D-pi-A type AIE-TADF near-infrared luminescent material as well as preparation method and application thereof
A luminescent material, near-infrared technology, applied in luminescent materials, chemical instruments and methods, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, etc., can solve the high cost of transition metal complex phosphorescent materials, heavy metal environmental pollution, and the difficulty of obtaining organic near-infrared luminescent materials High-efficiency luminescence, reduction of luminous efficiency of organic near-infrared luminescent materials and other issues, to achieve excellent carrier transport performance, reduce non-radiative transitions, and promote the effect of reverse intersystem jumping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The preparation of DPA-ThPh-QCN, the synthetic route is as follows:
[0037]
[0038] Preparation of 6-(4-bromophenyl)quinoxaline-2,3-dicarbonitrile (1)
[0039] In a 500mL two-necked flask, add diaminomaleonitrile (20.0g, 92.5mmol), acetonitrile (350mL), stir to dissolve, add dichlorodicyanobenzoquinone (DDQ) (42.0g), and stir at room temperature for 30min After filtration, the filtrate was concentrated and dried to obtain a reddish-brown solid, which was directly used in the next step without further purification. The intermediate product oxalimide dicyanide (22.0g, 207mmol) and 4-bromo-o-phenylenediamine (25.8g, 118mmol) were mixed, and trifluoroacetic acid (500mL) was added in batches, stirred at room temperature for 8h, and then poured into ice water , filtered, washed. Separation by column chromatography (PE / EA=5 / 1) afforded 12.0 g of an off-white solid (compound 1) (yield: 50.0%). 1H NMR (400MHz, DMSO) δ8.69 (d, J = 2.0Hz, 1H), 8.37 (dd, J = 9.0, 2.1Hz, 1H)...
Embodiment 2
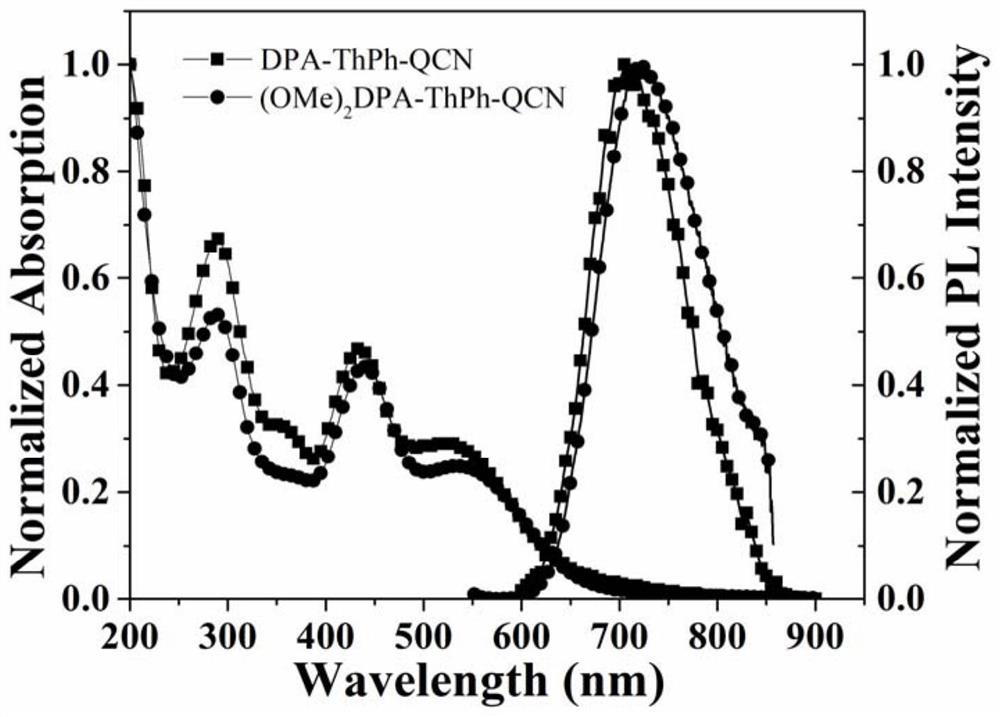
[0055] DPA-ThPh-QCN and (OMe) in embodiment 1 2 AIE performance test of DPA-ThPh-QCN:
