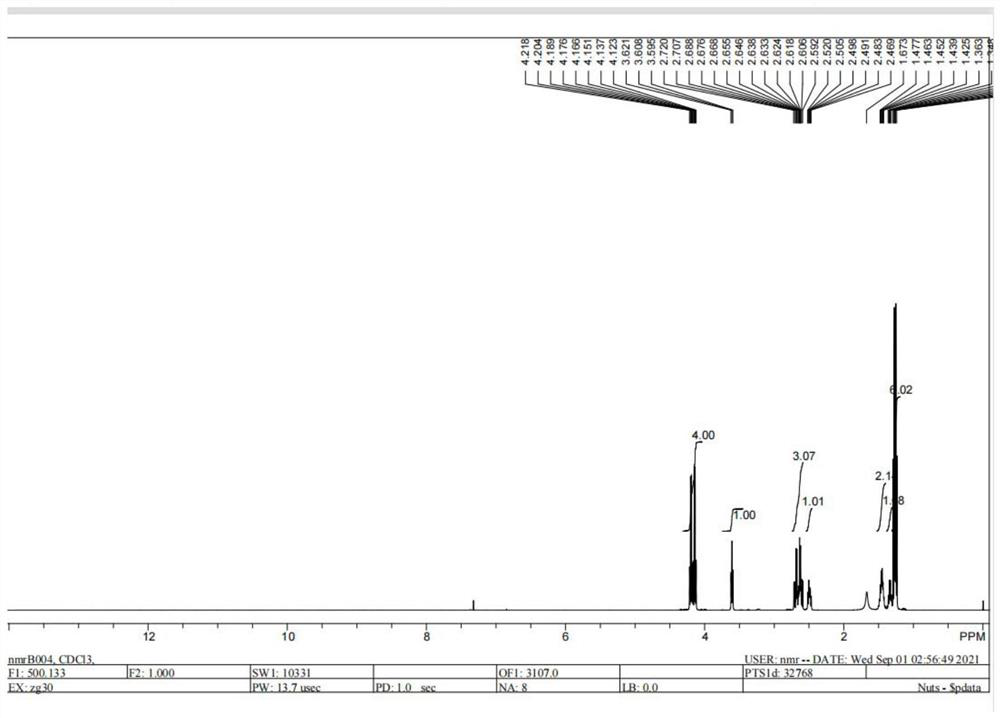
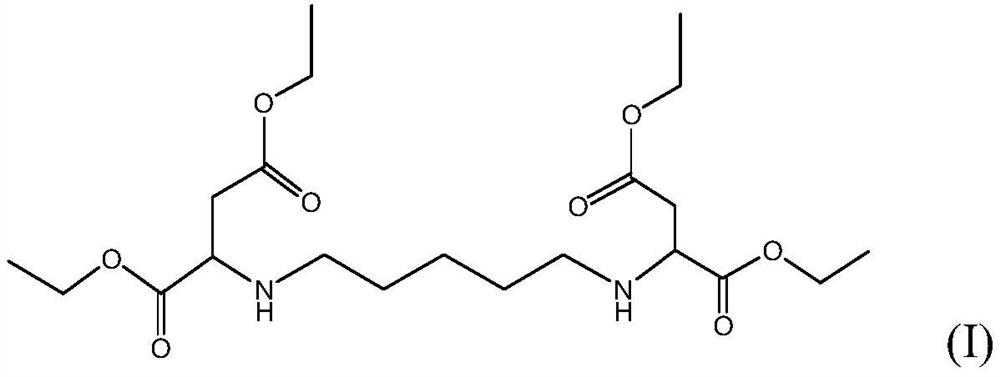
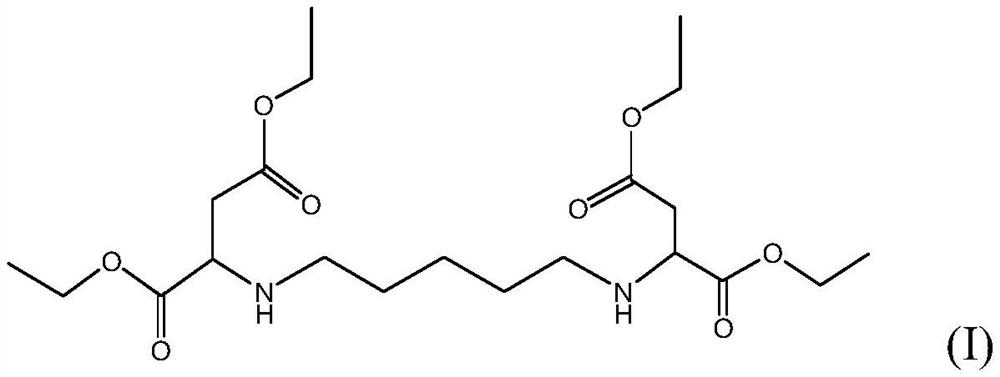
Improved method for preparing polyaspartic acid esters from 1, 5-pentamethylene diamine salts
A technology of pentamethylenediamine hydrochloride and pentamethylenediamine, which is applied in the directions of polyurea/polyurethane coatings, cyanide reaction preparation, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as affecting the quality of downstream products of resin and reducing resin yield.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment A
[0085] Example A: General Materials and Methods
[0086] The following references are used in the examples: Recombinant DNA manipulations generally follow the methods described in: Sambrook et al., 2001 . Restriction enzymes, T4 DNA ligase, Quick DNA Ligation Kit, SanPrep Column DNA Gel Extraction Kit, Plasmid Mini-Prep Kit and agarose were purchased from Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China). TE buffer contains 10mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) and 1mM Na 2 EDTA (pH 8.0). TAE buffer contains 40mM Tris-acetate (pH 8.0) and 2mM Na 2 EDTA.
[0087] In Example B, restriction enzyme digestion was performed in buffer provided by Sangon Biotech.
[0088] A typical restriction enzyme digest contains: 0.8 μg DNA in 8 μL TE, 2 μL restriction enzyme buffer (10x concentration), 1 μL bovine serum albumin (0.1 mg / mL), 1 μL restriction enzyme, and 8 μL LTE. Reactions were incubated for 1 hour at 37°C and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. DNA for cloning experiments was digested, the reaction...
Embodiment B
[0091] Example B: Cloning, expression and activity testing of lysine decarboxylase expressed in Escherichia coli
