Embolism microsphere capable of slowly releasing medicine and preparation method of embolism microsphere
A slow-release drug and microsphere technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problems of inability to select the desired drug, limit the use of particles, etc., and achieve the effects of good drug loading speed, fast drug loading rate, and good drug loading capacity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
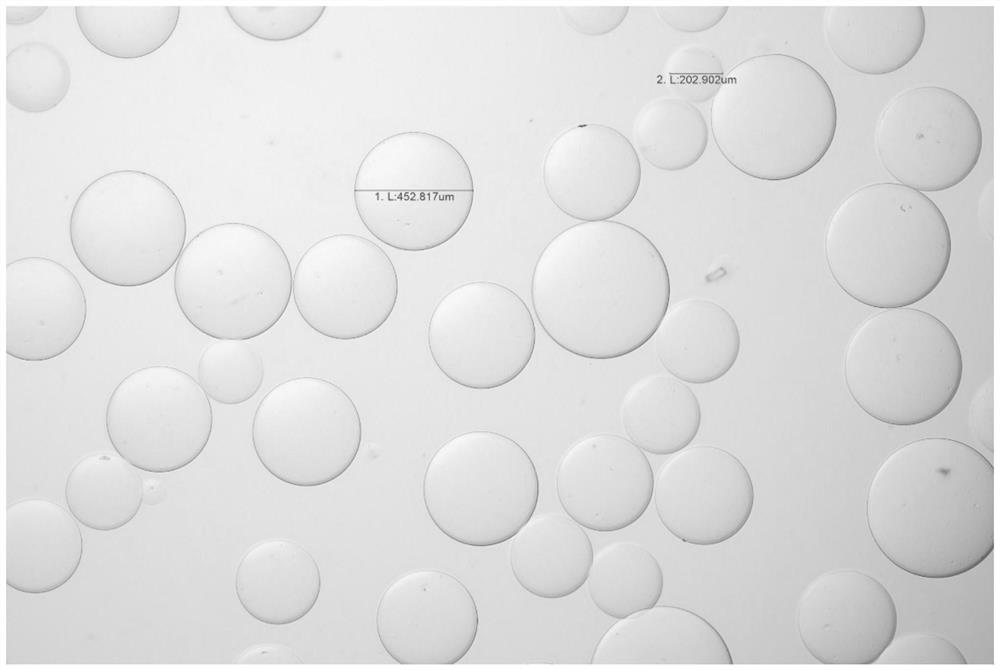
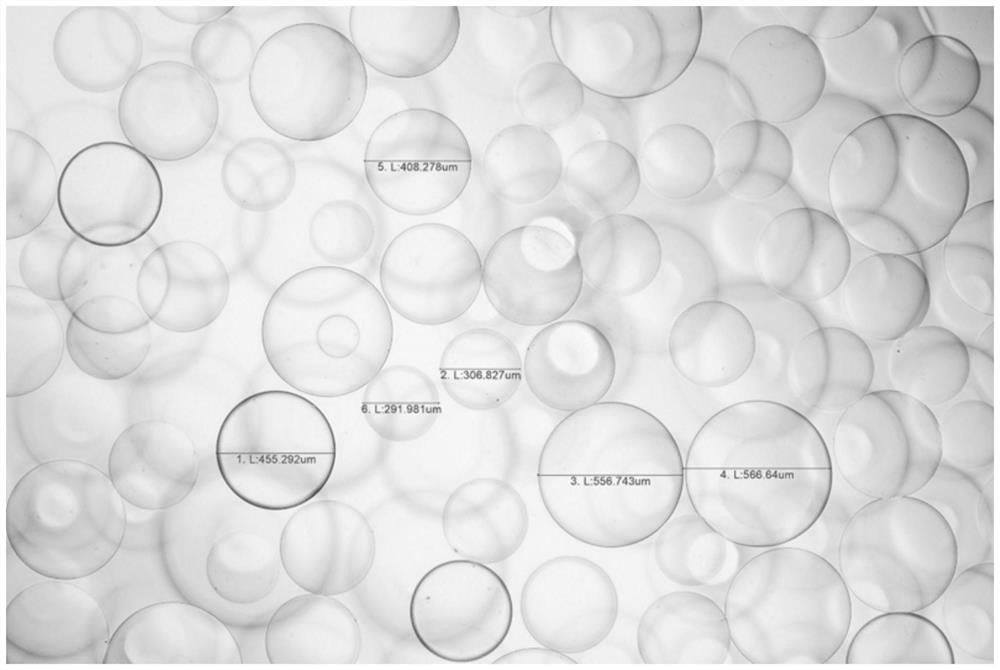
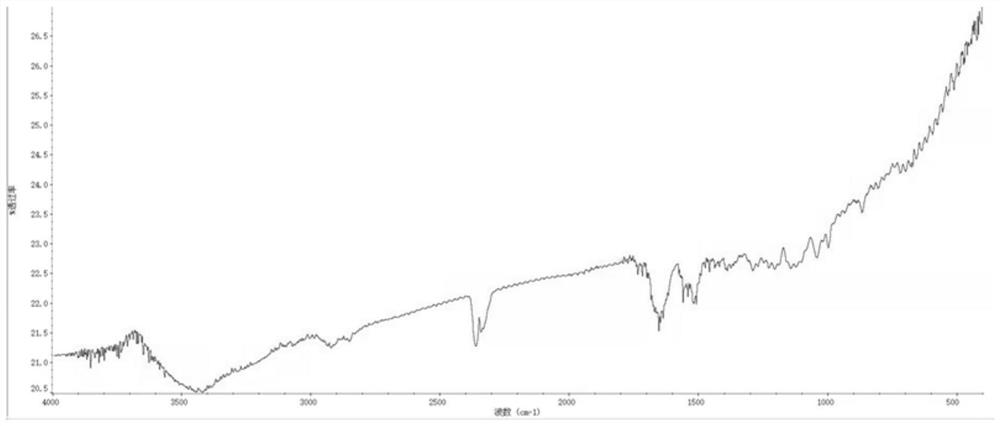
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] This embodiment provides a method for preparing polyvinyl alcohol embolic microspheres capable of sustained drug release by using N-(2,2-dimethoxyethyl)-benzamide, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0068] S1. Preparation of polyvinyl alcohol embolization microspheres:
[0069] S11. Add 60 g of polyvinyl alcohol with a weight average molecular weight of 67,000 into 400 mL of purified water, and dissolve completely at 90° C. Then add 0.9g of N-(2,2-dimethoxyethyl)-2-acrylamide and 35mL of 37.5wt% concentrated hydrochloric acid, and react at 30°C for 6h. After the reaction, the pH of the reaction system was adjusted to 7.5 with 2mol / L sodium hydroxide solution. Finally, the solution was concentrated to a viscosity equal to 1800 cps to obtain a microsphere intermediate.
[0070] S12. 15g of the above-mentioned microsphere intermediate, 1.7g of 2-acrylamide-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid sodium salt and 0.45g of potassium persulfate were completely dissolved...
Embodiment 2
[0074] The present embodiment provides a kind of method that prepares the chitosan embolization microsphere that can release medicine with benzoyl chloride, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0075] S1. Preparation of Chitosan Embolization Microspheres:
