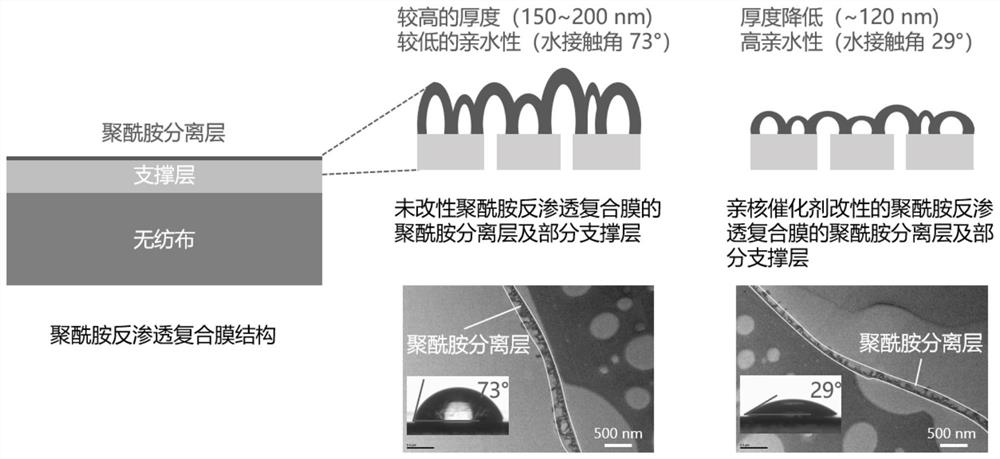
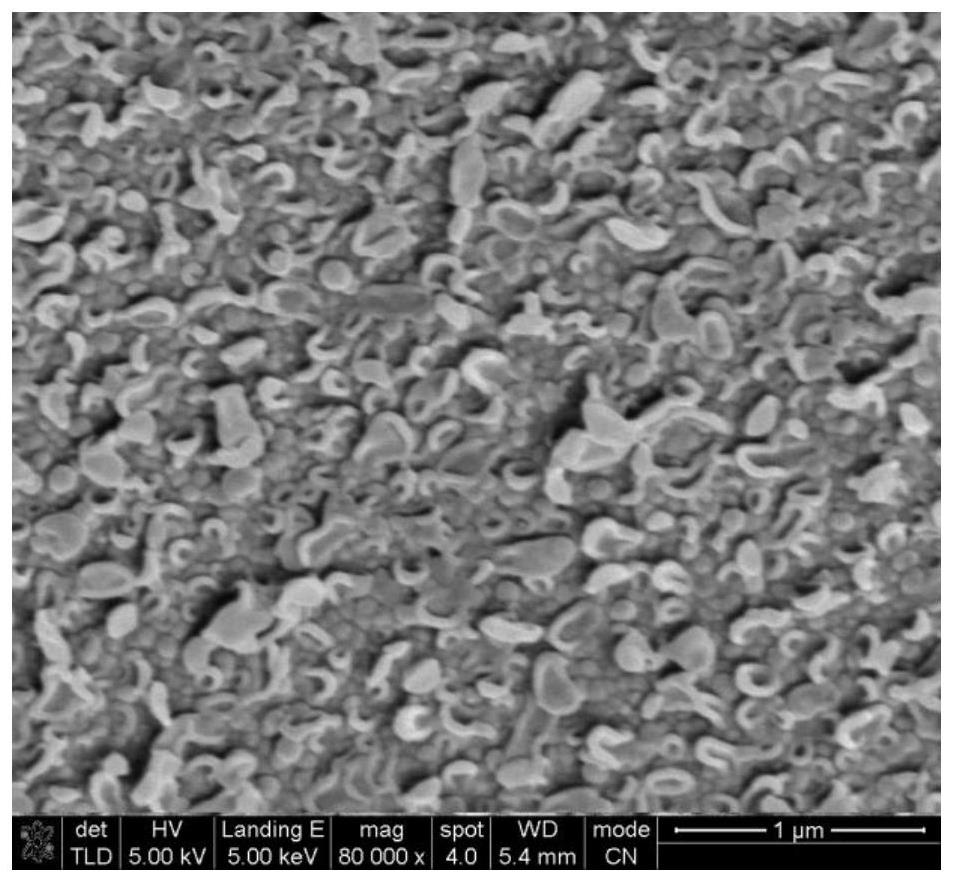
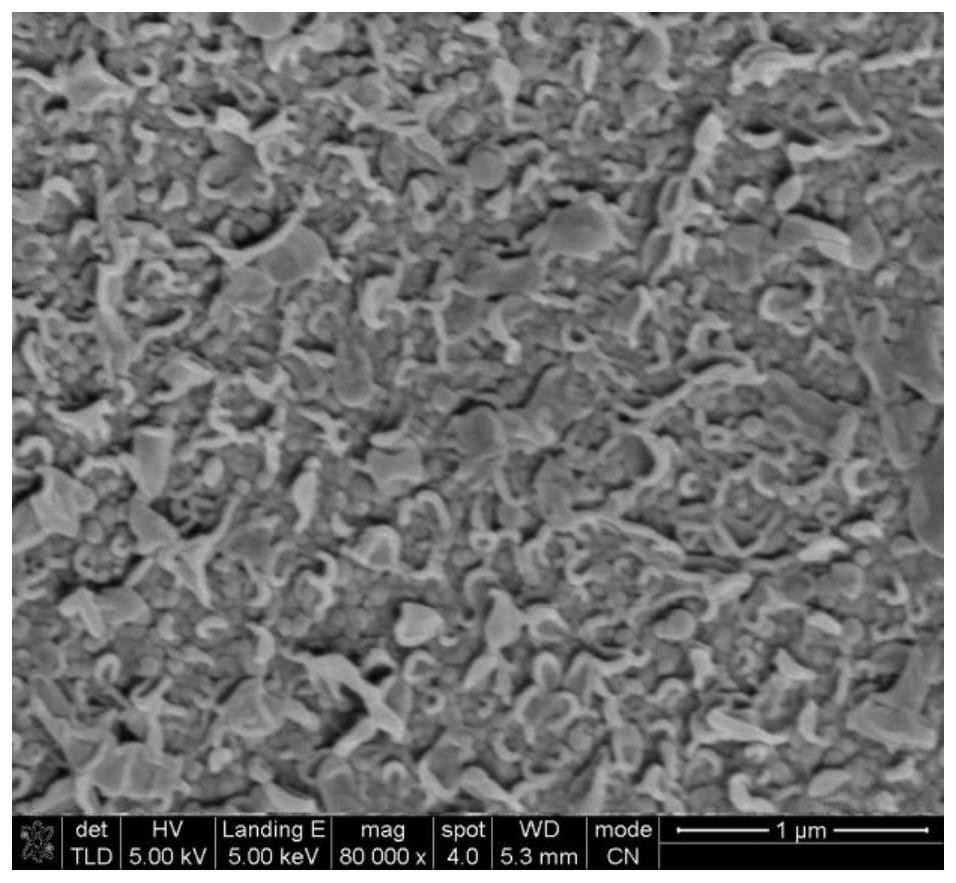
Method for preparing reverse osmosis composite membrane with high salt rejection rate and high flux by reforming polyamide separation layer
A technology of reverse osmosis composite membrane and rejection rate, which is applied in the field of preparation of liquid separation membranes. Significant increase in throughput, easy industrial scale-up, and simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) Prepare polyamide nascent membrane by interfacial polymerization: soak the polysulfone-based membrane in room temperature containing 3.0wt.% m-phenylenediamine, 2.6wt.% camphorsulfonic acid, 1.1wt.% triethylamine, 0.1 Wt.% Sodium dodecylsulfonate aqueous phase solution for 30s; use a rubber roller to remove the residual aqueous phase solution; Triformyl chloride was interfacially polymerized in n-heptane oil phase solution for 1 min, and then heat-treated in an oven at 80°C for 5 min and 30 s to prepare a nascent film.
[0024] (2) After soaking the nascent membrane in pure water for 10 minutes, soak the membrane in 5wt.% 4-dimethylaminopyridine modified aqueous solution to react for 5 seconds, pour off the remaining modified solution, and rinse the membrane surface repeatedly with pure water, Prepared modified polyamide reverse osmosis membrane.
[0025] Under the cross-flow test conditions of operating pressure 1.55MPa, test temperature 25°C, and test cross-flow ...
Embodiment 2