[0092] The E. coli lysine decarboxylase kdc (2-keto-acid decarboxylase) gene was synthesized and cloned into pET21a (Millipore Sigma, formerly Novagen). The wild-type kdc nucleic acid sequence from Escherichia coli strain BW25113 (E.C.4.1.1.18) is represented by SEQ ID NO: 1, and the amino acid sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO: 2, annotated as lysine decarboxylase.
[0093] The plasmid containing the kdc gene was transformed into BL21(DE3) E. coli cells. Empty plasmid pET21a was also transformed as a negative control. For enzyme expression and characterization experiments, flasks containing 40 mL TB were inoculated at 5% from overnight cultures and shaken. The flask was incubated at 30°C with shaking at 250rpm for 2 hours, then induced to produce protein with 0.2mM isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG), and shaken at 30°C Simultaneously an addition...
Embodiment C
[0096] Example C: Fermentation of transformed Escherichia coli overexpressing KDC
[0097] For the present examples, growth medium was prepared as follows: All solutions were prepared in distilled deionized water. LB medium (1L) contains: Bacto TM tryptone (i.e., an enzymatic digest of casein) (10 g), Bacto TM Yeast extract (ie, the water-soluble fraction of autolyzed yeast extract) (5 g), and NaCl (10 g). LB-glucose medium in 1L LB medium contains: Glucose (10g), MgSO 4 (0.12g), and thiamine hydrochloride (0.001g). LB-freezing buffer contains in 1L LB medium: K 2 HPO 4 (6.3g), KH 2 PO 4 (1.8g), MgSO 4 (1.0g), (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 (0.9g), sodium citrate dihydrate (0.5g), and glycerol (44mL). M9 Salt (1L) Contains: Na 2 HPO 4 (6g), KH 2 PO 4 (3g), NH 4 Cl (1 g), and NaCl (0.5 g). M9 Minimal Medium in 1L M9 Salts contains: D-glucose (10g), MgSO 4 (0.12g), and thiamine hydrochloride (0.001g). Antibiotics were added when appropriate to the following final concentra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com