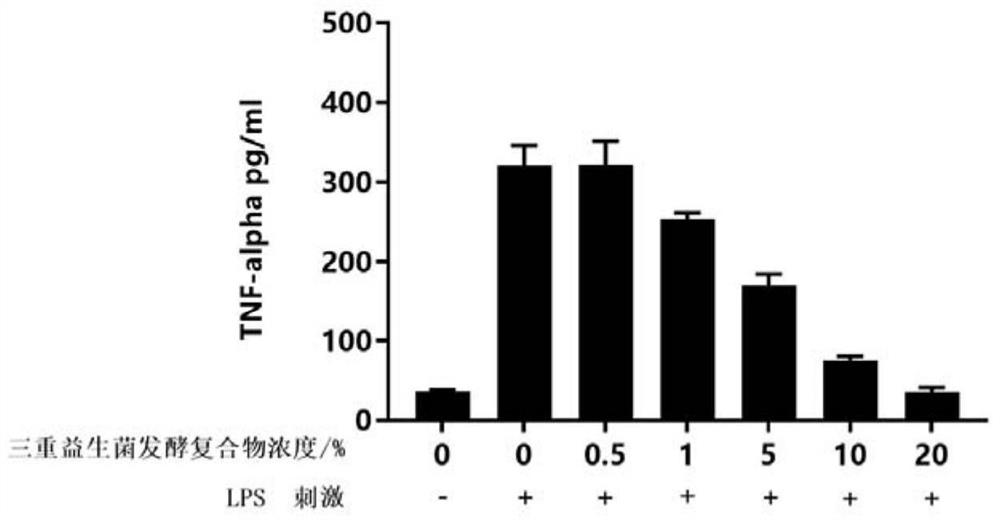
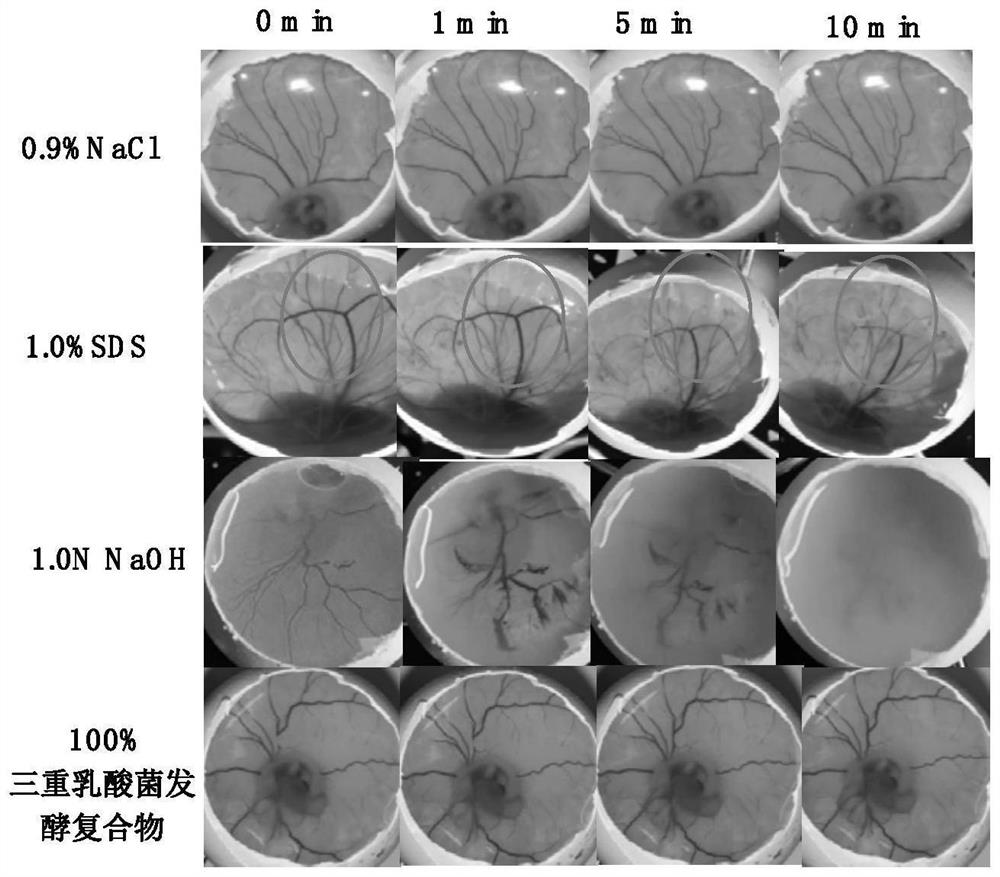
Preparation method and application of triple probiotic fermentation compound with anti-inflammatory effect
A composition and functional technology, applied in the field of microbial fermentation, can solve the problem that probiotic fermentation products are difficult to achieve anti-inflammatory effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Screening of NO-resistant probiotics
[0034] Probiotic medium (g / L): peptone 10.0, yeast powder 5.0, glucose 20.0, beef extract 10.0, Tween-801mL, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 2.0, sodium acetate 5.0, diammonium hydrogen citrate 2.0, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.58, manganese sulfate 0.25, pH 6.5-6.8, solid contains 20g / L agar, sterilized at 121°C for 20min for later use.