[0076] S11. Take 15g of chitosan with a weight average molecular weight of about 100,000, add it to 50g of water, heat to 95°C, stir for 3 hours to dissolve completely, add 0.55g of N-acrylamido diethyl acetal and 2mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, 25 ℃ reaction 5h. After the reaction, the pH of the reaction system was adjusted to 7.2 with 0.5 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution. Finally, the solution was concentrated to a viscosity equal to 1800 cps to obtain a microsphere intermediate.
[0077] S12. Weigh 1.6 g of potassium 3-sulfopropylacrylate and 0.86 g of potassium persulfate, dissolve them completely in 10 mL of deionized water, and add 30 g of the above-mentioned microsphere intermediate. Add 300 mL of ethyl...
Embodiment 3
[0081] This embodiment provides a method for preparing sodium hyaluronate embolic microspheres capable of sustained release of drugs by using benzaldehyde, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0082] S1. Preparation of sodium hyaluronate embolization microspheres:
[0083] S11. Take 20g of sodium hyaluronate with a weight-average molecular weight of 140,000, add it to 50g of water, heat to 80°C, stir for 2 hours to dissolve completely, add 0.3g of N-acrylamidoacetaldehyde and 8mL of 37.5wt% concentrated hydrochloric acid, and heat at 30°C Reaction 3h. After the reaction, the pH of the reaction system was adjusted to 7.3 with 0.5 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution. Finally, the solution was concentrated to a viscosity equal to 2000 cps to obtain a microsphere intermediate.
[0084] S12. Dissolve 20 g of the above-mentioned microsphere intermediate, 1.5 g of sodium acrylate and 0.2 g of sodium persulfate in 20 mL of deionized water. Add 180 mL of soybean oil and 1....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com