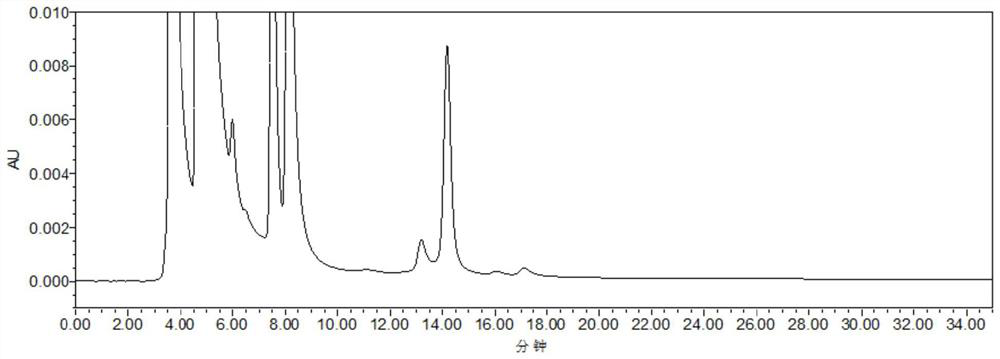
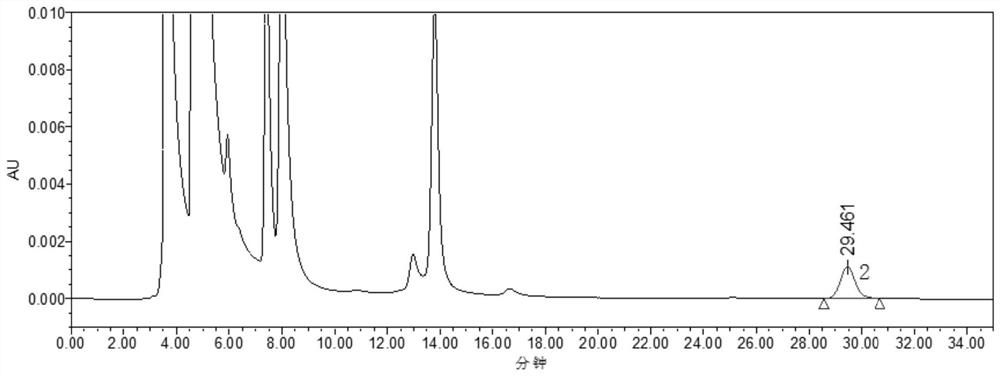
HPLC detection method for statins starting material and enantiomer thereof
A technology of enantiomers and detection methods, which is applied in the field of HPLC detection of statin drug starting materials and their enantiomers, can solve complex operation steps, unsatisfactory accuracy and sensitivity, and low detection efficiency problem, to achieve the effect of improving detection efficiency, improving and controlling quality, high accuracy and sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] 1. Instrument and conditions Chromatographic column: chiral chromatographic column with cellulose-tris(4-methylbenzoate) coated silica gel as filler; specification: 150mm×4.6mm, 5μm;
[0036] Mobile phase: sodium acetate buffer and acetonitrile with a volume ratio of 68:32; wherein, the sodium acetate buffer is 0.151 mg / mL sodium acetate aqueous solution plus glacial acetic acid to adjust the pH to 5.0;
[0037] Column temperature: 30°C;
[0038] Detection wavelength: 242nm;
[0039] Injection volume: 10μL;
[0040] Flow rate: 0.5mL / min;
[0041] Elution method: isocratic elution;
[0042] Solvent: water and acetonitrile are obtained by mixing uniformly at a volume ratio of 1:1;
[0043] Derivatization reagent: adding salicylic hydrazide to the solvent to obtain a reagent with a salicylic hydrazide concentration of 1 mg / mL;
[0044] Need testing solution: get the test sample of the statin drug starting material, add solvent and ultrasonically dissolve to make a sol...
Embodiment 2
[0093] 1. Instrument and conditions Chromatographic column: chiral chromatographic column with cellulose-tris(4-methylbenzoate) coated silica gel as filler; specification: 150mm×4.6mm, 5μm;
[0094] Mobile phase: sodium acetate buffer and acetonitrile with a volume ratio of 65:32; wherein, the sodium acetate buffer is 0.148 mg / mL sodium acetate aqueous solution plus glacial acetic acid to adjust the pH to 4.5;
[0095] Column temperature: 28°C;
[0096] Detection wavelength: 240nm;
[0097] Injection volume: 8μL;
[0098] Flow rate: 0.4mL / min;
[0099] Elution method: isocratic elution;
[0100] Solvent: water and acetonitrile are obtained by mixing uniformly at a volume ratio of 1:0.8;
[0101] Derivatization reagent: adding salicylhydrazide to the solvent to obtain a reagent with a concentration of salicylhydrazide of 0.8 mg / mL;
[0102] Need test solution: take the test sample of the statin drug starting material, add solvent and ultrasonically dissolve to make a solut...
Embodiment 3
[0109] 1. Instrument and conditions Chromatographic column: chiral chromatographic column with cellulose-tris(4-methylbenzoate) coated silica gel as filler; specification: 150mm×4.6mm, 5μm;
[0110] Mobile phase: sodium acetate buffer and acetonitrile with a volume ratio of 70:32; wherein, the sodium acetate buffer is 0.153 mg / mL sodium acetate aqueous solution plus glacial acetic acid to adjust the pH to 5.5;
[0111] Column temperature: 32°C;
[0112] Detection wavelength: 244nm;
[0113] Injection volume: 12μL;
[0114] Flow rate: 0.6mL / min;
[0115] Elution method: isocratic elution;
[0116] Solvent: water and acetonitrile are obtained by mixing uniformly at a volume ratio of 1:1.2;
[0117] Derivatization reagent: adding salicylhydrazide to the solvent to obtain a reagent with a concentration of salicylhydrazide of 1.2 mg / mL;
[0118] Need test solution: take the test sample of the statin drug starting material, add solvent and ultrasonically dissolve to make a solu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com