Synthesis method of azo small molecules for zinc oxide nanoparticle stable ligands
A technology of zinc oxide nanoparticles and nanoparticles, which is applied in the field of material chemistry, can solve problems such as potential safety hazards, and achieve the effects of preventing tailing, good separation effect, and enhanced absorption spectrum
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0036] The invention discloses a method for synthesizing an azo-based small molecule used for a nanoparticle stabilizing ligand, comprising the following steps:
[0037] (1) 4-N-phenylbenzamide, potassium carbonate and N,N-dimethylformamide were added to a pre-dried round bottom flask under argon atmosphere, and then N-(6-bromo hexyl)phthalimide and the mixture was stirred at 120°C until the reaction was complete. The resulting suspension was placed in a separatory funnel and some ethyl acetate, chloroform and water were added. Using the organic phase as the raw material and ethyl acetate as the extractant, extract the residue in the aqueous solution. The organic phase was collected and washed with saturated sodium hydroxide solution. The obtained solution was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain an intermediate white solid, as shown in the following formula 1
[0038]
[0039] (2) The ethanol suspension of th...
Embodiment 1
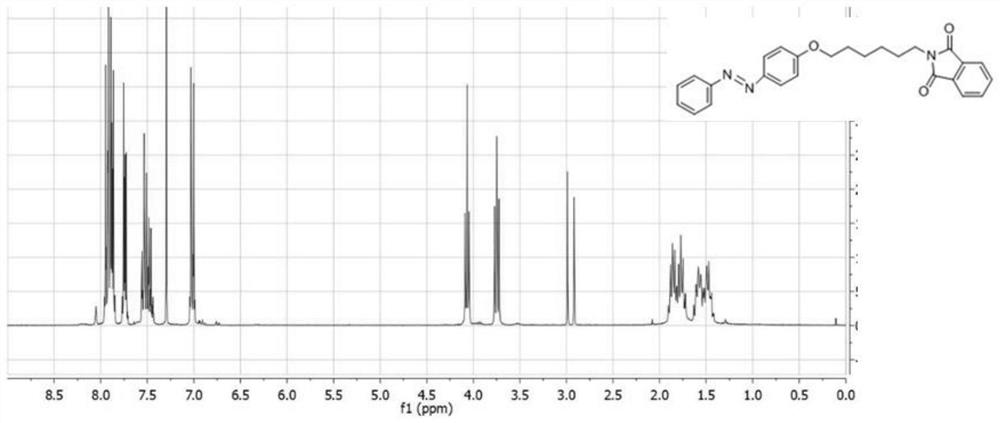
[0044](1) 4-N-Phenylbenzamide (1.88g, 9.47mmol), potassium carbonate (2.35g, 17.0mmol) and N,N-dimethylformamide (50ml) were added to a preliminarily In a dry round bottom flask, N-(6-bromohexyl)phthalimide (2.63 g, 8.5 mmol) was then added and the mixture was stirred at 120°C until the reaction was complete. The resulting suspension was placed in a separatory funnel and 100 mL of ethyl acetate, chloroform and water were added (3:2:5 by volume). Using the organic phase as the raw material and ethyl acetate as the extractant, extract the residue in the aqueous solution. The organic phase was collected and washed with saturated sodium hydroxide solution. The obtained solution was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain a white solid (3.25 g, yield 90%), which was characterized by hydrogen NMR ( figure 1 ), 1 H NMR(500MHz, DMSO-d6)δ7.91-7.84(m,6H),7.71-7.62(m,2H),7.58-7.37(m,2H),6.88-7.05(m,2H),4.03(t , J=6.5Hz, 2H),...
Embodiment 2
[0048] (1) 4-N-Phenylbenzamide (2.15g, 10.85mmol), potassium carbonate (2.70g, 19.5mmol) and N,N-dimethylformamide (50ml) were added to a preliminarily In a dry round bottom flask, N-(6-bromohexyl)phthalimide (2.70 g, 9.8 mmol) was then added and the mixture was stirred at 120°C until the reaction was complete. The resulting suspension was placed in a separatory funnel and 100 mL of ethyl acetate, chloroform and water were added. Using the organic phase as the raw material and ethyl acetate as the extractant, extract the residue in the aqueous solution. The organic phase was collected and washed with saturated sodium hydroxide solution. The resulting solution was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain a white solid (3.45 g, yield 83%).
[0049] (2) The ethanol suspension of the product obtained in step (1) was placed in a pre-dried two-neck round bottom flask. The mixture was heated to 90°C and hydrazine hydrate (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com