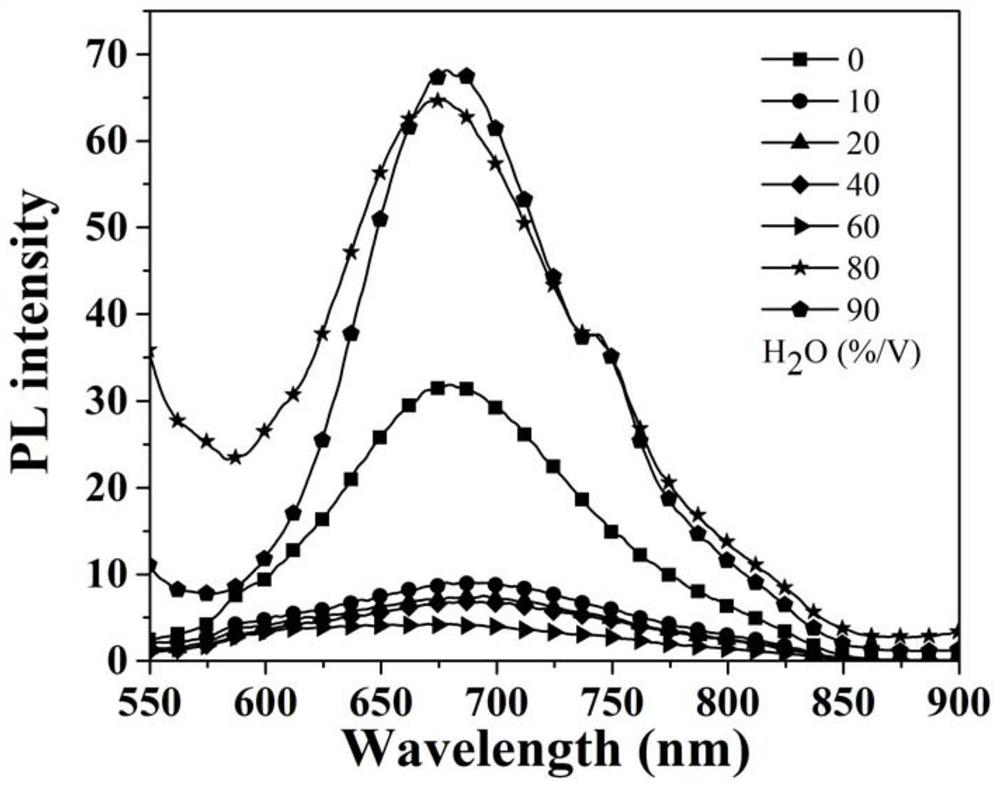
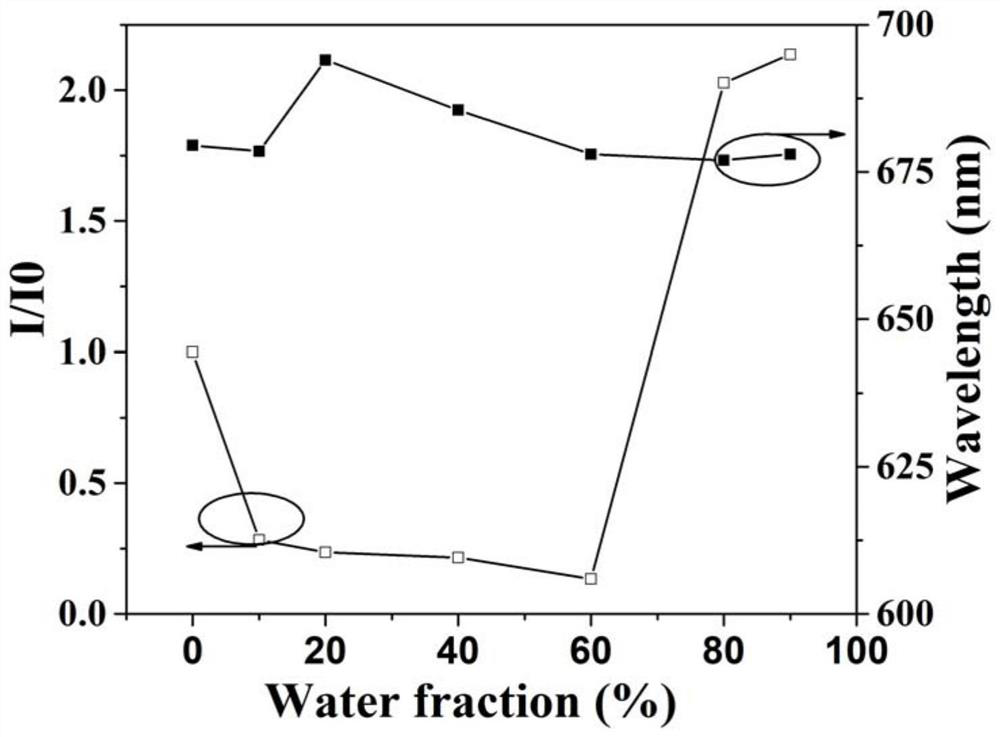
[0056] Make DPA-ThPh-QCN into 10 -5 M tetrahydrofuran / water (THF / H 2 O) mixed solution, measure the photoluminescence property of different ratio water content respectively at room temperature, as figure 2 with image 3 shown.
[0057] from figure 2 It can be seen that: when the excitation wavelength is 500nm, DPA-ThPh-QCN in f w (Water content) w When it is 70%, a stronger emission peak appears at 680nm; when f w =90%, the emission intensity is the largest, the luminous intensity is increased by 14 times, and the maximum emission peak is red-shifted by 10nm. Water content (f w ) and luminous intensity (I / I 0 ), water content (f w ) and the maximum emission peak wavelength as image 3 shown.
[0058] When the excitation wavelength is 500nm, (OMe) 2 DPA-ThPh-QCN also showed a similar phenomenon, such as Figure 4 shown in f w In w =80%, a stronger emission peak appears at 70...
Embodiment 3
[0060] DPA-ThPh-QCN and (OMe) in embodiment 1 2 TADF characteristic test of DPA-ThPh-QCN:
[0061] Combine DPA-ThPh-QCN and (OMe) 2 The film made of DPA-ThPh-QCN is evenly adsorbed on the inner wall of the small test tube, sealed and deoxygenated for more than 30 minutes. Measure its transient decay life at room temperature and nitrogen atmosphere, such as Figure 7 shown.
[0062] from Figure 7It can be seen from the figure that the transient decay lifetime curve of the DPA-ThPh-QCN thin film in a nitrogen atmosphere presents an obvious second-order exponential decay, and the data fitting results show a longer delayed lifetime: T d = 26 μs. Similarly, if Figure 7 As shown, (OMe) 2 The transient attenuation lifetime curve of DPA-ThPh-QCN solid thin film presents obvious second-order exponential attenuation. d = 19 μs. Microsecond-scale lifetimes indicate typical TADF features.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com