Bacillus species level identification method based on high-throughput sequencing technology
A bacillus and sequence technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of cumbersome analysis, inability to meet rapid detection, low efficiency, etc., and achieve the effects of accurate detection results, saving identification time and identification cost, and high resolution ability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Construction of Bacillus-specific primers based on the high-resolution core gene of Bacillus
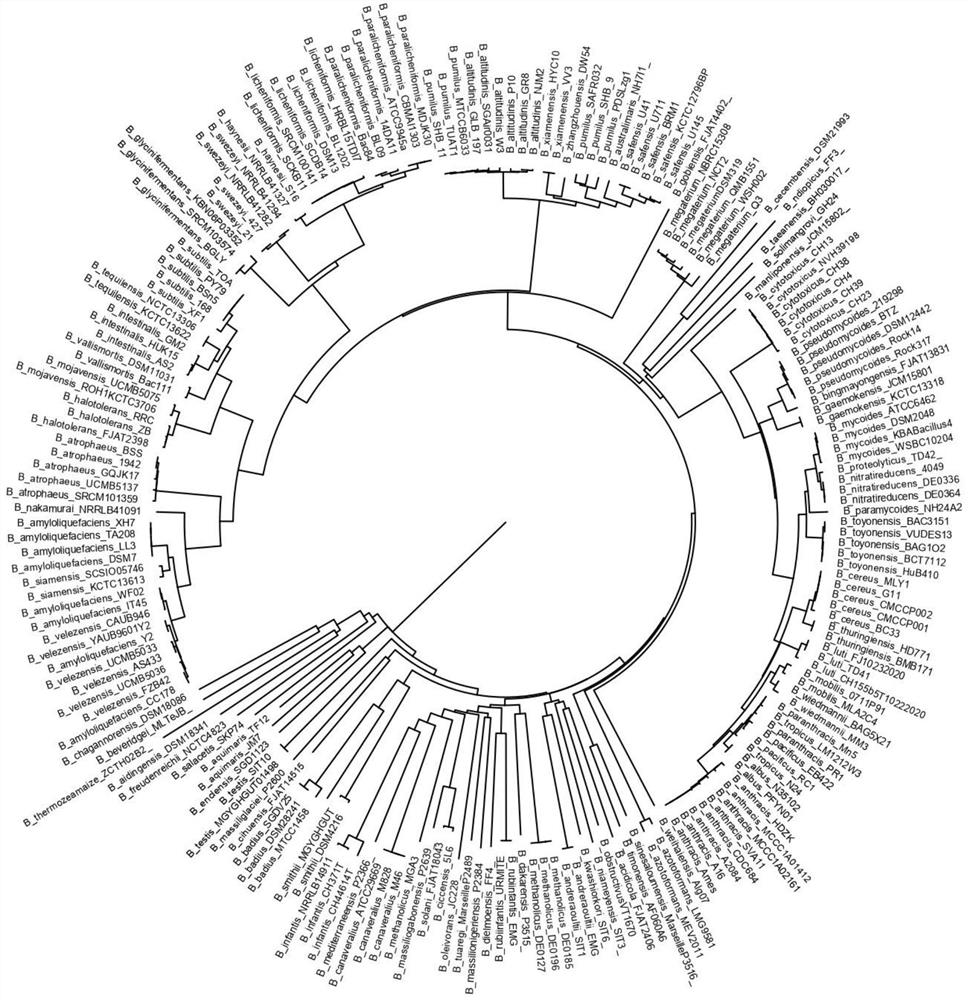
[0037] 1. Collected and summarized 85 species of spores that have been reported in the databases of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and whose genomes have been sequenced Bacillus, and according to the completeness of their sequencing, each selected several, and downloaded a total of 202 whole-genome sequences (some species contain only one strain, which is included as an outer branch of the evolutionary tree in the later stage). Prokka software was used to analyze these genomes Re-annotation was performed and pan-genome analysis was performed by Roary software. The phylogenetic tree of the annotated genes was constructed by MEGA7 software, and a fragment on the sigA gene with the ability to distinguish different species was screened. Such as figure 1 It can be seen from the figure that...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Example 2: Validation of Bacillus-specific primers at the genus level
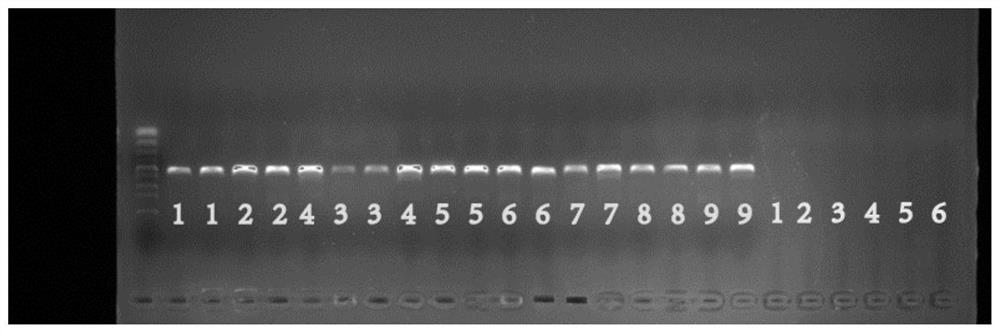
[0074] Select 9 species of bacillus that are frequently reported in raw milk: 1. Bacillus licheniformis, 2. Bacillus cereus, 3. Bacillus subtilis, 4. Thuringiensis Bacillus (B.thuringiensis), 5. