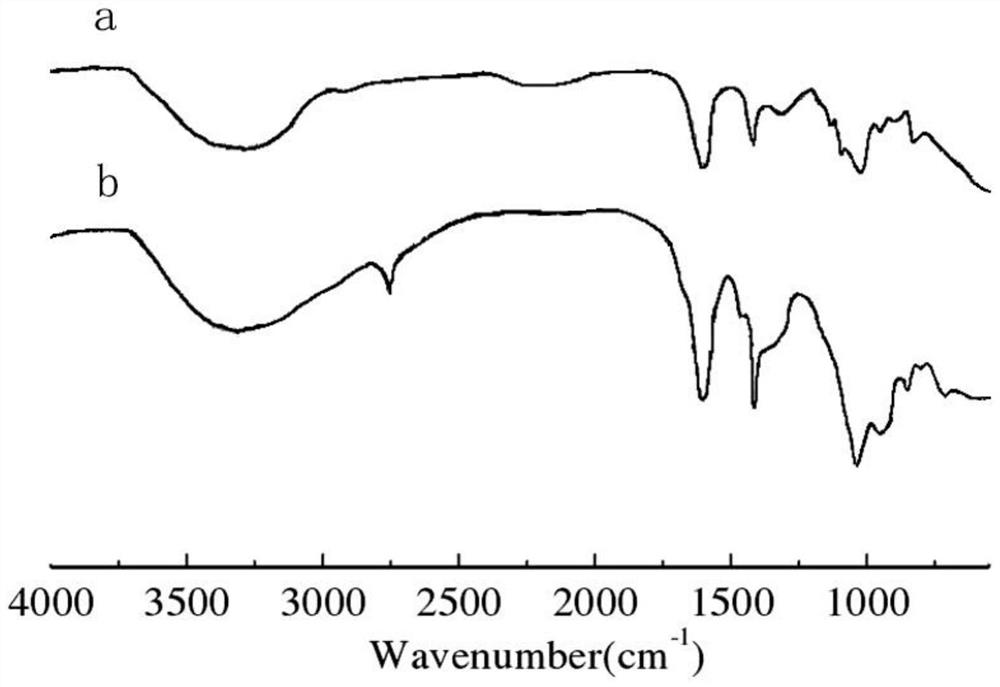
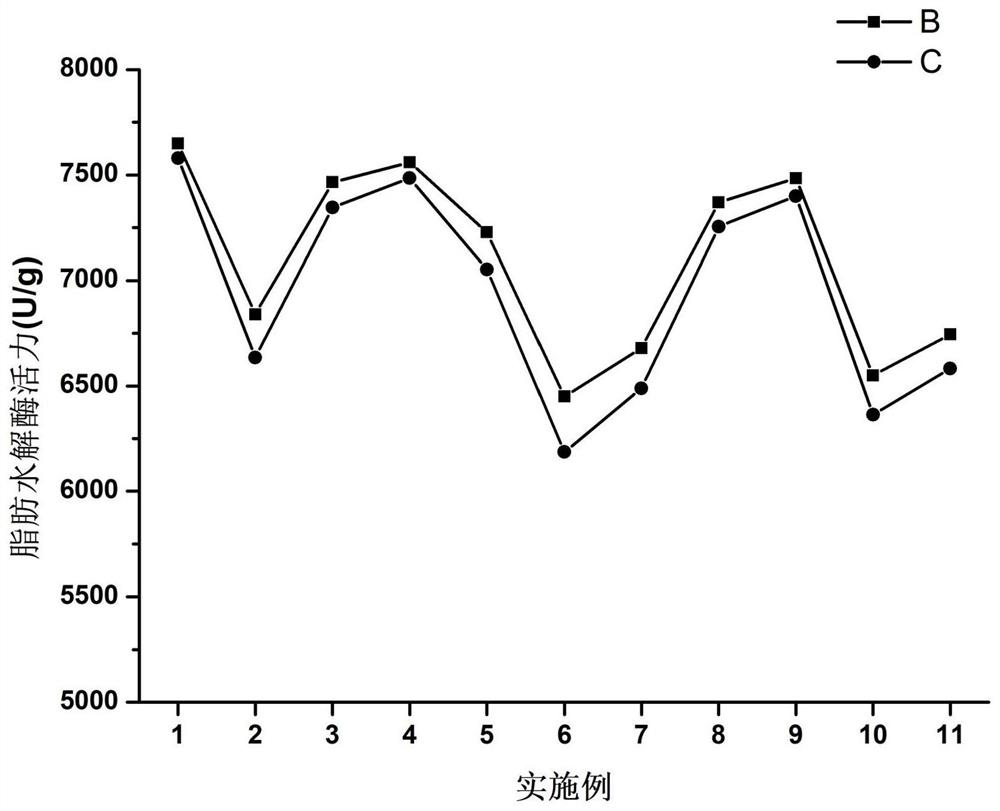
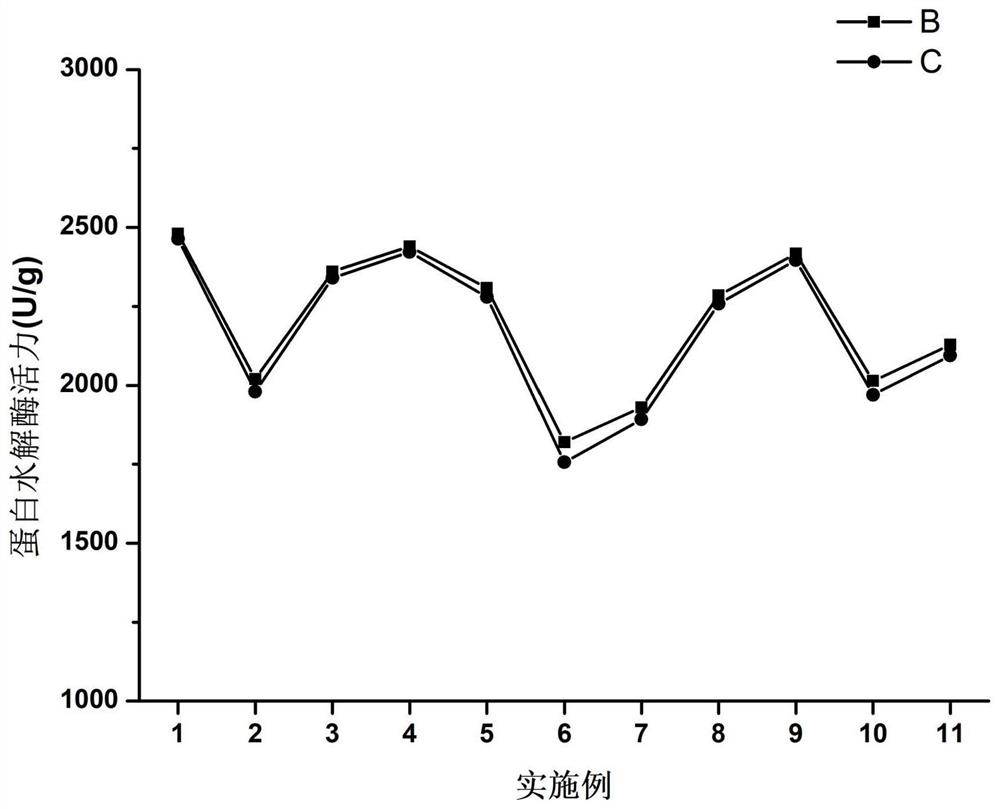
Complex enzyme preparation capable of degrading kitchen waste and preparation method and application thereof
A composite enzyme preparation, kitchen waste technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, hydrolytic enzymes, enzymes, etc., to achieve the effects of high loading, improved degradation rate, and improved strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Example 1: A compound enzyme preparation that can degrade food waste:
[0064] This example provides a compound enzyme preparation that can degrade food waste, which is specifically prepared by the following method:
[0065] 1) Riboflavin and mercaptobutyric acid are mixed according to the molar ratio of 1:1.4, then 12% of the riboflavin molar weight of magnesium perchlorate and 50% of the riboflavin molar weight of cyclohexane are added, and stirred at room temperature , the stirring rate was 200r / min, and the water was separated by reflux until no more water was generated; the reaction product was washed with distilled water, and then extracted with ether, and the organic phase was extracted with anhydrous MgSO 4 Dry, filter, remove ether, and distill under reduced pressure at 82°C and 1.35kPa to obtain riboflavin ester derivatives;
[0066] 2) 4g enzyme activity is 6000U / g phosphatase, 4g enzyme activity is 12000U / glucose diclease, 5g enzyme activity is 1600U / g papa...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Example 2: Another compound enzyme preparation that can degrade food waste:
[0070] This example provides another compound enzyme preparation that can degrade food waste. Its preparation method is basically the same as that of Example 1, except that in this example, sodium alginate grafted N-(2-aminobenzene Base)-N-phenylthiourea process, the addition amount of sodium alginate, N-(2-aminophenyl)-N-phenylthiourea is respectively 1g, 0.2g, and N-(2-aminophenyl) The grafting ratio of phenyl)-N-phenylthiourea to sodium alginate was 17.2%.
Embodiment 3
[0071] Example 3: Another compound enzyme preparation that can degrade food waste:
[0072] This example provides another compound enzyme preparation that can degrade food waste. Its preparation method is basically the same as Example 1, except that in this example, sodium alginate, N-(2-aminophenyl) The addition amounts of -N-phenylthiourea were 1 g and 0.35 g respectively, and the grafting rate of N-(2-aminophenyl)-N-phenylthiourea to sodium alginate was 24.7%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of grafting | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of grafting | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com