Heat-resistant modified polylactic acid material and preparation method thereof
A polylactic acid material and modification technology, which is applied in the field of heat-resistant modified polylactic acid material and its preparation, can solve problems such as difficult processing, high brittleness, and difficulty, and achieve improved mechanical stress, improved heat resistance, and excellent The effect of mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0034] A preparation method of heat-resistant modified polylactic acid material, such as figure 2 , the method includes:
[0035] S1. Mix lactide, catalyst, chitosan and single-walled carbon nanotubes, and disperse and form them to obtain polylactic acid with single-walled carbon nanotubes;
[0036] S2. Blending and molding single-walled carbon nanotube polylactic acid, polyimide, flame retardant and toughening agent in a molten state to obtain a blank;
[0037] S3, irradiating, stretching, cooling and solidifying the blank to obtain a polylactic acid material.
[0038] In the embodiment of the present application, carbon nanotube polylactic acid, polyimide, flame retardant and toughening agent are blended in a molten state, and corresponding compatibilizers or crosslinking agents can be added for reaction.
[0039] In the examples of this application, the stretching treatment can also increase the crystallinity of the polylactic acid blend material to 45-68%. The increase ...
Embodiment 1
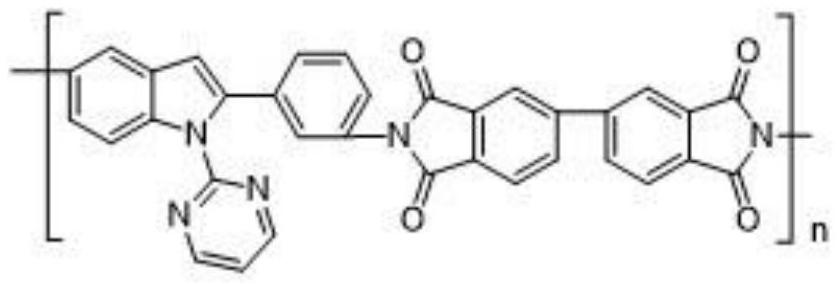
[0063] A heat-resistant modified polylactic acid material, in parts by weight, the components of the polylactic acid material include: 50g lactide, 2g catalyst, 10g chitosan, 10g single-walled carbon nanotubes, 10g polyamide Imine, 3g flame retardant, 0.5g toughening agent. The polyimide is a polyimide containing an asymmetric indole structure, wherein the general chemical formula is:
[0064]
[0065] N is 8.
[0066] The catalyst includes alumina. The toughening agent comprises ethylene-methyl acrylate-glycidyl methacrylate random copolymer. The mass ratio of the toughening agent and single-walled carbon nanotube polylactic acid blended is 1:50. The polyimide is a polyimide containing an asymmetric indole structure. Add chitosan (molecular weight: 300,000, degree of deacetylation: 60%) into the reaction vessel, add lactide, catalyst, chitosan and single-walled carbon nanotubes, mix and disperse for 3 hours, heat the reaction product to 120°C and dry for 2 hours Obtai...
Embodiment 2
[0068] A heat-resistant modified polylactic acid material, in parts by weight, the components of the polylactic acid material include: 80g lactide, 4g catalyst, 30g chitosan, 26g single-walled carbon nanotubes, 20g polyamide Imine, 9g flame retardant, 1g toughening agent.
[0069] The melting and the stretching are each carried out above the glass transition temperature of the billet. The crystallization temperature in the cooling and solidification is 155° C., and the cooling and solidification of the catalyst includes alumina. The toughening agent comprises a hydrogenated polystyrene-polybutadiene-polystyrene triblock copolymer. The mass ratio of the toughening agent and polylactic acid blended with single-walled carbon nanotubes is 1:95. The polyimide is a polyimide containing an asymmetric indole structure.
[0070] Add chitosan (molecular weight: 300,000, degree of deacetylation: 70%) into the reaction vessel, add lactide, catalyst, chitosan and single-walled carbon na...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| heat deflection temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crystallization temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com