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (B.amyloliquefaciens), 6. Bacillus pumilus (B.pumilus), 7. Bacillus megaterium (B.megaterium), 8. Bacillus mycoides (B. .mycoides), 9. Bacillus anthracis (B. anthracis). And 10 kinds of non-Bacillus raw milk: 1. Flavobacterium maritypicum, 2. Escherichia coli, 3. Lactobacillus fermentum, 4. Enterococcus faecalis, 5. Golden grape Staphylococcus aureus, 6. Pseudomonas fluorescens.
[0075] The genomic DNA of the above-mentioned bacterial strains was extracted respectively, and the microbial genome was extracted with reference to the instructions in the bacterial genomic DNA extraction kit (Tiangen Biochemical Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd., Beijing, China), using sequences such a...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Example 3: Construction of a rapid detection method for Bacillus and its verification at the species level
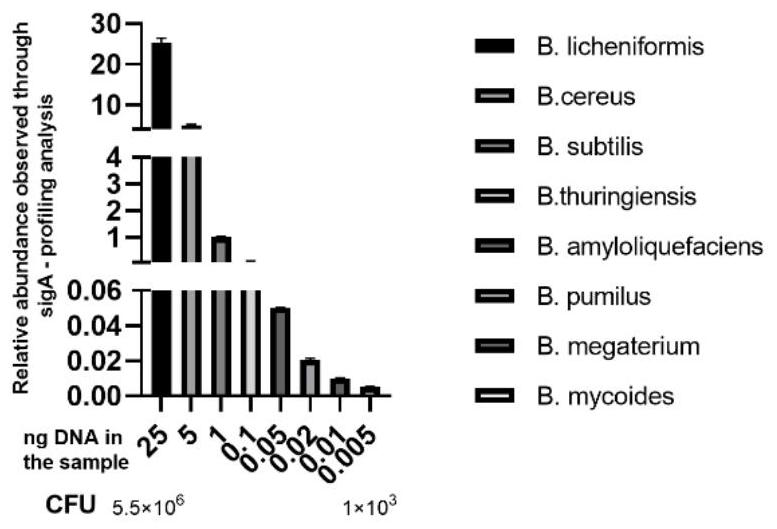
[0083] In order to verify the accuracy of primers SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2 in analyzing Bacillus, Bacillus licheniformis (B.licheniformis), Bacillus cereus (B.cereus), Bacillus subtilis (B.subtilis ), B. thuringiensis, B. amyloliquefaciens, B. pumilus, B. megaterium, B. mycoides, total The genomes of 8 species of Bacillus (as shown in Table 3) are at a concentration of 25-0.005ng / μL (the concentration of the DNA before mixing is shown in Table 3, respectively 0.005, 0.01, 0.02, 0.005, 0.1, 1, 5 and 25ng / μL) Mixing is used to simulate the detection of different species of Bacillus in complex samples. Based on the newly designed bacillus identification primers combined with a next-generation sequencer, then the simulated sample sequencing was carried out according to the method steps described in Example 2, and finally the sequence information of the sigA gen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com