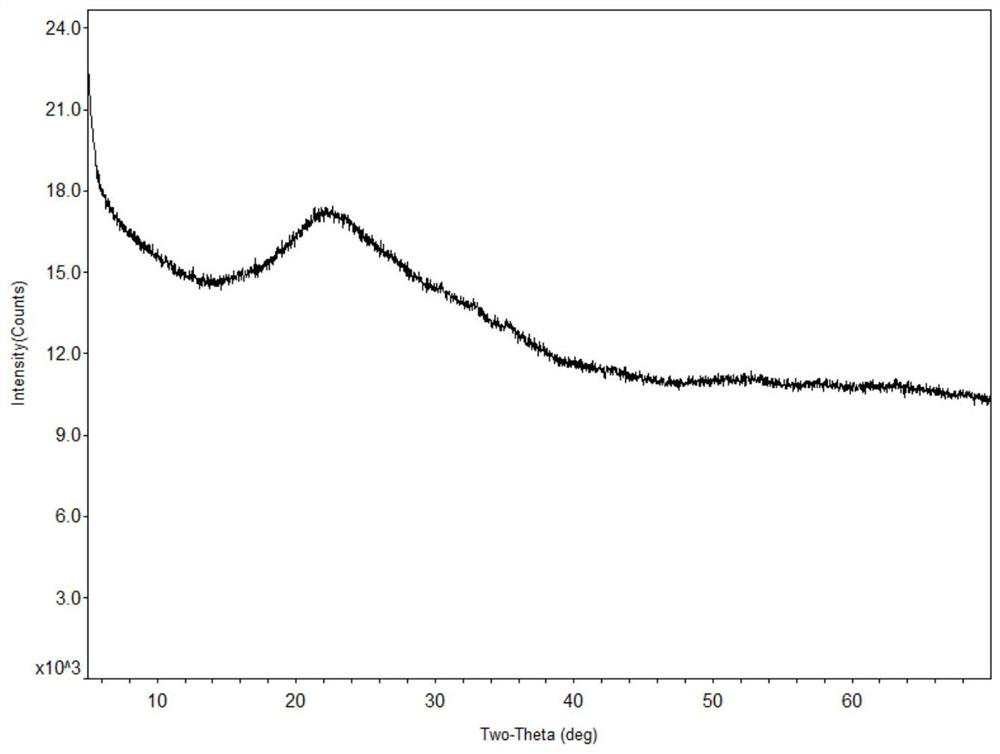
[0052] Mix arsenic-containing materials, quartz sand, and sodium carbonate at a mass ratio of 21:57:22, grind them to a powder with a particle size of 0.4mm, preheat at 550°C for 10 minutes, and then heat up to 1350°C for high temperature melting and heat preservation for 1 hour. After the reaction is completed, it is naturally cooled with the furnace to obtain arsenic-containing glass solidified body. The composition (mass percentage) of the arsenic-containing glas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com