Silver-aluminum paste for P + electrode of solar cell and solar cell
A technology for solar cells and silver-aluminum paste, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of reducing photoelectric conversion efficiency, excessive etching compound increase, and contact resistance increase, etc., and achieves environmentally friendly production and application, mild etching reaction, and reduced contact The effect of resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
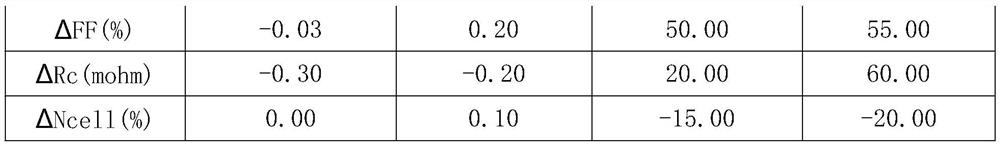
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0032] Conductive silver powder
[0033] In conjunction with the first aspect of the present invention, in an optional embodiment, the conductive silver powder is in any one or more forms of flakes, spheres, granules, crystals, powders or other irregular forms. Preferably, the conductive silver powder is in spherical form.
[0034] In conjunction with the first aspect of the present invention, in an optional embodiment, the conductive silver powder is provided in the form of a colloidal suspension.
[0035] In conjunction with the first aspect of the present invention, in an optional embodiment, the silver-aluminum paste for solar cell P+ electrodes of the present invention contains 80-99.5 wt% conductive silver powder in spherical form.
[0036] In conjunction with the first aspect of the present invention, in an optional embodiment, the silver-aluminum paste for solar cell P+ electrodes of the present invention comprises 80-95wt% spherical conductive silver powder and 1-20...
Embodiment 1
[0062] (1) Preparation of glass powder
[0063] Referring to Table 1, take by weighing 50g of glass powder raw material, including: 40g of Bi 2 o 3 , 2.5g of B 2 o 3 , 7.5g of SeO 2 , mix the above-mentioned glass powder raw materials evenly, pour them into a crucible, put them into a muffle furnace, raise the temperature to 1000°C, keep them warm for 40 minutes, and then pour the melted glass frit into the inverted stainless steel rollers for quenching. Then put into the ball mill, ball milled for 24 hours, and the obtained particle size was glass powder A of 2um 1 .
[0064] (2) Preparation of silver-aluminum paste for solar cell P+ electrode
[0065] Take by weighing 850g the conductive silver powder of spherical form, 30g aluminum powder, 40g glass powder A with oleic acid as surfactant 1 And 80g of organic vehicle, wherein, 80g of organic vehicle contains 37.1g of 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol monoisobutyrate, 1.2g of ethyl cellulose, 6.7g of N - Tallow-1,3-diam...
Embodiment 2~3
[0068] (1) Preparation of glass powder
[0069] The glass powder was prepared by the same method as in Example 1, except that the raw materials and proportions were different. For the raw materials and proportions used in Examples 2-3, see Table 1 for details. Obtain glass powder A by embodiment 2~3 3 ~A 4 .
[0070] (2) Preparation of silver-aluminum paste for solar cell P+ electrode
[0071] Adopt the same method as Example 1 to prepare the silver-aluminum paste for the solar cell P+ electrode, the difference is only the glass powder in the raw material, that is, the glass powder A is used in Examples 2 to 3 respectively 3 ~A 4 Preparation, except for glass powder, other material components and contents are the same. Silver-aluminum paste PA for solar cell P+ electrodes was obtained through Examples 2-3 3 ~PA 4 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Brookfield viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com