[0027] (1) The preparation of the primary film is the same as in Example 1.
[0028] (2) After soaking the nascent membrane in pure water for 1 min, soak the membrane in 2wt.% 4-dimethylaminopyridine modified aqueous solution to react for 1 min, pour off the remaining modified solution, and rinse the membrane surface repeatedly with pure water, Prepared modified polyamide reverse osmosis membrane.
[0029]Under the cross-flow test conditions of operating pressure 1.55MPa, test temperature 25°C and test cross-flow flow rate 1.5L / min, the rejection rate of the modified reverse osmosis membrane to 2000mg / L sodium chloride solution is 99.13%, and the flux is 61.65 L·m -2 h -1 .
Embodiment 3
[0031] (1) The preparation of the primary film is the same as in Example 1.
[0032] (2) After soaking the nascent film in pure water for 30 minutes, soak the film in an isoparaffin modification solution containing 5wt.% 4-dimethylaminopyridine to react for 3 minutes, pour off the remaining modification solution, and repeat with pure water The membrane surface is washed to prepare a modified polyamide reverse osmosis membrane.
[0033] Under the cross-flow test conditions of operating pressure 1.55MPa, test temperature 25°C, and test cross-flow flow rate 1.5L / min, the rejection rate of the modified reverse osmosis membrane to 2000mg / L sodium chloride solution is 99.33%, and the flux is 54.80 L·m -2 h -1 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Water contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com