High-water-resistance magnesium oxychloride-based road base soil curing material and preparation method thereof
A technology for road base and soil solidification, applied in soil conditioning materials, chemical instruments and methods, organic fertilizers, etc., can solve the problems of poor water resistance, high cost and insufficient water resistance of magnesium oxychloride cement, and achieve significant social and economic benefits. , low carbon emissions, good water resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
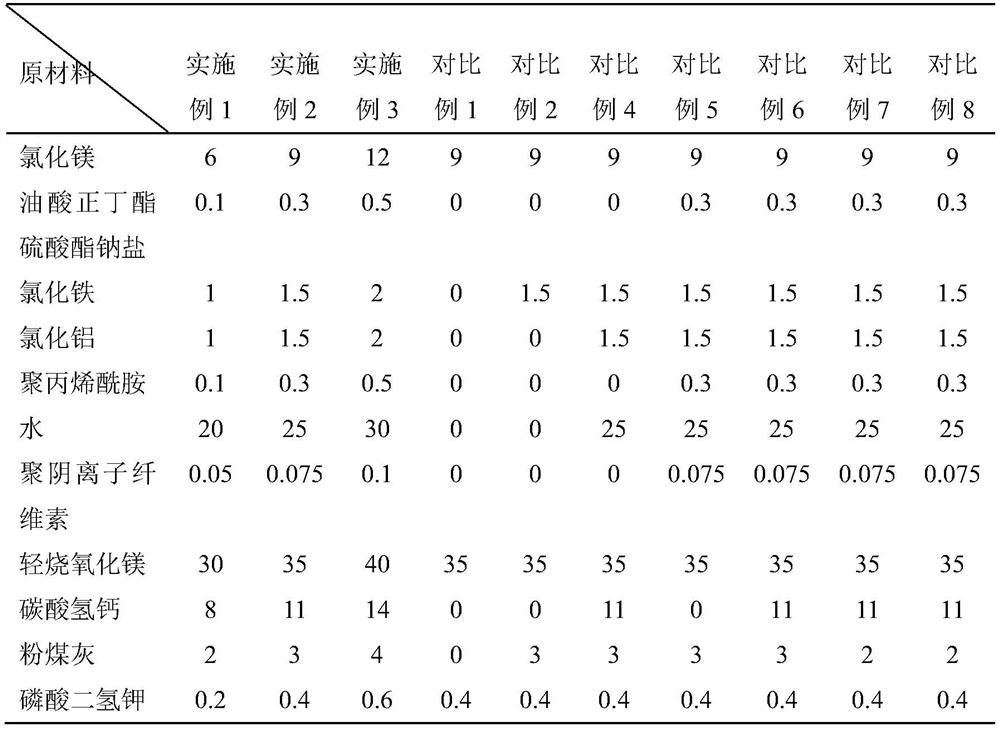
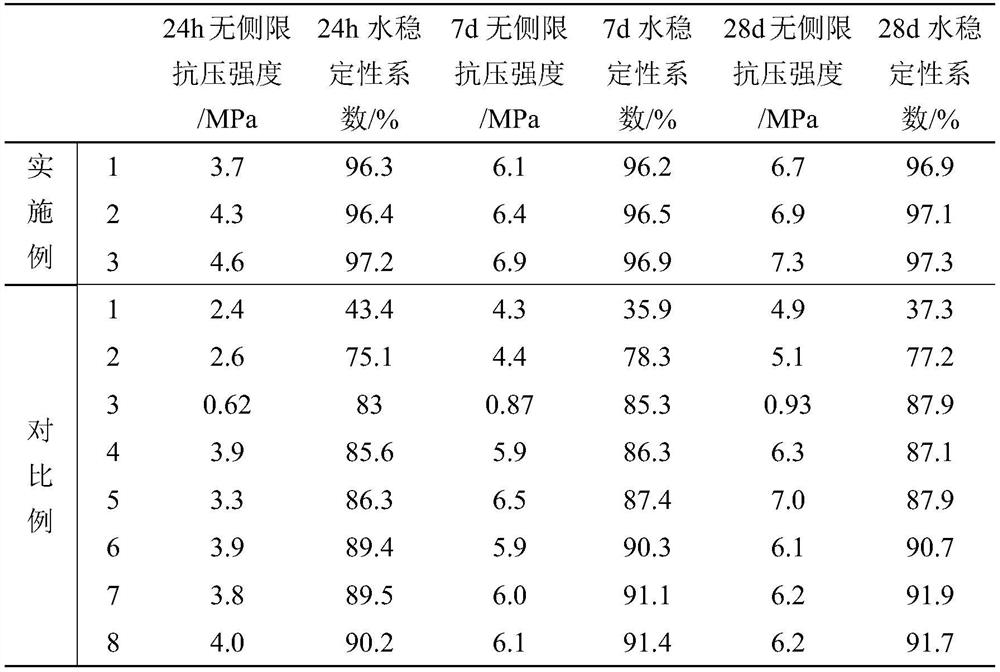
[0038] Take by weighing each raw material according to the proportioning corresponding to Example 1 in Table 1, magnesium chloride, n-butyl oleate sulfate sodium salt, ferric chloride, aluminum chloride, polyacrylamide, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, water, mix And ultrasonically stirred for 30min at a stirring speed of 2000r / min to obtain material A; secondly, polyanionic cellulose was added to the mixture A, mixed and ultrasonically stirred for 45min at a stirring speed of 3500r / min to obtain material B; the mixture B was put into Dry in an oven at 45°C to obtain material C; mix light-burned magnesia, calcium bicarbonate, and fly ash, and stir for 15 minutes to obtain material D. Finally, mix material C and material D and stir evenly for 15 minutes to obtain high Water resistant magnesium oxychloride based road base soil stabilization material.
Embodiment 2
[0040] Take each raw material according to the proportioning ratio corresponding to Example 2 in Table 1, and mix magnesium chloride, n-butyl oleate sulfate sodium salt, ferric chloride, aluminum chloride, polyacrylamide, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, water, and ultrasonically stirred for 30min at a stirring speed of 2500r / min to obtain material A; secondly, polyanionic cellulose was added to the mixture A, mixed and ultrasonically stirred for 45min at a stirring speed of 3000r / min to obtain material B; the mixture B was put into Dry in an oven at 40°C to obtain material C; mix light-burned magnesia, calcium bicarbonate, and fly ash, and stir for 15 minutes to obtain material D. Finally, mix material C and material D and stir evenly for 15 minutes to obtain high Water resistant magnesium oxychloride based road base soil stabilization material.
Embodiment 3
[0042] Take by weighing each raw material according to the proportioning ratio corresponding to Example 3 in Table 1, magnesium chloride, n-butyl oleate sulfate sodium salt, ferric chloride, aluminum chloride, polyacrylamide, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, water, mix and ultrasonically stirred for 30min at a stirring speed of 3000r / min to obtain material A; secondly, polyanionic cellulose was added to the mixture A, mixed and ultrasonically stirred for 45min at a stirring speed of 3000r / min to obtain material B; the mixture B was put into Dry in an oven at 50°C to obtain material C; lightly burned magnesia, calcium bicarbonate, and fly ash were mixed and stirred for 15 minutes to obtain material D. Finally, material C and material D were mixed and uniformly stirred for 15 minutes to obtain a high Water resistant magnesium oxychloride based road base soil stabilization material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Unconfined compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com