[0035]NO resistance screening medium (g / L): peptone 10.0, yeast powder 5.0, glucose 20.0, beef extract 10.0, Tween-80 1mL, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 2.0, sodium acetate 5.0, diammonium hydrogen citrate 2.0, heptahydrate Magnesium sulfate 0.58, manganese sulfate 0.25, sodium nitroprusside 2g / L, pH 6.5-6.8, solid contains 20g / L agar. Sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes for later use.
[0036] Steps:
[0037] Step 1: Activation of strains
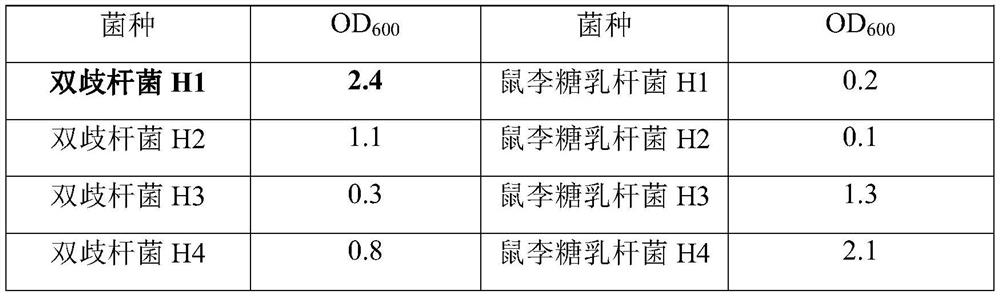
[0038] Put 24 strains of probiotics including Bifidobacterium plantarum, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus s...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: The test of the NO inhibition rate of the fermented products of the three probiotic strains screened in Example 1.
[0050] Steps:
[0051] step 1:
[0052] In the anaerobic glove box, pick a single colony of the three strains of NO-resistant probiotics obtained through screening and inoculate them into a shake flask containing 400 mL of sterile probiotic culture medium. Incubate at 37°C for 24h.
[0053] Step 2:
[0054] Preparation of probiotic fermentation filtrate: divide the cultured probiotic fermentation liquid into 50mL centrifuge tubes, centrifuge at 9000rpm for 10min, collect the supernatant, filter it with a 0.22μm filter membrane, and place it in a clean centrifuge tube to obtain the probiotic fermentation filtrate;
[0055] Preparation of probiotic lysate: Collect the sludge of each strain at the bottom of the centrifuge tube, resuspend the bacteria with an appropriate amount of sterile deionized water, centrifuge again at 9000rpm for 10 minu...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 3: Proportion test of fermented products of active probiotics with high NO inhibition rate.
[0065] The three strains of active probiotic lysates screened in Example 2 were compounded, and a combination with a synergistic NO inhibition rate was selected after mixing according to different mass ratios.
[0066] step 1:
[0067] Bifidobacterium H1 lysate (BH1L), Lactobacillus plantarum H2 lysate (PH2L), Lactobacillus acidophilus H4 lysate (AH4L) prepared in Example 2 were mixed according to the mass ratio shown in Table 3 , diluted 2 times with ultrapure water and used as a sample for later use.
[0068] Step 2:
[0069] NO inhibition rate test—take a 96-well plate, add 50 μL of 0.5 mM sodium nitroferricyanide dihydrate (SNP) solution, add 10 μL of the sample in step 1, and add Griess reagent after UV-A irradiation for 60 minutes A (1% sulfonamide dissolved in 2% phosphoric acid aqueous solution) 50 μL, Griess reagent B (0.1% N-(1-naphthyl) ethylenediamine hyd...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com